Key Takeaways:
- Cyber criminals exploit multiple attack vectors, including direct attacks, threatening both network security and overall aspects of security.
- Examples of cybercrime include various categories of cybercrime attacks, from security breaches to theft of electronic evidence.
- The effects of cybercrime compromise economic security, exposing organisations to significant financial losses.
With the advent of the technology era, cyber criminals pose one of the biggest threats to global security as well as personal privacy.
Technology is becoming more sophisticated by the minute, along with the techniques employed by criminals looking to take advantage of weaknesses within the systems, networks, or people.
To match the growing complexities of cybercrimes, information security measures are also improving.
The focus of this article is on the intersection of cybercrime and information security with an in-depth focus on the risks, ways to counter them, and the current and future possibilities of this constantly evolving digital world.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is defined as any type of unlawful act that includes a computer, system, or the internet in one way or another.
There are multiple kinds of cybercrimes which can include, but are not limited to, hacking, identity theft, data breaches, and online scam.
Cyber crime in its simplest form is the use of devices to conduct illegal activities.
Types of Cybercrime
As cybercrime has become a common phenomenon, there are multiple categorised forms which have different techniques and targets. Some of the most commonly known cyber crimes include:
- Hacking: The unauthorised access to computer systems or networks to exploit their data or functionality.
- Identity Theft and Financial Fraud: Cybercriminals can carry out financial fraud and identity theft by stealing personal data like Social Security numbers, credit card numbers, or bank account data.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Phishing attacks frequently utilise misleading email, message, or website to deceive people into divulging personal details. These mechanisms take advantage of human psychology to get around technical protection measures.
- Ransomware attack: A malware that encrypts or locks a victim’s information and requires payment of a ransom for its release.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: Hacking attacks when more than one infected computer sends an overwhelming volume of traffic towards a target machine in order to crash it.
The Global Impact of Cybercrime
The advancement of technology has shifted entirely towards the digital world, and so have cybercrimes.
It is said that in 2021, cybercriminals are said to have caused losses of over $6 trillion, and that figure will rise as new sensitive information and services are stored online.
As cybercriminals develop new techniques, safeguarding one’s system becomes increasingly more challenging. It is now far more complex to defend systems against attacks from cybercriminals because they are constantly evolving tactics.
Long-term impacts include loss of astonishing reputations, a decline in faith towards digital systems, and aid in endangering whole nations.
Moreover, cybercriminals like hackers who are capable of attacking vast power grids along with healthcare systems can severely put the general population’s health at severe risk.
The Role of Information Security in Preventing Cybercrime
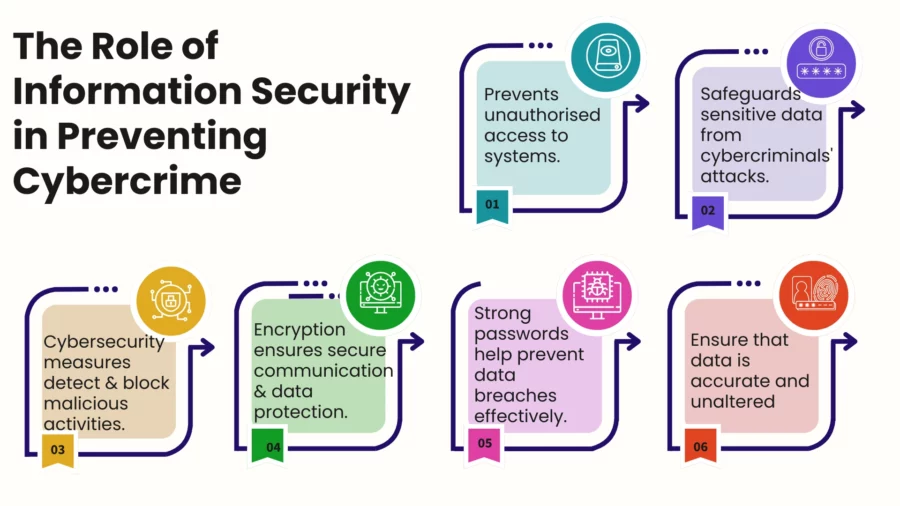
The primary goal here is establishing information security which revolves around defending information systems from unauthorised access.
The goal is to safeguard information alongside maintaining relevant privacy and appropriate functionality of these sensitive systems using designed policies, strategies, and technologies.
Key Principles of Information Security
Information security has 3 key principles and they are referred to as the CIA triad:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
- Integrity: Ensuring that data is accurate and unaltered by unauthorised parties.
- Availability: Ensuring that data and systems are accessible to authorised users when needed.
By adhering to these principles, organisations can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to cybercrimes, safeguarding both their own operations and the sensitive data of their customers or users.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Measures
Cybersecurity, a subset of information security, focuses specifically on protecting digital assets and systems, including networks, devices, and data from cyber threats.
Effective information security requires the implementation of various security measures. Some of the most essential include:
- Encryption: The process of encoding data so that it can only be read by those with the appropriate decryption keys.
- Firewalls: Security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Antivirus Software: Programs designed to detect and remove malicious software (malware) such as viruses, worms, and trojans.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): An authentication process that requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to a system or application.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Tools that monitor networks and systems for suspicious cyber activity, alerting administrators to potential threats.
By adopting a layered approach to security, businesses and individuals can build a robust defense against the diverse and growing range of cyber threats.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Intersection of Cybercrime and Information Security
Cybercrime as a Catalyst for Innovation in InfoSec
The dynamic nature of cybercrime has been a driving force behind innovation in information security.
As criminals develop new methods to infiltrate systems, security professionals are compelled to innovate and enhance defensive mechanisms.
For example, the rise of ransomware has spurred advancements in backup technologies, cloud security solutions, and threat detection algorithms that employ machine learning.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Governments and international bodies have recognised the need for robust cybercrime laws and regulations. These legal frameworks aim to protect citizens’ data and ensure that organisations adhere to high security standards.
Key regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enacted in the European Union, GDPR sets stringent requirements for data protection and privacy, affecting any organization handling EU citizens’ data.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): In the United States, HIPAA governs the protection of sensitive patient health information.
- Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA): This act facilitates the sharing of cyber threat information between the government and private entities, enhancing collective security.
While these regulations impose responsibilities on organisations, they also create frameworks that help guide best practices in information security.
The Indian Information Technology Act (ITA 2000) and Its Amendments

The Information Technology Act (ITA) 2000 was India’s first comprehensive law that addressed issues related to information technology, electronic commerce, and cybercrimes.
It laid the foundation for electronic governance and provided a legal framework for cyber activities.
Nevertheless, the ITA 2000 had its own limitations in adequately addressing the complex and extensive nature of cybercrime and information security.
Thus, in the year 2008, the Act is said to have advanced along with IT and the ever changing cyber warfare. The ITA 2008 changes the previous amended version of the ITA 2000 by outlining a broader view on information security and cybersecurity in India.
Key Provisions of ITA 2008
The Information Technology (Amendment) Act 2008 made some key provisions for improving information security and inhibiting cybercrime in India. Some of the most significant amendments are:
- Section 66E: Section 66E stipulates the unlawful act of taking photographs of another person’s private parts or sending or publishing those photographs without their prior consent. The penalty for this provision is a maximum term of imprisonment for 3 years or a monetary fine not exceeding two lakh rupees.
- Section 66F: Whoever attempts to threaten the integrity, sovereignty, or security of India or compromise the unity of India by hindering people authorised to access a computer resource from doing so, from gaining access to a system which is protected, or by causing contaminants in a system shall be punished with imprisonment for life.
- Section 69B: It gives the Indian government the power to monitor and intercept electronic communication for national security purposes. This provision is crucial for countering cyber espionage and preventing online terrorism.
- Section 70: It states that critical infrastructure is a protected system and any form of unauthorised access to such systems is a criminal offense. This further goes on to define critical infrastructure as the banking, energy, telecommunications and transport sectors.
Focus on Information Security in India
Information security had received adequate attention within the Indian legislative framework after the the amendments introduced by ITA 2008, and it was one of the central focuses of concern.
The Act also highlights the importance of adequate protection measures to be put in place by organizations, particularly those that deal with sensitive personally identifiable information, to avert any unauthorised access or data infringement.
Furthermore, the Act defined a new administrative position called the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team, CERT-In, a body set up to manage cyber emergencies and assist with security incidents in the country as well as provide education on best practices of cybersecurity.
As well as the National Cyber Security Policy (2013), many other government programs were developed with the aim of enhancing information security at national scale, and building a national cybersecurity architecture. All are intended to ensure a secure cyberspace for the economy and citizens.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Emerging Trends in Cybercrime and Information Security
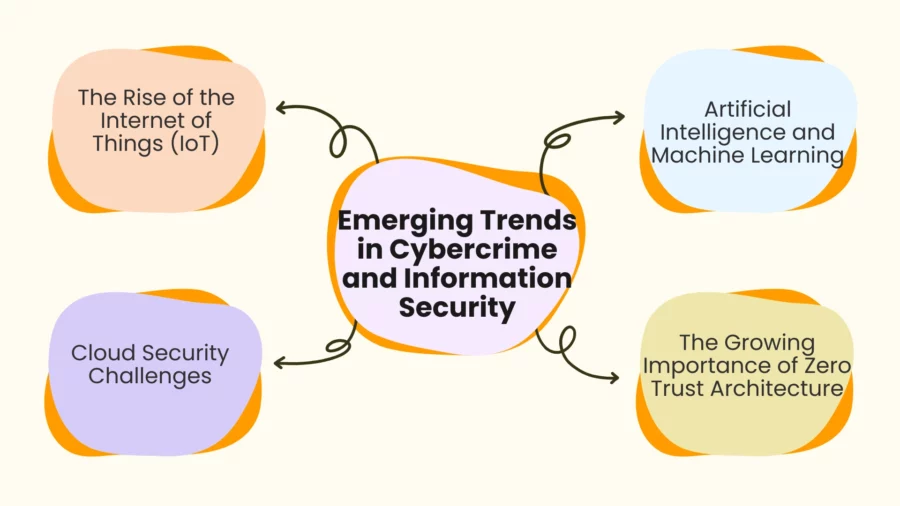
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The impact of Artificial Intelligence is noticeable in almost every aspect of society, including the realm of information security and cybercrime.
Phishing messages can be crafted with greater ease, vulnerabilities can be exploited automatically through bots, and various forms of cybercrimes can be automated to a great extent. All of these pieces point towards a more sinister use of AI.
On the other side, AI and machine learning are empowering security experts to forecast the incoming cyber threats, identify irregularities in the traffic within the network, and deal with incidents instantly.
The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT)
Cybercriminals are able to expand their target range wider and wider due to the rise of IoT devices, which include, but are not restricted to, industrial sensors and smart thermostats.
Unfortunately, a great number of IoT devices are bound to have poor security measures, making it easier for attackers to infiltrate them and launch serious network level attacks.
As automation through IoT deepens its roots in our society, ensuring information security for all devices must be prioritised.
Cloud Security Challenges
Cloud computing has transformed how data is stored and processed, but it also introduces new security challenges.
While cloud service providers invest heavily in security, the shared responsibility model means that organisations must also implement robust security practices.
Data breaches in the cloud can be particularly damaging due to the vast amounts of sensitive information stored in centralized repositories.
The Growing Importance of Zero Trust Architecture
The traditional perimeter-based security model is becoming less effective as organizations adopt remote work and cloud services.
Zero Trust architecture is gaining traction as a security framework that assumes no implicit trust—whether inside or outside the network perimeter.
By verifying every access request and continuously monitoring activity, Zero Trust provides a more resilient defense against modern cyber threats.
Preventive Measures: How to Protect Yourself from Cybercrime
While the threat of cybercrime is ever-present, there are several proactive steps that individuals and organizations can take to reduce their vulnerability.
Regular Software Updates
A very simple and basic approach to lower the chances of cyber attacks is keeping the software systems and applications up to date.
With the every advancement in technology, new sets of weaknesses are acquired, therefore, software developers continuously provide security patches.
Failing to apply these updates leaves a system prone to unaddressed exploits.
Strong Passwords and MFA
Another approach criminals use to accesses valuable data is through weak passwords.
A strong password with upper case letters and unique characters, together with a password manager, is a great way to start. Furthermore, a multi-factor authentication (MFA) feature can also be easily enabled.
MFA replaces the conventional one password security with several, for example a password, fingerprint scan, or facial scan.
Data Backup and Recovery
One of the most common and easiest ways to resolve the fallout of a successful ransomware attack is regularly backing up data.
Creating redundancy files of laptops or PCs that are updated regularly is a fail-proof plan. If one copy is breached, one can restore the most up to date copy without paying a ransom.
Employee Training and Awareness
Each organisational investment that focuses on staff training and education has a purpose.
Employees should be trained as part of the cybersecurity awareness programs so that they can identify phishing calls, make use of strong password, and appreciate how data needs to be protected.
This is useful especially in this era of cybercrimes where human mistakes account for a large portion of the risk.
Securing Networks and Devices
Both individuals and businesses should protect their networks and systems with firewalls, encryption, and secure Wi-Fi usage.
Other devices must be secured by proper passwords or biometric locks to ensure that no unauthorised personnel have access to them.
What’s Next?
Cybercrime is a growing concern, driven by malicious activities conducted by cybercriminals targeting individuals, businesses, and even government institutions.
These criminal activities encompass various categories, including credit card fraud, bank fraud, internet fraud, and attacks on computers, often resulting in significant financial losses.
Digital attacks on networked devices can lead to breaches of access control and the theft of sensitive financial transactions or personal data.
Copyright infringement and other illegal online activities also continue to rise, impacting businesses and creators alike.
Federal agencies and cybersecurity firms play a crucial role in combatting these threats, but it’s vital for individuals and organisations to remain vigilant about online security. Protecting your data and digital identity from unknown people online is no longer optional.
Bytescare helps protect your digital world from the dangers of cybercrime by offering state-of-the-art solutions to secure your data and digital identity.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—explore our advanced protection tools and get a head start in defending your online presence. Take control of your cybersecurity now. Book a demo now to secure your digital future!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is cybercrime in information security?
Cybercrime in information security refers to criminal activities conducted via digital means that target or exploit information systems. This includes unauthorized access, data theft, and other cyber attacks that compromise the integrity and confidentiality of electronic evidence.
What is the relationship between cybercrime and information security?
Cybercrime and information security are interlinked; while cybercrime encompasses illegal activities such as hacking and fraud, information security aims to protect systems from these threats. Effective security measures help mitigate the risks posed by cyber criminals and prevent security breaches.
What is cyber security in information security?
Cyber security is a subset of information security focused on protecting computer systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. It involves implementing technologies, policies, and practices that defend against direct attacks and various attack vectors.
What are the types of information security?
The types of information security include physical security, technical security (such as network security and access control), and administrative security. Each aspect of security addresses different vulnerabilities, from preventing unauthorized access to ensuring the safe handling of electronic evidence.
How can individuals and organisations improve their cybersecurity?
Improvements can be achieved through regular risk assessments, robust access control measures, continuous monitoring, and comprehensive employee training. Staying updated with the latest cybercrime repository information and implementing advanced protection tools are also critical steps.
How information security and cybersecurity overlap?
Information security is the broader field focused on protecting data in all forms, while cybersecurity specifically addresses the protection of digital data from cybercrime. They overlap in areas such as network security, policy development, and incident response, all aimed at mitigating security threats.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

