Key Takeaways:
- Cybersecurity is essential in banking to protect against fraud and suspicious activities.
- Advanced security measures like fingerprint scans and encryption safeguard sensitive data.
- Proactive cybersecurity efforts are necessary to counter evolving threats and stay ahead of cyber criminals.
The global economy rests on several pillars, and the banking industry is one of the most important.
Since financial institutions use digital infrastructure to offer services and interact with customers, these organisations become targets for cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity within the banking sector is no longer a technical issue; it is a strategic matter that sustains trust and economic welfare in countries.
This article lets you know why is cyber security important in banking sector by examining key factors. This piece also analyse the evolving problem, and discuss measures that can be taken by the institutions to protect their operations.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Digital Transformation of Banking
From Traditional to Digital
All that is done today in the banking sector of a country is carried out through the use of computers and mobile devices, unlike a few decades back where banking was a branch based, paper heavy discipline.
Online banking, mobile apps, and payment system automation have revolutionized customer access to banking. While this digital revolution ushered in unparalleled convenience and efficiency, it opened new channels for cyber attacks.
The Convergence of IT and Operational Technology
The banking sector nowadays makes use of IT systems wherein all IT infrastructure is centralised. This includes customer transactions, internal communications and risk management.
The merging of information technology IT and operational technology OT translates as a weakness in one section. This can bring problems to the other parts of the system.
Thus, cybersecurity is not just about protecting customer sensitive information but ensuring the whole banking ecosystem is reliable and trusted.
What is Cyber Security in Banking?
Cybersecurity in banking is a specific set of strategies, processes, and technologies that seek to save the sensitive digital infrastructure of the bank or its customer details from the harm of cyber-attacks.
As more and more automated transactions and services are started to be offered by the banks, the digital security has to be on point.
Key examples and components include:
- Encryption: Banks use advanced encryption to secure data during transmission. For instance, SSL/TLS protocols ensure that online transactions remain private and tamper-proof.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Customers often encounter MFA when logging into their online banking accounts. This process requires more than just a password—typically a code sent to a mobile device—enhancing security by adding an extra verification layer.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems continuously monitor network traffic for unusual patterns, alerting security teams to potential threats.
A recent study noted that cybercrime is expected to cost the global economy over $10.5 trillion by 2025, highlighting the growing financial risks.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Threats and Challenges to Cyber Security in Banking
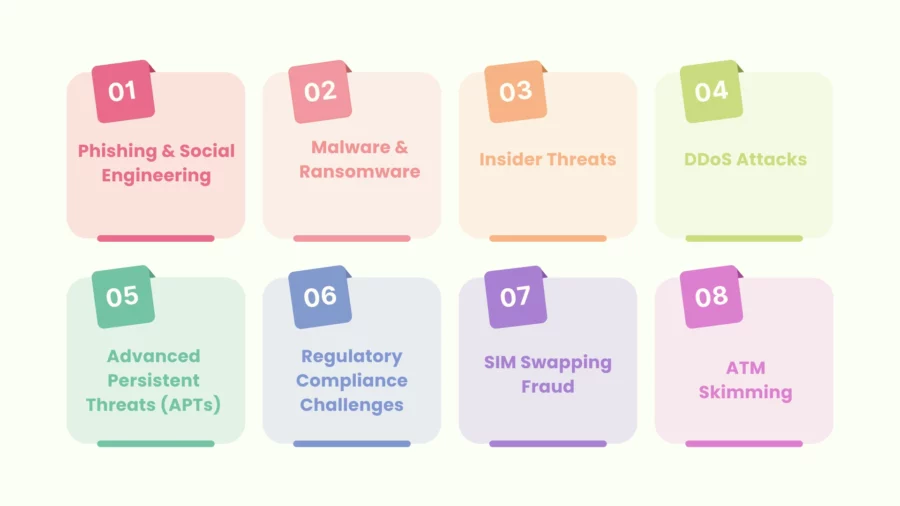
Cyber threats have grown in both frequency and sophistication over the years.
Financial industry are attractive targets due to the vast amounts of money and sensitive data they handle. Some common types of attacks include:
| Threat/Challenge | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing & Social Engineering | Fraudulent tactics that trick employees or customers into revealing confidential information. | An employee receives a fake email prompting them to update login credentials, leading to account breaches. |
| Malware & Ransomware | Malicious software designed to disrupt systems or hold data hostage until a ransom is paid. | A ransomware attack encrypts customer data, forcing a bank to consider paying a ransom to restore operations. |
| Insider Threats | Cyber risks posed by employees or contractors misusing their authorised access. | A disgruntled employee leaking sensitive financial data, causing reputational and financial damage. |
| DDoS Attacks | Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm networks, causing service interruptions. | A coordinated DDoS attack floods a bank’s website, rendering online banking services unavailable. |
| Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) | Sophisticated, long-term cyberattacks aimed at gaining continuous access to sensitive systems. | Hackers infiltrate bank networks over months, stealing proprietary information and customer data. |
| Regulatory Compliance Challenges | Difficulty in adapting to continuously evolving cybersecurity laws and standards. | Failure to comply with new data protection regulations can result in heavy fines and mandatory system overhauls. |
| SIM Swapping Fraud | Criminals fraudulently obtain a duplicate SIM card by impersonating the victim, intercepting SMS-based authentication messages, and taking over bank accounts. | An attacker gathers personal information via phishing, convinces a telecom provider to issue a replacement SIM, and intercepts OTPs to execute unauthorised banking transactions. |
| ATM Skimming | A technique where criminals attach a device to an ATM machine to capture the information on a card’s magnetic stripe and record the PIN, facilitating counterfeit card creation. | A skimming device is discreetly installed on an ATM, allowing criminals to capture card details and PINs, which are later used to clone cards and withdraw funds illicitly. |
Each of these attack types poses significant risks. The potential financial losses, operational disruptions, and damage to reputation underscore the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Why is Cyber Security Important in Banking Sector?
Banking cybersecurity is not only an operational requirement, but it is also essential for preserving confidence in the financial system while safeguarding clients’ sensitive and financial information.
As traditional banking systems give way to digital banking, mobile apps, websites, and emerging fintech solutions, hackers have more avenues to attack. Here’s why cybersecurity is vital:
Protecting Sensitive Financial Data
Banks have a great amount of personal data, for example, account numbers, social security numbers, credit card numbers, and other personal financial data. Cyber attacks can result in these data being stolen, which can result in identity theft, financial fraud, and other severe losses for victims.
The consequences for both the bank and its customers can be severe.
- Personal Information Theft: Cybercriminals may use this data to gain unauthorized access to accounts, make fraudulent transactions, or even open new accounts in the victim’s name.
- Corporate Data Breaches: Sensitive financial data of businesses and their customers can also be stolen, leading to loss of trust and legal liabilities.
Maintaining Customer Trust and Reputation
A bank’s best asset is its reputation. Consumers want a promise of security for their personal financial information when banking. This can be seriously compromised in a breach, which can result in lost business and a tarnished reputation. In an industry where customer loyalty is hard-earned, cybercrime and cybersecurity threats can erode a bank’s market position in no time.
- Customer Loyalty: Banks that fail to protect customer data risk losing their clients to competitors with stronger security practices.
- Brand Damage: A publicised cyber attack can lead to negative press and a lasting loss of confidence among customers and investors.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with security and privacy measures in the financial sector is at the stringent end of the spectrum.
Cybersecurity practices allow banks to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and a wide range of other domestic and foreign laws.
Prevention of Financial Loss and Fraud
Cybercrime and cyber fraud is among banking’s greatest threats. Criminals employ a variety of different methods, such as phishing, social engineering attack, and malware, in a bid to have clients supply personal information.
With mobile banking on a growth trend, such practices have spread widely. Effectively practiced cybersecurity helps in avoiding fraudulent transactions and reducing fraudulent risk, which protects the institution’s assets as well as its clients’ funds.
Safeguarding Operational Continuity
Banking systems can experience a breach and can cease to function, resulting in a reduction in productivity and an increase in retrieval and recovery expenses.
Cyber security guarantees that banking systems can endure cyber attacks and remain functional at all times.
Adaptation to a Growing Threat
A myriad of cyber threats is emerging day by day. The improvement of cybercriminals has expanded their scope, and therefore, banks need moreover protections such as Intrusion prevention systems, data encryption, multi-factor authentication, security checks, and other advanced methods to prevent them from being overpowered by their expectations.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Why Banks Are Prime Targets for Cybercrime: Key Vulnerabilities and Drivers?
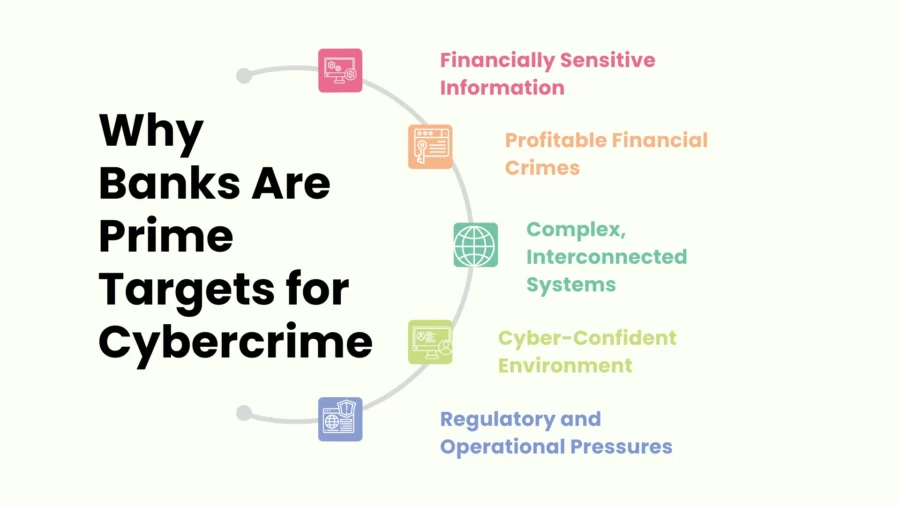
Banking sectors are also among the most sought after sectors for cyberema and cybersecurity attacks due to these reasons:
Financially Sensitive Information: Cybercriminals can capitalize on diced identities by selling sensitive financial details stored in bank account and credit card records, transaction history, dates of birth, and identification details online in the black market for identity theft.
Profitable Financial Crimes: Ransom through credit card scams and identity theft profit criminals, making banking institutions a repetitive target for such crimes. Cybercriminals steal funds, initiate fraudulent transactions, and attack computers using malware and ransomware.
Complex, Interconnected Systems: In addition to legacy systems, modern digital platforms pose a combination of interconnected systems that banks are reliant on. Attackers expertly exploit outdated systems that are neither regularly updated or patched, exposing vulnerabilities and weaknesses introducd through the complexity.
Cyber-Confident Environment: Sophisticated techniques to social engineer bypass traditional security measures allows cybercriminals to take advantage and profit from the overconfident reputation associated with banking institutions abusing the belief of advanced security infrastructure.
Regulatory and Operational Pressures: While banks are required to comply with strict regulatory standards, the pressure to maintain operational continuity sometimes results in security shortcuts or delayed updates, creating exploitable gaps.
These factors, combined with the evolving nature of cyber threats, make the banking sector particularly susceptible to cybercrime.
How Prevalent is Bank Cyber Crime?
Bank cybercrime has become a critical concern for financial institutions worldwide, with several indicators highlighting its rapid increase and severe impact:
Rapid Growth in Incidents: Between 2014 and 2019, data breaches and cyberattacks in the banking sector increased by nearly 500%, with each incident causing an average financial loss of around $18 million.
High-Profile Breaches:
- In 2019, the Capital One breach compromised the personal information of over 100 million customers.
- In 2018, a cyberattack in Atlanta’s financial services led to significant monetary losses.
- In 2020, HSBC experienced an insider attack that resulted in the theft of private customer information.
Widespread Fraud in India: According to data from the Reserve Bank of India:
- Between FY2020 and FY2024, cyber fraud resulted in losses of ₹3,207 crore over 5,82,000 cases.
- FY2024 saw a sharp spike, with incidents rising from 75,800 in FY2023 to 292,800, and the financial loss increasing from ₹421.4 crore to ₹2,054.6 crore.
States like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu are particularly affected, with Maharashtra accounting for more than one-fourth of the total losses.
Increased Digital Transactions: The explosion in digital payments is also a significant factor. The RBI Governor noted that digital transactions have grown 90-fold over the past 12 years, which has correspondingly expanded the target base for cybercriminals.
Impact on Private vs. Public Sector Banks: The analysis of fraud cases over five years shows that the top five banks—Kotak Mahindra Bank, Axis Bank, State Bank of India, HDFC Bank, and ICICI Bank—accounted for about 62% of the total fraud losses and 53% of the incidents.
Notably, private sector banks are more frequently targeted than public sector banks, suggesting that a focus on user-friendly digital services might come with increased cybersecurity risks.
Effective Cybersecurity Solutions for Banks
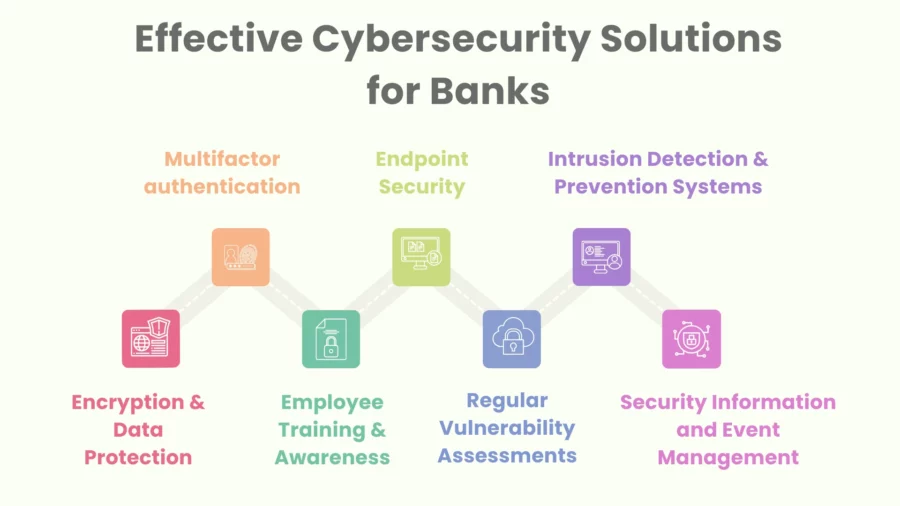
Banks have been adopting a multi-staged security system based on latest technologies, best practices, and constant surveillance in a quest to protect sensitive financial information and uphold customer trust.
Some of these effective banking cybersecurity solutions have been enumerated below.
Multifactor authentication, MFA for short, is an authentication process which prompts users for more than a password.
For example, in conjunction with a password, users may be prompted to provide a code sent via a mobile phone, or authenticate based on biometric data, such as a fingerprint, or face recognition. This is an additional security barrier, which makes it more difficult for an attack.
Encryption & Data Protection: When data is sent over the network, these measures are very important to use in order to protect data.
Encryption prevents attackers from being able to read the information even if they manage to gain access to it.
Encryption is used in most banks to safeguard sensitive client details, transaction information, and internal messages.
- End-to-End Encryption: Data is encrypted from the time the user device transmits the information to the bank server.
Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDPS): Together with a reputable cyber security company, banks set up a systemized monitoring of the network traffic that banks run to identify any abnormalities that could potentially lead to attacks, and if detected, preemptively stop them.
- Real-Time Monitoring: The systems preset within the banks with the partnered security firm allow identification of any unwanted penetration into the banks which, in turn, allows the banks to act before any potential danger turns to devastation.
- Automated Responses: A compromised account will automatically send a signal and the system will immediately stop any suspicious actions from occurring. This is the most rudimentary action taken, and is done without human intervention using IDPS.
Endpoint Security: Numerous devices, such as laptops, tablets, and smartphones, all connecting to the central banking system require stronger security protocols than just a firewall. Therefore, endpoint protection is crucial.
These solutions prevent digital attacks and unauthorised access to specific devices and put an end to any malware before it can infect the system.
With various devices connecting to the central network, they serve as the first line of defense. If they are attacked, the broader network will remain secure.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM Consolidates log files from various sources and offers continuous analysis, alerts based on the severity of incidents, and all relevant information is sorted to be accessible and usable.
Employee Training & Awareness: Relies on training staff properly so that they can accurately identify attacks on the company and act accordingly. Employees should also learn appropriate best practices to avoid falling victim to phishing attacks.
Regular Vulnerability Assessments: Routine audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability scans help identify weaknesses in the system. By addressing these vulnerabilities promptly through patches and updates, banks can proactively reduce the risk of an exploit or breach.
Together, these solutions create a robust defense framework that helps banks stay ahead of evolving cyber threats while complying with regulatory standards.
Top Cybersecurity Framework for Banks
Here are some of the top cybersecurity frameworks widely adopted by banks:
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): A risk-based approach that outlines best practices across five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. This framework helps banks assess current security postures and build robust defense strategies.
ISO/IEC 27001: An internationally recognized standard for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). It guides banks in managing risks and protecting sensitive financial data.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Specifically designed for organisations handling credit card transactions, this framework ensures that banks implement security measures to protect cardholder data and reduce fraud risks.
CIS Controls: A set of 20 prioritized actions designed to mitigate the most common cyber threats. These controls offer practical, actionable steps for banks to strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): Focused on IT governance and management, COBIT helps banks align IT goals with business objectives, manage risks effectively, and ensure robust security and compliance.
Each framework offers a unique approach to cybersecurity, and banks often integrate elements from multiple frameworks to create a comprehensive defense strategy.
What’s Next?
Cybersecurity is indispensable in the banking sector as digital banking transforms financial systems and demands a robust layer of security to prevent fraudulent activities and malicious breaches.
Regulatory requirements and a comprehensive security policy—utilising fingerprint scans and decryption keys—are essential to counter phishing attempts and phishing attacks.
A proactive approach, backed by insights from Cybersecurity Ventures and evolving cybersecurity trends, helps banks mitigate risks and refine their cybersecurity efforts.
These measures ensure social security, protect sensitive data, and maintain customer trust. This commitment safeguards assets and fosters innovation.
As digital banking continues to grow, valuable insights drive the need for continuous improvement in defense strategies against ever-more sophisticated threats.
Bytescare helps protect your digital world from the dangers of cybercrime by offering state-of-the-art solutions to secure your data and digital identity.
Don’t wait until it’s too late—explore our advanced protection tools and get a head start in defending your online presence. Take control of your cybersecurity now. Book a demo now to secure your digital future!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
How does strong cybersecurity contribute to customer trust?
When customers know their data and financial transactions are secured by robust measures like encryption and multi-factor authentication, it reinforces confidence in the bank’s reliability and commitment to safety.
What role do evolving regulations play in shaping banking cybersecurity?
Regulatory mandates (e.g., GDPR, PCI DSS) force banks to continuously update their security protocols, ensuring they meet high standards for data protection and potential risk management, thus safeguarding both the institution and its clients.
How does digital transformation impact cybersecurity in banking?
As banks adopt digital channels and fintech innovations, the attack surface expands. Cybersecurity for banks becomes integral to every digital initiative, ensuring new technologies are introduced without compromising security.
What are some proactive measures banks can take against emerging threats?
Investing in advanced threat detection systems, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and fostering a culture of security awareness among employees are key to staying ahead of cybercriminals.
How do banks assess the financial impact of a cyber breach?
Beyond immediate losses, banks consider long-term impacts like customer attrition, reputational damage, regulatory fines, and increased cybersecurity insurance costs when evaluating breaches.
How can banks create a robust incident response plan to handle cybersecurity incidents effectively?
Banks can create a robust incident response plan by leveraging the advancement of technology to ensure adequate protection against cyber attacks on online banking platforms. This plan must include clear roles, continuous training, risk assessments, threat intelligence, and coordinated communication with regulators and stakeholders for a rapid, effective, and efficient response.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.


