Key Takeaways:
- India faces a growing cybercrime wave, with incidents rising sharply in recent years. This poses a significant threat to national security, the economy and individual privacy.
- India’s current cyber laws, primarily the Information Technology Act of 2000, are considered outdated and inadequate to address the complexity of modern cybercrime.
- The lack of clear legal provisions for emerging threats like ransomware, cyberstalking, and sophisticated cyber fraud makes it difficult to hold perpetrators accountable.
As India grows in its use of digital technology, it faces more cyber crime. This includes problems like online financial fraud, identity theft, cyber terrorism, and espionage. These threats are complex and changing quickly.
There are laws, such as the Indian Penal Code and the Information Technology Act, that help with legal actions. However, these laws are not the best because they are old and technology is advancing fast. For India to fight this rising threat, it needs strong legal actions and better cybersecurity measures.
This article on “challenges to Indian law and cybercrime” gives you useful insight into the rising concern of cybercrime that our country faces.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Cybercrime in India: An Overview
Cybercrime is no longer just something rare. It has become a serious issue affecting countries all over the world, including India. Cybercrime is any illegal act done using computers and networks. This includes many cyber offences like hacking, data breaches, financial fraud, and cyber terrorism.
The growth of cybercrime happens for several reasons.
One reason is the rising number of people using the internet. Another is the increase in digital devices and the move to online banking. Sadly, these changes also give criminals more chances to find weak spots in digital systems and take advantage of people and businesses who might not see the danger.
The Rise of Cybercrime in Recent Years
The fast growth of information technology has changed our lives a lot. However, it has also created new chances for crime.
Cybercrime has increased quickly in recent years. It affects businesses, people, and even national security. The internet connects everyone, which helps cyber criminals act freely across borders. This makes it hard for law enforcement agencies to catch them.
Cyber terrorism is a big concern. Terrorist groups are using the internet more to recruit people, spread messages, and plan attacks. They take advantage of the privacy and wide reach that technology offers. For example, the attempted cyberattack on the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant shows the serious real-world damage that can happen.
Law enforcement agencies have a tough job fighting cybercrime. Technology is changing fast, so they need to keep learning and adapting to stay ahead of criminals.
There are also challenges like different legal areas, collecting digital evidence, and needing help from other countries. To win against cybercrime, it is important for governments, law enforcement, and private businesses to work together.
Major Types of Cybercrimes Affecting India
The many online activities in India have led to a wide range of cybercrimes that affect people, businesses, and the government.
There are financial scams that trick innocent individuals. Some attacks are aimed at important systems. It’s important to know the different forms of cybercrime. This knowledge helps us create better safety legal measures and laws.
Here are some major types of cybercrime in India impacting India:
Financial Frauds: Many people face phishing attacks, online scams, and credit card fraud, especially those who do not know much about cybersecurity.
For example, a malware attack on the SWIFT system of City Union Bank resulted in unauthorised transactions totaling USD 2 million in March 2020.
Identity Theft: Stealing personal information, like Aadhaar numbers, PAN card details, and bank account information, is a big problem. This can lead to money loss and misuse of identity.
Cyberstalking and Harassment: Online platforms are often used to harass, stalk, or defame individuals. This can have serious emotional and social effects on victims.
Cyber Espionage: Cyber espionage involves using cyber attacks to spy on or disrupt the interests of other nations or organisations. Like many other countries, India is a target for cyber espionage aimed at stealing confidential information to gain a strategic advantage. Such activities can impact India’s national security, foreign policy, and economic growth.
For instance, in 2020, a cyber espionage operation called “Operation SideCopy,” attributed to a Pakistani threat actor, was uncovered. This campaign targeted Indian military and diplomatic personnel through malware and phishing emails.
These examples show how cybercrime keeps changing. Law enforcement agencies and policymakers must update their methods to handle these issues effectively.
Legal Framework Against Cybercrime in India
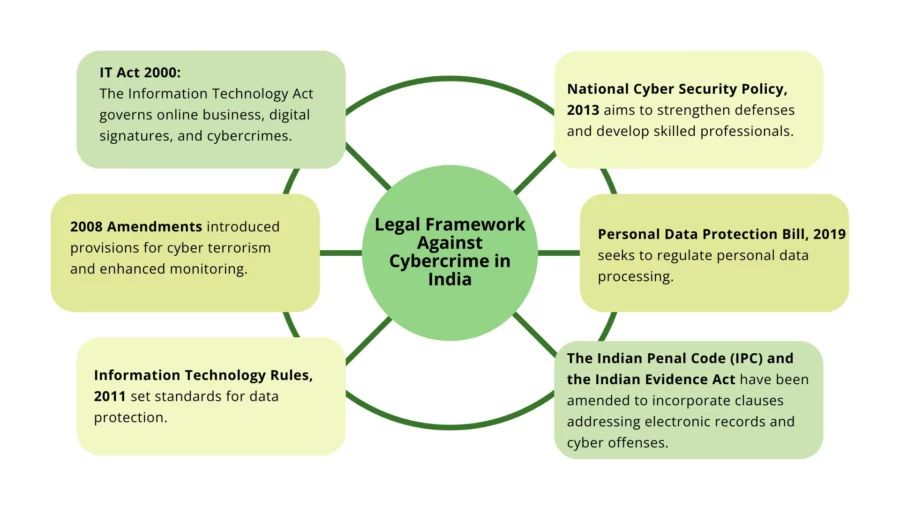
India’s laws on cybercrime mainly come from the Information Technology Act of 2000 (IT Act). This law aims to manage electronic business, digital signatures, and crimes involving computer systems. Still, it has had a hard time adapting to the new challenges and changes in online crime.
India faces several problems in its cybercrime legal framework. These include not having enough rules to deal with new threats, issues with jurisdiction in cross-border cybercrime, and a lack of specialised training and resources for law enforcement agencies.
Amendments to the IT Act have tried to fix some of these issues. However, we need a stronger and more flexible approach to effectively deal with the increasing threats.
The IT Act 2000 and Its Limitations
The Information Technology Act of 2000 (IT Act) is important in India’s fight against cybercrime. It covers things like online business, digital signatures, and crimes involving computer systems. When it was created, the IT Act was innovative, but technology has changed quickly, showing that the Act no longer fully meets today’s cyber challenges.
One big issue is that the Act does not have strong rules for new cybercrimes like ransomware, complex phishing scams, and cyberbullying.
It mainly addresses older cybercrimes, leaving empty spaces in the law that criminals can take advantage of. Additionally, electronic records, which are key in cybercrime investigations, can be tricky. The rules about evidence in the IT Act are not always clear, making it hard to use them in complicated cases.
To fix these issues, we need to take several steps. This means changing laws, building skills in law enforcement agencies, and raising public awareness. Reviewing and updating the IT Act is vital to keep it effective against new cyber threats.
Amendments to the IT Act
The IT Act was amended in 2008 to tackle emerging cyber threats.
Notable changes included the introduction of provisions for cyber terrorism (Section 66F), enhanced government monitoring powers (Sections 69, 69A, and 69B), and penalties for intermediaries that violate government directives (Section 67C).
While these amendments aimed to strengthen the legal system, they have not fully addressed the evolving landscape of cybercrime.
Information Technology Rules, 2011
An important component of India’s cybersecurity legislation under the IT Act is the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules, 2011 (commonly referred to as the Privacy Rules).
Key amendments within these rules include regulations for intermediaries, updated penalties and violation fees for cybercrime, online fraud, defamation, and the non-consensual publication of private images, as well as measures for censoring or restricting certain types of speech.
Both the Information Technology Act (ITA) and the IT Rules play a crucial role in governing how Indian entities and organisations handle sensitive information, ensuring data protection, data retention, and the collection of personal and other sensitive data.
Additionally, various sectors in India, such as banking, insurance, telecommunications, and healthcare, incorporate data privacy provisions within their own specific statutes.
National Cyber Security Policy, 2013
In 2013, the Department of Electronics and Information Technology (DeitY) launched the National Cyber Security Policy (NCSP) to provide a security framework for public and private organisations against cyber attacks.
The policy aims to enhance India’s cyber ecosystem by developing dynamic strategies and creating a workforce of over 500,000 skilled IT professionals within five years.
Key objectives include establishing a resilient cyberspace for individuals and organisations, safeguarding cyber infrastructure, reducing vulnerabilities, and strengthening defenses. Additionally, the NCSP encourages organisations to align cybersecurity policies with strategic goals and fosters cooperation to mitigate the impact of cybercrime.
The Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019
The introduction of the Personal Data Protection Bill represents a significant advancement in addressing data protection and privacy concerns. This bill aims to regulate the processing of personal data and establish a Data Protection Authority. However, its effectiveness will largely depend on its implementation and how well it integrates with existing laws.
Provisions in Other Laws
In India, various laws contain provisions related to cybercrime. The Indian Penal Code (IPC) and the Indian Evidence Act have been amended to incorporate clauses addressing electronic records and cyber offenses.
Additionally, intellectual property laws, including the Copyright Act and the Trademarks Act, offer legal remedies for cyber offenses involving intellectual property.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Challenges to Indian Law and Cybercrime
The challenges to Indian law in addressing cybercrime are multifaceted.
Key issues include outdated legislation that struggles to keep pace with rapidly evolving cyber threats, a lack of procedural rules for investigating cyber offenses, and insufficient technical expertise among law enforcement.
Additionally, there is a significant gap in public awareness regarding cybersecurity, which complicates the enforcement of existing laws. Here are some of the main challenges:
Outdated Legislation
The primary legislation governing cybercrime, the Information Technology Act of 2000, is over two decades old and does not adequately address modern cyber threats.
Despite its amendments, the IT Act lacks specific provisions to tackle numerous emerging cyber threats. Issues such as ransomware attacks, cyberstalking, and advanced financial fraud are not thoroughly addressed. This gap in the legislation hinders law enforcement agencies from effectively prosecuting these crimes.
Similarly the Indian Penal Code (IPC) is also outdated, with many provisions not applicable to current nature of cybercrime scenarios.
Fragmented Regulatory Framework
- India lacks a comprehensive, unified cybersecurity law, relying instead on multiple sector-specific regulations that can lead to inconsistencies and confusion.
- The absence of clear guidelines makes it difficult for organisations to comply with cybersecurity standards.
Public Awareness and Education
- Many people lack knowledge about cybersecurity risks and best practices, which makes them more vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Awareness campaigns and educational initiatives are essential to empower individuals and organisations to protect themselves.
Rapidly Evolving Threat Landscape
- Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with new types of attacks emerging regularly, making it challenging for existing laws to remain relevant.
- The speed of technological advancement often outpaces legislative processes, resulting in gaps in legal protections.
Privacy Concerns
- Provisions in existing laws, such as the IT Act, can lead to privacy violations, particularly with government surveillance capabilities.
- Balancing cybersecurity measures with individual privacy rights remains a contentious issue.
International Cooperation
Cybercrime frequently crosses national borders, leading to significant jurisdictional challenges. A cybercriminal based in another country can easily target victims in India, complicating the ability of Indian law enforcement agencies to investigate and prosecute these offenses.
While international cooperation and treaties are crucial for addressing these challenges, the processes involved are often slow and cumbersome.
Compliance Burden on Businesses
- Organisations face challenges in meeting compliance requirements due to the complexity and ambiguity of existing regulations.
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) may struggle to implement necessary cybersecurity measures due to resource constraints.
Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from the government, law enforcement, businesses, and the public to create a more robust and effective legal framework for combating cybercrime in India.
Enhancing Cyber Security Measures
Strengthening India’s cybersecurity needs several important steps. We require new technology, strong laws, teamwork with other countries, and better awareness among the public. Taking action before problems happen is key to reducing risks from changing cyber threats.
We should invest in better cybersecurity technology. We also need to support research and development in this area. Working together with the government and private companies is important for improving national safety.
By creating a culture of cybersecurity awareness through education and training programs, we help people and organisations protect themselves from cyber threats.
Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not just the job of governments or law enforcement agencies. It needs everyone to work together, including private companies, communities, and individuals.
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are very important for sharing information, responding to cyber threats, and creating new cybersecurity solutions. Key areas like financial institutions, energy grids, and healthcare systems attract cybercriminals.
PPPs help government groups and private firms share threat information, best practices, and useful resources. This teamwork helps spot cyberattacks early and respond in a smart way. It also helps in creating strategies for defending against future attacks. Joint training sessions and exercises can further improve how well they work together.
It’s also important to raise awareness about cybersecurity among people. PPPs can help promote this through educational programs, campaigns to inform the public, and training for both individuals and businesses. This way, everyone can help make national cybersecurity stronger.
Innovations in Cybersecurity Technologies
The constant evolution of cyber threats necessitates continual innovation in cybersecurity technologies to protect sensitive information, critical infrastructure, and individual users.
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain, are driving advancements in threat detection, prevention, and response mechanisms.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms analyse vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive threat detection and automated incident response.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralised and tamper-proof nature, enhances data security and prevents unauthorised access.
| Cybersecurity Technology | Description |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Powers threat detection systems by analysing data to identify and respond to malicious activities |
| Machine Learning (ML) | Enables predictive analysis for identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities in systems |
| Blockchain Technology | Enhances data security and integrity through its decentralised and tamper-proof ledger system |
| Biometric Authentication | Provides an additional layer of security by verifying user identity based on unique biological traits. |
| Cloud Security Solutions | Offers secure data storage and processing in the cloud while ensuring data privacy and compliance. |
Investing in research and development of cutting-edge cybersecurity technologies is essential to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. Collaboration between governments, the private sector, and academic institutions can accelerate innovation and strengthen the cybersecurity posture of nations.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What’s Next?
Cybercrime in India is changing quickly. This creates big challenges for current laws. As cyber threats become more complex, protecting privacy is more important than ever. Indian cyber laws must adapt and strengthen their rules. Here are some important steps to take:
- Deal with crimes across borders.
- Update the laws we have.
- Promote partnerships between the public and private sectors for better cybersecurity.
Individuals can also help by staying informed and taking steps to protect their online activities. By working together to face these challenges, India can fight cyber threats better and keep its citizens’ digital rights safe.
Benefit from Bytescare proactive approach to cybersecurity, keeping your business and personal information safe from evolving cyber threats.
Ready to secure your digital environment? Contact us today and experience Bytescare’s solutions firsthand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What steps can individuals take to protect themselves from cybercrime?
Internet users can improve their information security by using strong passwords. They should also be careful of phishing attempts and keep their devices updated. It is important to regularly back up important data. Using reliable service providers with strong security can help reduce the chances of data breaches and lessen any possible damage.
How does the Indian government plan to update its cyber laws?
The Indian government is looking into changes in its laws about cybercrime. This effort comes from the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology. They want to create a better plan to handle these issues. Part of this plan includes updating the National Cyber Security Policy. They also aim to improve the skills of law enforcement agencies. This way, these agencies can fight new online threats more effectively.
What role do international collaborations play in combating cybercrimes within the Indian legal framework?
International collaborations enhance India’s cybersecurity infrastructure by facilitating information sharing and joint investigations. They help address the threat of cybercrime, ensuring that current legislation effectively tackles illegal activities across borders, especially in critical sectors.
What are the issues and challenges of cyber security?
Challenges include outdated current legislation, vulnerabilities in electronic forms, and the protection of customer identities. Additionally, both critical and commercial sectors face increasing risks from sophisticated cyber threats and illegal activities.
How can individuals protect themselves from cybercrime in light of legal challenges?
Individuals can take proactive steps such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, being cautious with personal information online, and staying informed about common cyber threats and scams.
What are the implications of inadequate cybersecurity laws for businesses in India?
Inadequate cybersecurity laws can expose businesses to increased risks of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Companies may also face legal liabilities if they fail to protect customer data adequately.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

