Key Takeaways:
- Cybercrime targets individuals or businesses for financial gain, while cyber warfare involves state-sponsored digital attacks to disrupt national security and essential infrastructure.
- Cybercriminals use phishing, malware attacks, and fraud for profit, whereas cyber warfare includes espionage, sabotage, and political disruption between nations.
- Cybercrime is prosecuted under legal frameworks, while cyber warfare falls into geopolitical conflicts, often lacking clear international regulations and accountability.
Cybercrime & cyber warfare are two separate but equally dangerous categories that have emerged as cyber threats. Both operate in the digital world but their goals or effects are very different.
Cybercrime is a booming illegal business. Cybersecurity Ventures says that the cybercrime costs around the world will rise from $3 trillion in 2015 to $10.5 trillion per year by 2025.
In order to steal private information or demand ransoms hackers attack even government computer systems. Identity theft or phishing emails are two types of cybercrime that happen all the time. As a result it can harm reputations or drain financial networks.
However countries can use cyber warfare as a weapon. To get strategic benefits or governments spy on people online.
The size of current cyber warfare attacks is shown by the fact that a hack on SolarWinds in 2020 touched over 18,000 organisations including U.S. government agencies.
Cybercriminals want to make money but state-sponsored attacks want to weaken national security systems.
As digital threats grow everyone must know the difference between cybercrime and cyber warfare. The first steps to keeping safe in this constantly changing online battlefield are to plan your defenses ahead of time.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Cybercrime?
Cybercrime is any kind of criminal activities that is done on computers or the internet. Some examples of cybercrime are as follows.
- Hacking
- Identity theft
- Ransomware attacks
- Financial fraud
- Online scams
Cybercrime has spread around the world as digital data sharing grow quickly.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making it more profitable than the global drug trade.
In 2023 alone, ransomware attacks surged by 74%, crippling businesses and demanding millions in ransom payments.
Phishing scams have also gone through a spike. Every day 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent to trick people into giving out private information.
Cybercriminals get into network equipment by taking advantage of mistakes made by humans or old security systems.
As technology improves so do cyber threats. This makes it more important than ever to protect yourself from cyber threats. The best way to lower your cyber risks is to put strong security measures in place.
Common Types of Cybercrime
| Hacking | Gaining unauthorised access to systems or networks to steal, alter, or delete data. | Can lead to data breaches, loss of sensitive information, and financial damage. |
| Phishing | Deceptive emails, messages, or websites that trick real users into providing personal or financial information. | Leads to identity theft, unauthorised transactions, and account takeovers. |
| Identity Theft | Stealing someone’s personal information (like SSN, bank details) to commit fraud. | Result in financial losses Credit score damage Legal troubles |
| Ransomware | Malicious software that holds your files or systems captives until you pay a fee. | Can paralyze businesses, cause data loss, and lead to financial extortion. |
| Online Fraud | Scams involving fake websites, investment fraud, or e-commerce deception. | Can lead to money loses or lessened financial security. |
Real-life Examples of Cyber Incidents
Yahoo Data Breach (2013-2014)
Hackers got into 3 billion Yahoo accounts along with stole information from them. This was one of the biggest cybercrimes in history. People’s names or passwords were stolen which affected millions of people around the world.
WannaCry Ransomware Attack (2017)
A global ransomware attack that infected 200,000 computers in 150 countries, locking users out of their files until they paid a ransom in Bitcoin. It caused problems for businesses as well as the government.
Facebook Data Leak (2019)
Personal information about 530 million Facebook users like phone numbers or email addresses was posted online. As a result which increased privacy issues along with the risk of identity theft.
Colonial Pipeline Hack (2021)
A ransomware attack in 2021 shut down the largest fuel pipeline in the U.S., which led to widespread gas shortages. The business paid a $4.4 million ransom to get back in.
Twitter Bitcoin Scam (2020)
Hackers gained access to high-profile Twitter accounts, including Elon Musk and Barack Obama, posting a Bitcoin scam that tricked users into sending money.
Impacts of Cybercrime
Cybercrime affects a lot of people from individuals to large companies around the world. People can have identity theft or privacy breaches due to cybercrime.
If a victim’s identity is used illegally they could lose their funds or even get in trouble with the law.
Studies show that one in three people around the world have been affected by cybercrime at some point. Cyberattacks can cost companies money or even stop them from running normally.
One ransomware attack can cost a business millions of dollars( like when Colonial Pipeline paid a $4.4 million payment in 2021). Customers lose trust when data is stolen which makes it harder to get back on track.
Cybercrime puts national security or critical infrastructure at risk for businesses. Cyber warfare can hurt businesses which can affect the security of the whole world.
Strong cybersecurity measures are needed to lower the risks of cyber threats as they change over time.
How to Combat Cybercrime?
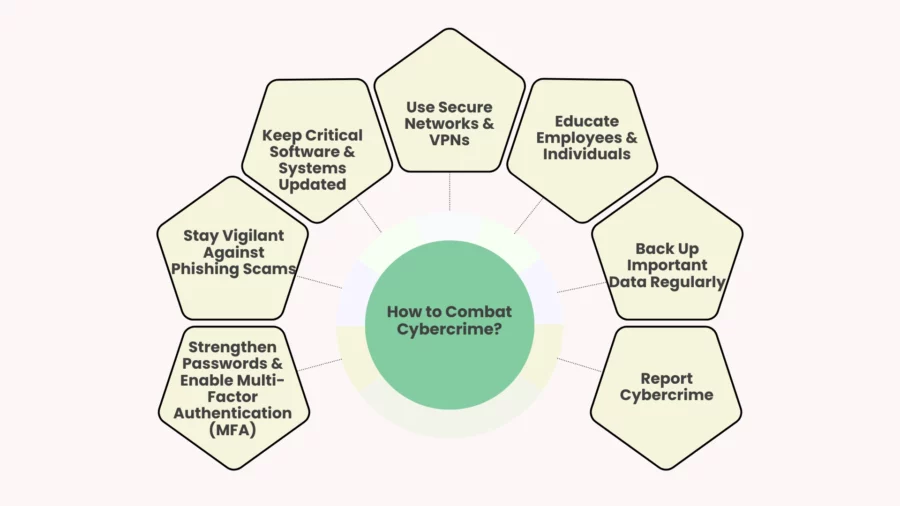
With cybercrime on the rise, protecting yourself, your business, and your organisation is more important than ever. Here’s how you can stay ahead of cyber criminal activities.
Strengthen Passwords & Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Hackers enjoy passwords that are easy to guess. For extra protection make sure each account has a strong unique password. Also turn on multifactor authentication for better protection.
Stay Vigilant Against Phishing Scams
Cybercriminals often use fake emails or messages to steal sensitive information. Don’t click on links that look suspicious or give out personal information until you know for sure where they came from.
Keep Critical Software & Systems Updated
Hackers can get in through software that is too old. Keep your antivirus software or operating systems up to date so that any vulnerabilities are fixed.
Use Secure Networks & VPNs
When you’re on public Wi-Fi don’t do any banking or log in to private accounts. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) encrypts your data which makes it harder for other people to read it.
Educate Employees & Individuals
Cybersecurity education can prevent costly mistakes. Teach your employees how to keep private information safe or report anything that seems fishy.
Back Up Important Data Regularly
Ransomware attacks can lock you out of essential files. Regular backups ensure you don’t lose valuable information, even if an attack happens.
Report Cybercrime
If you become a target of cybercrime you should tell the cyber security experts right away so that the attackers can’t do any more damage.
Cybercrime is a never-ending fight but you can safeguard yourself from potential threats by taking the right measures in the digital world.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Cyber Warfare?
Cyber warfare is when one country sends hackers into another country’s systems to damage or mess up their security.
Cybercrime is usually done to make money but cyberwarfare is usually done for political or military reasons. It includes things like getting into government systems or messing with important services like banks.
Reports on cybersecurity say that more than 30 countries have created cyberwarfare capabilities. These countries have spent billions of dollars on cyber defense as well as cyber offensive.
Stuxnet a very advanced virus that shut down Iran’s nuclear sites in 2010 was one of the most well-known cyber warfare operations. Russia’s hacks on Ukraine which hit power lines as well as government systems is another example.
Cyber warfare is now thought of as the fifth sphere of war after land, sea, air forces & space. This is because of the rise of digital conflicts.
To protect against these growing dangers governments all over the world are making their cybersecurity defenses stronger.
7 Types of Cyber Warfare Attacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks overwhelm a website or server with fake traffic, preventing legitimate users from accessing it. This can be used to mess up important services like government websites or military networks making it impossible for people to access them.
Espionage
To steal information from other countries espionage in cyber warfare means keeping an eye on them. Cyber attackers frequently use botnets or spear-phishing techniques to get into private systems. And then steal valuable information without being caught.
Electrical Power Grid Attacks
Attacking a country’s power grid can cause widespread chaos by disabling critical infrastructure. These attacks can disrupt not only electricity but also communication systems, making services like texting and phone calls unavailable, and potentially endangering lives.
Sabotage
Cyber sabotage is when important data or systems are damaged on purpose. Attackers may use insider threats such as frustrated employees or people with ties to the enemy. Or they may go after weak government agencies to cause chaos by leaking or removing important data.
Surprise Attacks
Like the unexpected attacks on Pearl Harbor or 9/11 these attacks are meant to catch the enemy off guard. They are meant to make defenses weaker often getting the ground ready for a physical attack. They can be part of a bigger strategy called hybrid warfare.
Propaganda Attacks
To influence public opinion propaganda is used in cyber warfare. Attackers can spread lies or embarrassing facts through misinformation to make people not trust each other or even get people to back the enemy’s cause.
Economic Disruption
Targeting the financial systems, such as stock markets, payment networks, or banks, can cripple a nation’s economy.
Attackers could make it impossible to get to savings or cause huge problems with the economy that make people lose faith in economic institutions.
Real-Life Examples of Cyber Warfare
Stuxnet (2010)
One of the most famous cyber warfare attacks, Stuxnet targeted Iran’s nuclear enrichment facilities. It was a very smart worm that was made to stop uranium enrichment by breaking centrifuges. Many people think that the U.S. & Israel worked together on the attack.
Russian Cyberattacks on Ukraine (2015-2017)
In a series of attacks, Russian hackers targeted Ukraine’s power grid, causing massive blackouts for hundreds of thousands of people.
Additionally they got into Ukrainian government systems which slowed things down in addition to stealing private information.
SolarWinds Hack (2020)
Russian hackers breached SolarWinds, a company that provides IT services to multiple U.S. government agencies and private companies. The attack compromised over 18,000 systems, giving attackers access to critical systems and corporate data.
NotPetya (2017)
It is believed that Russia was behind this attack on Ukrainian infrastructure. But the malware spread around the world along with caused billions of dollars in damage. It had an effect on businesses like Maersk as well as the pharmaceutical giant Merck.
North Korean Cyberattacks
North Korea has been linked to a number of cyberattacks such as the WannaCry ransomware virus as well as the Sony Pictures hack in 2014. The goals of these attacks were to make political statements or steal information.
How Cyber Warfare Impacts National Security?
Cyber warfare is a big threat to national security because it steals private data or attacks critical infrastructure. Cyberattacks can be hard for countries to see which makes it harder for them to respond quickly unlike traditional wars.
In 2015 Russia launched a hack on Ukraine’s power grid cutting power to 225,000 people. This showed how easily a country’s infrastructure can be broken into. In the U.S., the SolarWinds hack (2020) put national security secrets from 9 government departments at risk.
Cyberattacks can also happen against military systems making them less able to defend themselves. It is thought that the Stuxnet worm was an operation between the U.S. & Israel. It stopped Iran’s nuclear program showing how cyber tools can be used as a weapon.
Cybersecurity is an important part of national defense because dangers can come from anywhere in the world. The threat to national security keeps growing as more countries depend on digital systems.
How to Combat Cyber Warfare?
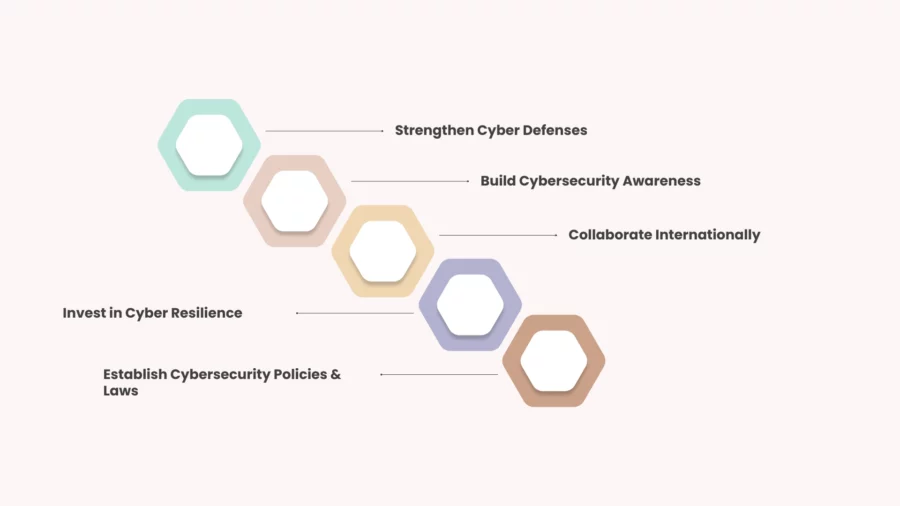
To stop cyber warfare we need to use strategic defense tactics in addition to working together as a global community. These steps will help to stay safe.
Strengthen Cyber Defenses
It is very important to put money into advanced cybersecurity technologies. To keep private data safe we should use firewalls or breach detection systems along with advanced threat analytics. Computer hackers can’t use flaws in old systems to launch attacks if software is regularly updated.
Build Cybersecurity Awareness
People are often the weakest link in cybersecurity. But educational programs can help stop them. Cyber spying are less likely to happen if employees or government officials are taught how to spot phishing attempts along with how to stay away from dangerous practices.
Collaborate Internationally
International cooperation is essential to fighting cyber warfare because it is frequently a threat to the whole world. Countries need to work together to protect themselves from cyber threats. Also should come up with laws for cyber warfare that apply to everyone.
Invest in Cyber Resilience
Cyber resilience is more than stopping attacks. It also means getting ready to get back online after an attack. To lessen the damage of an attack it’s important to regularly back up data in addition to have a clear incident response plan.
Establish Cybersecurity Policies & Laws
To protect national infrastructure governments should implement comprehensive cybersecurity regulations. Tough punishments for cyberattacks as well as ways to hold attackers responsible can stop people from attacking.
Because cyber warfare is becoming more dangerous countries can make their defenses stronger by staying alert to new threats.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Key Differences Between Cybercrime and Cyber Warfare
| Aspect | Cybercrime | Cyber Warfare |
|---|---|---|
| Motivation | Mostly driven by money or personal gain. | Because of military action or national interests. |
| Attackers | Typically individuals or organised criminal groups. | Nation-states or state-sponsored groups. |
| Targets | Individuals, businesses, and financial institutions. | Governments, military action, and critical national infrastructure. |
| Methods | Phishing, ransomware, identity theft, fraud. | Hacking, espionage, sabotage, disinformation. |
| Scale | Usually smaller scale, affecting specific victims. | Large-scale, potentially disrupting entire nations. |
| Impact | Financial loss, identity theft, data breaches. | National security threats, critical infrastructure disruption. |
| Legality | Illegal in all forms and punishable by law. | Often falls under international laws of warfare or military engagement. |
| Example | Yahoo data breach, ransomware attacks. | Stuxnet, Russian cyber attacks on Ukraine. |
How Cybercrime and Cyber Warfare Overlap?
While cybercrime and cyber warfare are distinct in many ways, there is a growing overlap, especially as nation-states recognise the power of cyber tools for both military and economic advantage.
Cybercriminals Working for Nation-States
Cybercriminals sometimes do things like data theft or financial scams on behalf of nation-states. In this case criminals might act like they are solo hackers while really working for a bigger global goal.
For example hackers with ties to North Korea have been linked to financial heists like taking millions of dollars from global banks.
However these crimes are often done for national security reasons like to fund the regime’s activities or mess up the global economy.
State-Sponsored Hacking Groups Engaging in Financial Crimes
Cybercrime & state-sponsored cyber attacks can sometimes be confused. Hacking groups from Russia have messed up financial systems by attacking banks as well as bitcoin platforms.
These attacks are done for financial along with political reasons. These cyber operations frequently use ransomware or steal financial information which are actions that are usually done by hackers but are done by governments to hurt economies.
Case Studies Where Cybercrime Tactics Were Used for Warfare
In some high-profile cyber warfare cases, tactics commonly used in cybercrime were repurposed for warfare. For example the NotPetya ransomware attack looked like a normal cybercrime plan at first. But it turned out to be an attack on Ukraine by Russia that was paid for by the Russian government.
This attack hurt Ukrainian businesses in addition to all the businesses around the world. This shows how hacking techniques can be used for political purposes.
Countries need to be more careful about protecting their digital assets as the lines between these two areas become less clear.
The Role of Governments and Law Enforcement
Governments and law enforcement agencies play a critical role in combating both cybercrime and cyber warfare. They are in charge of making laws or coming up with ways to protect national security.
Efforts to Combat Cybercrime
Governments have passed cybersecurity laws that make hackers responsible for their actions in order to fight cybercrime. In the U.S., the FBI Cyber Division works to stop cybercrime. Also INTERPOL coordinates efforts between countries to fight cyber threats across borders.
When people break the law they face harsh punishments like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the U.S. & GDPR in the EU.
On a national level agencies like the National Cyber Forensics and Training Alliance (NCFTA) work to fight new threats by giving people resources.
International Responses to Cyber Warfare
To stop cyber warfare on a global level organisations like NATO have made cybersecurity strategies. Also some countries have even made their own national cyber defense policies.
While countries like the US, China as well as Russia continue to fortify their own cyber defenses. Also NATO’s Cooperative Cyber Defence Center of Excellence assists member states in improving their defense against cyber attacks.
Challenges in Attribution & Enforcement
Attribution poses a serious problem in cybercrime as well as cyber warfare. Cyber attackers can hide behind proxies which makes it hard to find the person who did it. This is especially tough in attacks that are paid for by a government.
This makes it harder to enforce the law because many hackers work across foreign lines where the laws may be different. To successfully deal with these rising dangers there is a greater need for standardised laws.
How Can You Protect Against Cybercrime and Cyber Warfare?
Against Cybercrime
To stay safe against cybercrime we need to put in place strong security measures.
Strong Passwords
Using complex, unique passwords for each account significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access.
Two-Factor Authentication
Cybercriminals will have an even harder time getting in with two-factor authentication. This adds an extra layer of security.
Awareness of Phishing Scams & Safe Browsing Habits
Phishing scams are still a popular way to get private information. You can avoid these scams by being careful when hitting links. Companies should teach their employees how to spot messages that seem fishy.
Regular Software Updates
Cybercriminals often take advantage of gaps in old software. Updating operating systems or apps on a regular basis can help fix security flaws.
Anti-virus Software Protection
Installing antivirus software is another way to protect yourself because it gets rid of harmful threats before they can do any damage.
Against Cyber Warfare Threats
Protecting against cyber warfare scenario requires robust cybersecurity policies, strategic planning, and constant vigilance.
Importance of Cybersecurity Policies for Organisations & Governments
To protect their networks or critical systems businesses as well as governments must implement cybersecurity policies.
Security protocols or regular risk reviews to find gaps that can be used in cyber warfare should all be outlined in these policies.
Protection of Critical Infrastructure & Sensitive Data
Power lines or transportation systems are some of the examples of critical infrastructure that must be protected at all costs. In order to protect against cyber attacks that could stop essential services as well as jeopardize national security.
Governments need to implement strict data protection laws in addition to spending money on advanced technologies.
National Cybersecurity Initiatives & Training
Defense against cyber warfare is a top priority in national cybersecurity strategies like those made by NATO or the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
It is important for government officials as well as private-sector employees to get training on how to stop potential threats. This will make the country stronger as cyber threats evolve.
What’s Next?
The effects of cybercrime & cyber warfare are very different despite the fact that involve malicious activities online. Cybercriminals usually do bad things to make money. They target people or businesses to make money for themselves.
Cyber warfare is a state-sponsored effort to gain a political or economic edge. It frequently targets critical infrastructure along with national security.
It’s important for governments to stay alert because the line between these two threats is becoming less clear.
We can better fight against cybercrime as well as cyber warfare protecting our national security by enhancing cybersecurity measures. Also improving international cooperation plays a vital role in protection against cybercrime.
In this age of digital theft Bytescare uses advanced AI to keep your information safe from being stolen. Bytescare’s digital piracy monitoring quickly removes illegal content for protecting your work.
Let us help you take back control of the things you’ve made. Focus on what’s most important contact us for a personalised protection strategy!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is considered as cyber warfare?
Cyberwarfare operations refers to state-sponsored cyber attacks aimed at disrupting, damaging, or stealing information from a nation’s critical infrastructure, military systems, or government operations.
These attacks are intended to weaken a country’s economy, security, or political stability and can involve tactics like hacking, espionage, or denial-of-service attacks.
Can cybercrime lead to cyber warfare?
Yes, cyber crime can lead to cyber warfare, especially when criminal groups are sponsored or used by state actors to carry out politically motivated attacks.
Cybercriminals can also use cyber activities such as financial theft or disruption, which align with the objectives of cyber warfare, blurring the lines between the two.
What are some famous cyber warfare incidents?
Some famous cyber warfare incidents include the Stuxnet attack on Iran’s nuclear program (2010), the NotPetya attack that targeted Ukraine’s infrastructure (2017), and the SolarWinds hack which infiltrated United States government agencies (2020).
These attacks were state-sponsored and aimed at disrupting national security or gaining political advantage.
How do governments protect against cyber warfare?
Governments protect against cyber warfare by developing national cybersecurity strategies, enforcing cybersecurity policies, and investing in advanced defense technologies.
They also collaborate internationally to share intelligence, create response frameworks, and implement training programs for government agencies and military personnel to recognise and prevent cyber threats.
Are cybercriminals ever involved in cyber warfare?
Yes, cybercriminals can be involved in cyber warfare when they are hired or manipulated by nation-states to carry out attacks.
Cybercriminals may assist in activities like data theft, financial fraud, or denial-of-service attacks, often serving as proxies for state actors seeking to achieve strategic goals without directly engaging in conventional warfare.
How AI and advanced technologies are shaping cybersecurity?
AI and advanced technologies are revolutionizing cybersecurity by enabling faster threat detection, automated responses, and predictive analytics.
Machine learning algorithms can identify unusual patterns, detect potential vulnerabilities, and prevent cyberattacks before they occur.
AI helps strengthen defenses against increasingly sophisticated threats, making systems more resilient to both cyber crime and cyber warfare.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

