Key Takeaways:
- The counterfeit market spans multiple industries—luxury fashion, electronics, and pharmaceuticals—leading to substantial financial losses and job impacts worldwide.
- Counterfeit goods often bypass safety checks and can contain harmful materials, posing health and safety dangers to end-users.
- Modern solutions like AI, blockchain, and IoT tools are essential for identifying fake listings, verifying authenticity, and maintaining supply chain transparency.
In the economy of globalisation, counterfeit products have become a widespread problem for producers, sellers, and buyers alike.
With virtual stores and social networks becoming easier to open, access for counterfeiters to buyers has become easier.
Bargain-seeking buyers, in contrast, become increasingly susceptible to encountering counterfeit goods in disguise under real labels. Not only is a high proportion of counterfeit goods economically unsettling, but it is a critical matter in terms of health and security concerns as well.
For instance, counterfeit consumer goods such as drugs and cosmetics can have toxic chemicals, and such goods can have catastrophic consequences for ultimate buyers’ health.
This article provides examples of counterfeit items, tells you about how to detect and avoid counterfeit items, and tells you about technology use in countering the problem.
By reading, you will have a complete picture of the counterfeit problem—why it persists, how to stop it, and what can be anticipated in terms of eradicating counterfeit items in the global marketplace.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Global Counterfeit Market
The proliferation of counterfeited items is not geographically restricted, nor is it industrially delimited.
From luxury clothes to household goods, counterfeited items span industries and economies across the globe.
Scope and Scale
International trade in counterfeit goods has reached record levels. Various international groups have estimated illicit counterfeit consumer goods at several hundred billion dollars in annual loss of economy.
For example, counterfeiters capitalise on name value in apparel through creating high-end labels—items that in normal times would retail at a premium in actual stores.
Likewise, counterfeit electronics and drugs continue streaming onto cyberspace, bypassing traditional security tests and standards of quality. The digital economy played a significant role in driving such growth.
Online platforms, social networks, and even direct-to-consumer websites have become a source for providing fake products to unsuspecting buyers, and their detection and enforcement, therefore, become a global challenge.
Many global marketplaces see a surge in counterfeit products from China, contributing significantly to the overall counterfeit trade.
Economic and Social Impact
- Revenue Losses: Legitimate companies face considerable loss of revenue through competition with counterfeit goods. Even small knock-offs can steal sales from authentic goods, cutting into considerable profit over a period of years.
- Job Losses: As soon as a loss is incurred by companies, then they attempt to restrict expenses, and one of them can include cutting down manpower. Thus, counterfeiting not only destroys owners of brands but also affects job markets worldwide.
- Tax Evasion: Black markets and opaque web platforms are generally where counterfeited goods are exchanged. Taxation agencies can miss out on billions in unpaid taxes through such illicit deals.
- Consumer Deception: Consumers can believe that they have a great bargain for a name-branded item but then discover it is a shoddy, even lethal, counterfeit. That erodes trust in marketplaces and brands overall.
- Potential Support of Criminal Activities: In certain regions, profits gained through counterfeited merchandise can fund organised crime, supporting other illegal operations such as dealing in drugs or money laundering.
The impact of counterfeit products on global trade extends beyond lost revenue, influencing international regulations and cross-border enforcement efforts.
Top 5 Counterfeited Product Categories
| Product Category | Estimated Annual Loss (USD) | Primary Consumer Risk | Recent Seizure Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | $200 billion | Ineffective or harmful ingredients leading to health risks, antibiotic resistance | 2023 operation in Asia uncovered $7 million worth of fake antibiotics |
| Electronics | $100 billion lost as per Global Brand Counterfeiting Report | Potential fire hazards (due to faulty wiring/batteries), data security threats | BRIDEPI raided a Santiago factory, seizing counterfeit cell phones worth over $8 million. |
| Apparel & Footwear | $50 billion | Low-grade materials causing skin irritations, chemical exposure | Brands like Gucci, Louis Vuitton, Nike, and Adidas are particularly affected, facing billions in lost sales each year due to counterfeit goods. |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | $5.4 billion | Skin reactions, allergic responses, harmful chemical ingredients | In January 2020, LAPD seized over $300,000 in counterfeit Kylie Cosmetics products. |
| Automotive Parts | $45 billion | Malfunctioning components increasing the risk of accidents and injuries | In 2024, U.S. Customs and Border Protection seized over 211,000 counterfeit automotive parts |
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Common Types of Counterfeit Items
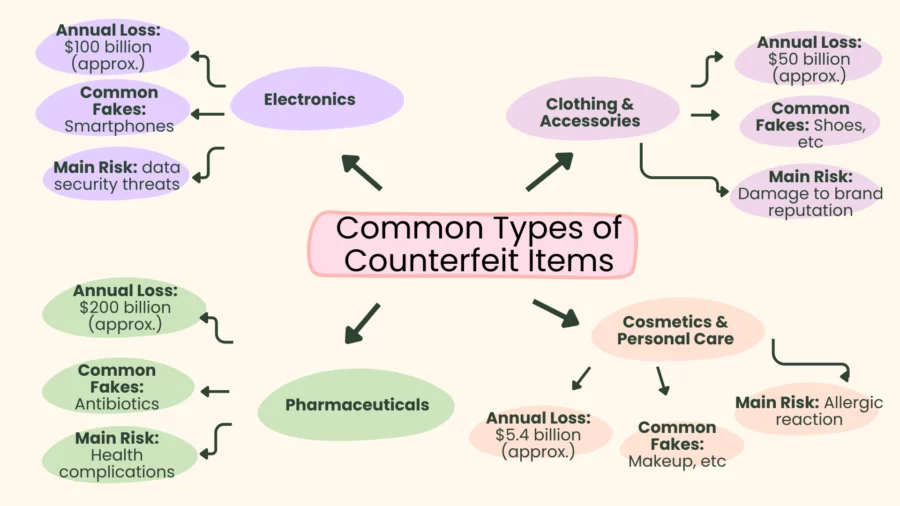
Counterfeit products can manifest in a variety of forms, including household items and high-value items such as high-end goods. Some of the most counterfeited items include:
Electronics
Counterfeit product examples: smartphones, chargers, headphones, batteries
Risks: potential fire hazards, electrical malfunctions, data security breaches
Pharmaceuticals
- Fake medicines, supplements, and medical equipment
- Risks: severe health consequences, treatment failures, antibiotic resistance
Clothing & Accessories
- Handbags, shoes, watches, jewelry
- Counterfeited because of high demand for brand-name luxury goods
Cosmetics & Personal Care Products
- Makeup, skincare, and haircare items
- Risks: skin irritation, allergic reactions, long-term health hazards
Toys & Baby Products
- Poorly made with unsafe materials or small parts
- Significant choking hazards and chemical concerns for children
Counterfeit Brands: High-Profile Targets
Many counterfeit brands originate from popular luxury or tech companies whose logos and trademarks carry substantial market value.
Fashion houses such as Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Chanel remain perennial targets because of their widespread recognition and the premium prices their goods command.
Electronics giants like Apple and Samsung also face rampant counterfeit challenges, with online marketplaces inundated by look-alike devices and accessories.
To know the broader impact of counterfeiting on the fashion industry, one must consider how such goods devalue brand exclusivity.
Counterfeit Products Examples & Real-Life Stories
- Luxury Handbags: In major cities, it’s common to see street vendors selling what appear to be designer purses for a fraction of the official retail price. Investigations often reveal hidden supply chains that mass-produce these knock-offs in substandard facilities.
- Online Pharmacies: Illegal websites sell prescription drugs with no real verification system in use. Toxic chemicals constitute part of such suspected “drugs,” and these have disastrous implications for buyers’ health.
- Electronics on E-commerce Platforms: Fake memory cards or USBs, with a larger capacity than actual ones, can corrupt and destroy data. Consumers won’t even become aware of fraud when it’s too late.
These real-life examples of counterfeit goods reveal the necessity for buyers to be ever aware and well-informed.
How Counterfeit Products Harm Businesses & Consumers
Brand Reputation Damage
One of the most significant impacts of counterfeit goods for real companies is loss of reputation.
Consumers, not knowing that they have purchased a counterfeit, when a counterfeit fails to work or ends up harming them, will target the real brand.
Negative feedback and word of mouth can go viral via social networks, ruining a company’s name.
Over a period, loss of trust can become a problem—if not an impossibility—to reverse.
Financial Losses
The presence of spurious goods in the marketplace will make buyers opt for cheap counterfeits in preference over originals. That will have a direct consequence in terms of sales revenue for originals.
Apart from that, companies will have to expend a significant amount on anti-piracy operations, lawsuits for protecting their trademark, and advertisements for convincing buyers regarding the genuineness of goods. All these will cost them in terms of millions of dollars annually.
Consumer Safety Risks
Counterfeit consumer products, in most instances, are manufactured with no consideration for controls over quality or for adhering to safety requirements.
For instance, counterfeit electronic goods can burn and overheat, and counterfeit drugs can contain toxic chemicals, including improper dosages of active ingredients.
Even a counterfeit toy, one that looks perfectly innocent, can produce a case of poisoning or choking. All such failures in terms of safety not only jeopardise individual consumers but also overload public health systems too.
“Counterfeiting poses not only an economic threat but also a grave danger to consumers who unknowingly purchase items that haven’t met safety standards.”
Legal and Ethical Concerns
Consumers who knowingly buy counterfeit items become complicit in intellectual property theft, undermining sound business practice.
Besides, companies that don’t act responsibly in stemming counterfeiting can become legally challenged, specifically when such inaction ends in widespread victimisation of buyers.
That comes with its complex moral dilemmas in which consumer rights, brand protection, and legality clash.
This not only erodes brand value but also puts a spotlight on the impact of counterfeiting on intellectual property rights, with infringement potentially causing costly lawsuits.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Identifying Fake vs. Genuine Merchandise
Given the expertise in counterfeiting these days, it takes a keen eye and, in a few instances, expert tools and information in order to detect a counterfeit article.
Red Flags & Warning Signs
- Unrealistic Pricing: If a brand-new luxury handbag is advertised at a drastically reduced price, it may be too good to be true.
- Poor Packaging: Look for mismatched colors, smudged labels, or incomplete branding information.
- Suspicious Online Listings: Sellers with sparse ratings, contradictory product descriptions, or an abundance of stock at impossible prices are major red flags.
Authenticity Verification Methods
- Holograms and Watermarks: Most authentic products—especially electronic goods and branded apparel—carry personalised labels or holographic stickers for genuineness assurance.
- Serial Numbers and Barcodes: Cross-checking them at the official website of the brand can confirm whether a product is real or not.
- Proof of Purchase: Legitimate dealers will have a proper invoice and receipt with discernible company information.
Seeking Expert Assistance
For high-value goods such as high-end watches or single-unit collectibles, professionals can undertake expert work in terms of authentication.
Jewellers, professionals in watches, and even a few pawn shops use high-tech tools to authenticate for markers of genuineness, such as metal grade or mechanical part accuracy.
The Role of Modern Tech in Fighting Counterfeit Goods
Technology stands at the forefront of counteracting counterfeit goods.
With sophisticated tracking tools and high-tech analysis, technology today introduces effective tools for counterfeiters’ detection and deterrence.
AI and Machine Learning
- Image Recognition: AI-driven software can scan product images, logos, and packaging to spot inconsistencies or deviations from authentic versions. This is particularly useful for e-commerce platforms hosting millions of product listings.
- Textual Analysis: Machine learning algorithms review product descriptions, customer feedback, and social posts for suspicious keywords and phrases most frequently associated with fraudulent products.
Implementing robust counterfeit goods detection methods is essential for timely identification and removal of fake listings.
“Advanced AI algorithms can spot even the smallest discrepancies, and real-time deletion of counterfeit listings can occur, protecting consumers from poor-quality goods.”
Blockchain Technology
- Transparency and Traceability: With blockchain, a unique ID can be added to each product. All stages in the distribution channel can be recorded and validated, and it will become increasingly challenging for counterfeiters to enter spurious goods into circulation.
- Smart Tags & Digital Certificates: QR codes, when scanned and referenced to a record in a blockchain, can authenticate a journey of a product, from maker to purchaser. In case a product’s digital certificate is absent or not valid, buyers can instantly detect a counterfeit.
Brands are increasingly utilising a counterfeit detection system to stop unauthorised sales and preserve consumer confidence.
IoT (Internet of Things)
- Connected Devices: Packaging and products can include smart sensors that report real-time information about environmental factors (temperature, humidity) that can affect authenticity.
- Automated Alerts: Automatic sensors can even be set to send an alert if a product strays from its planned route, minimising the chance for counterfeit goods entry.
Online Marketplace Enforcement
Platform-Wide Monitoring: Some larger e-commerce platforms use complex algorithms to scan new listings in real-time. Infringing and suspicious items can be taken down automatically or marked for review by a human.
From electronics to apparel, counterfeit goods on Amazon and other e-commerce sites pose a constant challenge for both legal sellers and buyers alike.
Brand Collaboration: Some platforms work with big brands directly in a move to have updated databases of real product photos, barcodes, and serial numbers in a move to make it easier to detect counterfeits.
Best Practices & Preventive Measures for Brands
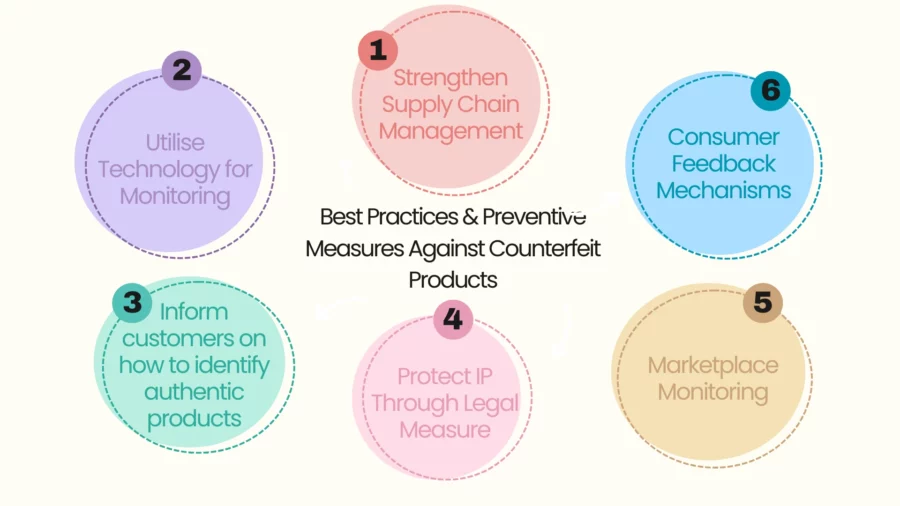
While technological aids matter, companies will have to apply overall strategies and best practices in a bid to guard against counterfeit goods for consumption.
Proactive Online Monitoring
Brands should regularly seek out signs of counterfeit products bearing their mark on web platforms, social networks, and online marketplaces.
By doing so, it can allow for rapid takedown, minimising the opportunity for irreparable loss of trust and goodwill in its name with its buyers.
Legal Action & Partnerships
- Collaboration with Law Enforcement: Working closely with local and international authorities can accelerate investigations and prosecutions against large-scale counterfeit operations.
- Industry Coalitions: By forming alliances with other companies facing similar counterfeiting threats, brands can pool resources, share intelligence, and mount stronger legal challenges.
Consumer Education
Brands can educate their base of buyers on how to identify counterfeit products by providing side-by-side comparisons, issuing warnings on red flags, and offering simple techniques on checking for legitimacy (e.g., QR codes, checking for a serial number).
Clear messaging generates a community of knowledgeable buyers who can report suspicious items or listings.
Protective Technologies
- Security Labels and NFC Tags: Having tamper-evident labels or inlaid NFC chips can enable immediate verification of a product’s authenticity with a simple smartphone scan.
- Unique Product Identifiers: Giving a single, specific code or serial number enables a brand to monitor an individual unit’s path, from creation through sales, minimising unauthorised reproduction.
Implementing a comprehensive strategy to protect the brand from counterfeits can drastically reduce your exposure to fake listings.
“Investing in brand protection early on saves companies far more than they lose to counterfeiting in the long run.”
Future Outlook of Counterfeit Prevention
Despite the challenge posed by well-established counterfeiting syndicates, anti-pirating operations have not yet exhausted hope.
Ongoing technological, policy, and consumption trends assure ever-improving anti-pirating approaches for fending off and discovering counterfeits.
Evolving Threat Landscape
As brands and law enforcement become ever more sophisticated in terms of detection, counterfeiters will respond in kind.
Some will utilise newer printing technology, and others will generate ever more sophisticated websites and virtual stores.
Anti-counterfeiting in the future will entail an ongoing seesaw between sophisticated security technology and counterfeiters’ emulative and circumventive capabilities.
Emerging Solutions
- Enhanced AI and Big Data Analytics: Enhanced AI and big-data analysis: Software in the future can possibly search through the web in real-time, detecting even faint indications of counterfeit products and ordering takedowns in real-time.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Authentication: It helps a buyer, using a smartphone camera, to scan a product for authenticity—whether it is truly a model of a certain brand.
- Smart Packaging: That alerts the consumer of any evidence of tampering or illicit reproduction by a change in colour or texture upon particular environmental stimuli.
Global Cooperation
Countries are beginning to recognise that tackling the counterfeit market requires cross-border collaboration.
Improved international treaties, data-sharing initiatives, and joint operations can disrupt global supply chains for counterfeiters more effectively than isolated efforts.
What’s Next?
Counterfeit products continue to pose a profound threat to consumers, businesses, and the global economy.
From financial losses and reputational harm to genuine safety hazards, the impact of counterfeit items extends well beyond mere imitation.
Fortunately, emerging technologies—ranging from AI-driven monitoring solutions to blockchain-based traceability—offer hope in mitigating these risks.
By staying vigilant, educating consumers, and forming robust alliances among stakeholders, we can work toward curtailing the prevalence of counterfeit goods worldwide.
As one of the best providers of brand protection, Bytescare offers innovative solutions to help businesses detect and eliminate counterfeit products online.
Book a demo and discover how Bytescare’s cutting-edge platform can safeguard your brand and genuine products and uphold consumer trust.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What are the most common counterfeit products examples today?
The most frequently counterfeited goods include luxury fashion items (handbags, shoes), electronics (smartphones, chargers), and pharmaceuticals (medicines, supplements). Additionally, cosmetics, watches, and even everyday household products are often targeted by counterfeiters due to high consumer demand.
How do counterfeit items affect consumer safety?
Counterfeit merchandise often bypasses quality control measures, using inferior or even toxic materials.
For instance, counterfeit cosmetics can contain harmful chemicals that irritate or damage the skin, while fake electronic chargers can pose fire or electrocution hazards.
Counterfeit pharmaceuticals, containing inaccurate dosages or dangerous substances, can lead to serious health complications.
Are counterfeit goods only sold in physical markets?
No. Although physical markets and street vendors are popular avenues for counterfeit consumer goods, the internet has rapidly become a major hub for distributing fakes. Online marketplaces and social media platforms can inadvertently serve as outlets for counterfeit products, making it critical for brands and consumers to remain vigilant in the digital sphere.
Why do some consumers knowingly purchase counterfeit brands?
Some buyers are attracted by the lower prices of fraudulent products, aiming to emulate luxury styles or trends without paying a premium. Others might undervalue or be unaware of the ethical, legal, and safety implications associated with supporting the counterfeit market.
How can businesses get started with brand protection measures?
Companies can begin by implementing proactive monitoring tools to scan for counterfeit goods online. They should also register trademarks in all relevant markets, collaborate with law enforcement agencies, and invest in protective technologies (e.g., unique serial numbers, tamper-proof packaging). Consulting with specialised firms and platforms offering end-to-end brand protection services is another effective step.
Where do most counterfeit sales occur?
Although counterfeit sales can happen anywhere—street markets, unauthorised retailers, or individual vendors—online marketplaces and social networks have become hotspots for distributing copies of products. These platforms let counterfeit sellers quickly reach large audiences, making them particularly appealing for sellers of fake products who want to evade detection.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

