Key Takeaways:
- China counterfeit market is the world’s largest, producing a wide range of fake goods that undermine global brands and industries.
- The counterfeit trade in China has evolved significantly over the decades, with advancements in manufacturing techniques and distribution channels.
- The economic impact of Chinese counterfeits is staggering, leading to substantial financial losses for authentic brands and creating market distortions.
China’s counterfeit market is huge and growing fast. It’s a big problem for global brands and industries. From fancy clothes to tech gadgets and medicines, the fake goods are everywhere. They harm real businesses and put people’s safety at risk.
China makes and sells the most fake products in the world. This has big effects on everyone. It’s a big issue that needs to be solved.
This article looks into China’s fake goods trade. We’ll explore how it started, how big it is, and its effects. We’ll also talk about the challenges of stopping it. By knowing this, we can work better to protect real products and fair trade.’
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Counterfeiting in China: A Byproduct of Economic Growth and Brand Culture
Economic Growth
The counterfeit industry in China is often viewed as a significant problem, but it can also be understood as a byproduct of the country’s economic growth.
Following Deng Xiaoping’s economic reforms in 1978, China opened its doors to foreign investments, attracting global brands like Nike and Adidas due to its low labor costs and vast market potential. This transformation positioned China as the world’s manufacturing hub, with approximately 70% of its exports consisting of manufactured goods.
While living standards in China improved dramatically, the burgeoning industrial power also paved the way for counterfeiting. Factories began to replicate brand products cheaply, leading many companies to lose control over their supply chains.
Although China has instituted anti-counterfeit measures—such as the State Intellectual Property Office and various laws to combat the international flow of counterfeit goods—the vast and loosely regulated ecosystem of suppliers complicates enforcement efforts. The sheer scale of the counterfeit market creates varying effectiveness in implementing national regulations.
Brand Culture
Additionally, since the early 1990s, the rise of brand culture in China, fueled by the opening of Western luxury stores, has further driven demand for counterfeit goods.
Fashion brands became symbols of status, and counterfeit products allowed consumers to access luxury items without the hefty price tag. This dynamic has significantly boosted both the popularity of luxury goods and the supply of counterfeit alternatives in the domestic market.
China Counterfeit Market Statistics: Know the Scale
The market for counterfeit products in China has expanded dramatically, evolving from a $30 billion issue in the 1980s to an estimated $600 billion by 2021, representing approximately 2.1% of global trade. Alarmingly, around 80% of the world’s counterfeits originate from China, highlighting the country’s central role in this illicit market.
Despite the implementation of intellectual property (IP) regulations aimed at curbing counterfeiting, projections indicate that the global counterfeit trade could surpass $3 trillion in the coming years.
The surge in e-commerce, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, has further facilitated the distribution of counterfeit goods. Illegal websites can be swiftly shut down and replaced, making enforcement increasingly challenging.
According to the 2020 U.S. Intellectual Property and Counterfeit Goods Landscape Review, global losses attributed to counterfeiting reached at least $1.7 trillion, with the counterfeit trade also resulting in the loss of approximately 2.5 million jobs worldwide. This significant economic impact underscores the urgent need for stronger enforcement of IP rights and international cooperation to combat the growing counterfeit market.
As the sphere continues to evolve, addressing the challenges posed by counterfeiting remains crucial for protecting consumers, businesses, and economies globally.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Market for Fake Goods in China

The market for fake goods in China is complex and multifaceted. While it’s challenging to quantify precisely due to its illicit nature, it remains substantial despite government crackdowns.
Key characteristics:
- Ubiquitous but shifting: While once openly prevalent in street markets, the market has shifted increasingly online, leveraging e-commerce platforms and social media for sales and distribution. Physical markets still exist, but they are becoming less prominent.
- Segmented demand: A diverse consumer base fuels the market. Some consumers knowingly purchase counterfeits seeking affordable alternatives, while others are sometimes deceived by increasingly sophisticated fakes. A growing middle class increasingly values authentic brands, yet price sensitivity remains a factor.
- Sophistication gradient: The market offers a spectrum of counterfeit quality, from crude imitations to highly sophisticated replicas that are difficult to distinguish from genuine products. This caters to different consumer preferences and price points.
- Geographic distribution: While major cities remain hubs for production and distribution, counterfeiting activity is dispersed throughout the country, leveraging regional manufacturing strengths and logistics networks.
- Evolving cat-and-mouse game: The market constantly adapts to enforcement efforts, employing decentralized production, encrypted communication, and agile logistics to evade authorities. This dynamic makes combating counterfeiting an ongoing challenge.
- Impact on legitimate businesses: The market for fake goods undermines legitimate businesses, erodes brand trust, and stifles innovation by discouraging investment in research and development. It also poses safety risks to consumers, particularly with counterfeit pharmaceuticals and electronics.
Despite government efforts, the market for fake goods persists, driven by economic incentives and consumer demand. The battle against counterfeiting in China continues to be a dynamic and complex issue.
Popular Categories of Counterfeit Products
Approximately 20 percent of all consumer products in the Chinese market are counterfeit. If a product is popular, there’s a good chance it has been counterfeited.
Among the numerous fake items for sale are Rolex watches, Gucci handbags, Duracell batteries, Gillette razor blades, Safeguard soap, Head & Shoulders shampoo, Viagra, and luxury automobiles.
Luxury Fashion and Accessories: Luxury items like designer handbags, watches, and clothes are often faked. Counterfeiters target famous brands like Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Rolex. They make convincing replicas to trick buyers. These “fake luxury goods” might be made poorly and lack the real product’s quality and craftsmanship.
Watches: Fake luxury watches from brands such as Rolex and Omega are widely available, often at a fraction of the price of genuine products.
Clothing: Many counterfeit apparel items, especially sportswear from brands like Nike and Adidas, are produced and sold at lower prices, appealing to budget-conscious consumers.
Electronics and Technology: “Counterfeit electronics” are also a big issue. Criminals copy everything from smartphones and laptops to parts and accessories. These “counterfeit electronics” can be risky. They might not be safe, could start fires, or even steal your data because of software and hardware flaws.
Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare Products: “Pharmaceutical counterfeits” are especially dangerous. Fake medicines, medical devices, and healthcare products can be very harmful. They might have wrong or dangerous ingredients. This is a big worry globally because it can hurt people’s health and trust in healthcare.
| Product Category | Potential Risks | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|
| Luxury Fashion and Accessories | Inferior materials, poor craftsmanship | Disappointment, financial loss, potential legal issues |
| Electronics and Technology | Fire hazards, data breaches, safety concerns | Property damage, personal data theft, physical harm |
| Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare Products | Incorrect/harmful ingredients, ineffective treatment | Serious health issues, life-threatening consequences |
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Major Manufacturing Hubs and Distribution Networks
China’s counterfeit production is a complex network of strategic hubs and global distribution channels. These centers are the heart of a booming illicit economy. They are fueled by China’s strong industrial base and its key position in global trade.
Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Yiwu are major counterfeit production centers in China. They are known for making fake fashion, electronics, and more. These places use their resources, skilled workers, and advanced facilities to make many replicas of popular items. They do this at a much lower cost than the real products.
| Counterfeit Production Center | Key Product Categories |
|---|---|
| Guangzhou | Luxury goods, electronics, toys |
| Shenzhen | Electronics, technology products, automotive parts |
| Yiwu | Textiles, accessories, household items |
These centers are linked to a huge distribution network that sends fake goods around the world. Counterfeiters use many middlemen, logistics, and online platforms to get their products to buyers everywhere. The supply chain includes shell companies, free trade zones, and secret shipping to avoid customs and law enforcement.
“China’s counterfeit trade is a multibillion-dollar industry that continues to evolve, posing significant challenges to brands, consumers, and global trade alike.”
The fight against these counterfeit production centers and networks is a big challenge. It affects brands, policymakers, and law enforcement agencies. They all face the ongoing battle against the illicit trade.
Technology’s Role in Counterfeit Production
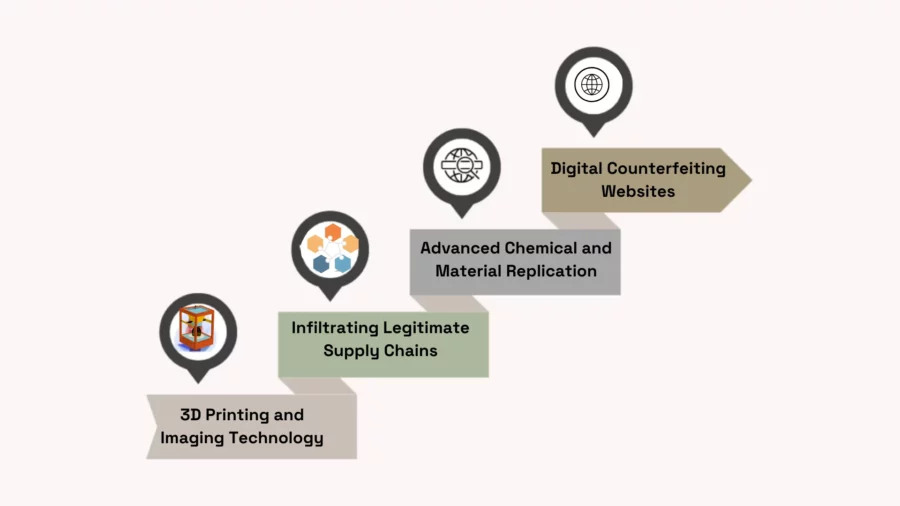
Technology has changed the world of counterfeiting a lot. It has brought new ways to make and copy fake goods. Now, counterfeiters use advanced tech to make their fake products look real.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
3D printing is a big reason why counterfeiting has grown. It lets counterfeiters make fake products fast and well. This tech is easy to get and use, making it a big problem for brands.
Digital Replication Methods
Counterfeiters also use digital tools to make and sell fake goods. They use software to make detailed digital models of products. Then, they share these online, making it easy for others to buy and sell fakes.
Quality Control Systems
Some counterfeiters use tech to make sure their fakes are good quality. They use machines to check products and keep them looking real. This makes it hard for brands and law enforcement to spot fakes.
These tech advancements have made fighting counterfeiting harder. It’s a big challenge for businesses, governments, and people who buy things. To win this fight, we need to keep up with new tech and protect our markets.
Legal Framework and Enforcement Challenges
China’s fight against fake goods is tough, with laws that keep changing. The country has made its intellectual property laws stronger, but enforcing them is hard. Counterfeiters use legal loopholes and China’s big manufacturing to get away.
China’s main enforcement agencies are the State Administration for Market Regulation, the National Intellectual Property Administration, and local ones. They try to stop fake goods, but it’s tough because of the problem’s size and the cleverness of counterfeiters.
To tackle this, China wants to work more with other countries and global enforcement agencies. They aim to break supply chains, share tips, and make laws the same everywhere. But, the secret and global nature of fake goods trade makes it hard.
“The battle against counterfeits in China is an ongoing struggle, requiring a multi-faceted approach that combines robust legislation, effective enforcement, and strong international partnerships.”
China keeps facing the big problem of fake goods. Its success in balancing economic growth and protecting intellectual property will shape the future of this complex issue.
Impact on Global Brands and Industries
Counterfeit products have hurt global brands and industries a lot. They cause problems with brand protection, money loss, bad reputation, and competition.
Financial Losses for Authentic Brands
Counterfeit goods hurt the sales of real products, leading to big money losses for brands. A recent report says fake and pirated goods could be worth over $2 trillion by 2022. This means businesses lose about $600 billion every year.
Brand Reputation Damage
Low-quality fake products can really hurt a brand’s image. People might think the brand is not good, leading to lost trust and less loyalty. Fixing this damage is hard and can hurt a company for a long time.
Market Share Erosion
Fake goods are often cheaper than real ones, attracting price-conscious buyers. This can make real brands lose market share. This loss can hurt a brand’s profits and make it less competitive.
| Impact on Global Brands | Estimated Annual Loss |
|---|---|
| Financial Losses | $600 billion |
| Reputational Damage | Significant, hard to quantify |
| Market Share Erosion | Varies by industry |
“The growth of counterfeiting has become a global epidemic, causing immense harm to businesses, consumers, and the economy as a whole. Addressing this challenge requires a comprehensive and collaborative effort from governments, law enforcement, and the private sector.”
Consumer Behavior and Counterfeit Purchases

The global counterfeit trade is a big problem. It’s important to know how people feel about buying fake products. Research shows that many factors affect their choices.
Price is a big reason. People like fake goods because they’re cheaper than real ones. This is especially true for those who want to save money.
How people see the product matters too. If they think fake goods are as good as real ones, they might buy them. This is true even if they know they’re fake.
| Factor | Impact on Counterfeit Purchases |
|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High – Consumers are attracted to significant price discounts offered by counterfeit goods |
| Product Perception | Moderate – Consumers may believe that some counterfeit goods offer a comparable experience to authentic products |
| Brand Loyalty | Low – Consumers are often willing to sacrifice brand loyalty in favor of lower prices |
| Ethical Considerations | Low – Many consumers disregard the ethical implications of supporting the counterfeit trade |
Fighting fake goods is a tough job. It’s because people’s attitudes and actions keep changing. Brands and governments need to work hard to stop fake products. They must protect both consumers and real businesses.
International Trade Relations and Diplomatic Tensions
China’s booming counterfeit market has deeply affected international trade. It has caused trade disputes, led to diplomatic talks, and brought economic sanctions.
The large scale and ongoing nature of this illegal trade have pushed global cooperation to its limits. It has also strained the relationships between China and its trading partners.
Trade Agreement Violations
The spread of counterfeit goods from China has been a major issue in international trade agreements.
These fake products often break intellectual property laws. They hurt the sales of real brands, causing big financial losses for industries worldwide. This has sparked trade disputes and intense diplomatic talks. Countries are trying to solve this problem through trade agreements.
International Pressure and Responses
As China’s counterfeit market keeps growing, the world is putting more pressure on China to act. This pressure has led to economic sanctions, tariffs, and demands for better anti-counterfeiting efforts.
China has pushed back with its own diplomatic moves. It aims to protect its economic interests and keep its place in global trade.
| Diplomatic Actions | Impact on International Relations |
|---|---|
| US tariffs on Chinese goods due to intellectual property violations | Escalated trade tensions between the US and China, leading to a prolonged trade dispute |
| EU’s pressure on China to combat counterfeiting and piracy | Increased diplomatic negotiations and a focus on strengthening intellectual property rights enforcement |
| International organizations’ calls for greater transparency and accountability in China’s counterfeit market | Heightened scrutiny of China’s efforts to address the issue, with potential consequences for its global standing |
The complex situation of trade disputes, diplomatic talks, and economic sanctions around China’s counterfeit market shows how crucial it is to tackle this problem. It’s key for the stability of international trade and the integrity of global markets.
Digital Marketplaces and Online Distribution

E-commerce platforms have changed the world of counterfeit goods. These online stores are now a big place for fake items. This makes it hard for brands and buyers to stay safe.
Setting up online shops is easy, and they can reach people all over the world. This lets fake sellers reach more people than before.
It’s tough to stop fake goods online. Fake sellers hide behind the internet’s anonymity. This makes it hard for brands and police to find and stop them.
Working together is key. E-commerce sites, law enforcement, and rules need to team up. This is the only way to fight the growing problem of fake goods online.
New tech helps fight fake goods. Online stores use smart tools to find and remove fake listings. They also work with brands to make sure products are real.
But, the battle against fake goods never ends. It’s a constant fight. Everyone needs to stay alert and keep finding new ways to stop fake goods.
The fight against fake goods online needs a big plan. We need better global cooperation and strong rules against fake goods. We also need to help people make smart choices when they buy online.
Anti-Counterfeiting Measures and Solutions
The fight against China’s counterfeit market is getting stronger. New tech and teamwork are key to solving this big problem. Blockchain technology is a big help, making it easier to check if products are real. It also makes supply chains more open and safe.
Brands are using new ways to keep their products safe. Things like special packaging and unique codes help. These steps make it easier for people to trust what they buy.
Technological Innovations
Big names and groups are working on new ways to stop fake goods. Blockchain is one of them, helping to prove if products are real. It also helps find fake goods in global supply chains.
RFID tags and DNA markers are also being used. They make it harder for fakes to get into the real market. This makes it tough for counterfeiters to sell their goods.
Collaborative Enforcement Efforts
Since fake goods are sold all over the world, working together is crucial. Law enforcement, customs, and companies are teaming up. They’re catching fake goods and sharing tips to keep everyone safe.
This teamwork is key in the ongoing battle against fakes. It helps break down the fake goods networks in China.
Government Regulation of the Counterfeit Market in China
Stakeholders have long expressed concerns that the penalties for selling counterfeit goods in China are insufficient to deter offenders. In February 2017, Alibaba reported 1,910 suspected counterfeiting cases to authorities, yet only 129 individuals were convicted.
In August 2018, the State Administration for Market Regulation intensified its efforts to combat the illegal production and sale of counterfeit products. The agency announced stringent penalties for online trading platforms that fail to cooperate with market regulators or protect the rights of consumers and trademark holders.
Additionally, the State Administration for Market Regulation called on other regulatory bodies, such as the Shanghai Administration for Industry and Commerce, to conduct targeted investigations into the sale of counterfeit goods, specifically focusing on platforms like Pinduoduo.
The new e-commerce law, effective January 1st, aims to further discourage counterfeiting in China by imposing heavier fines and increasing the responsibilities of digital platforms to remove sellers of fake goods. This law also addresses issues related to false advertising, consumer protection, data security, and cybersecurity.
The legislation targets three main groups: e-commerce platform operators such as Taobao, merchants selling goods online, and vendors with their own websites or social media accounts. Previously unregulated, merchants selling exclusively on social media are now required to register their businesses and pay applicable taxes.
Under the new regulations, both e-commerce platform operators and merchants share liability for the sale of counterfeit products. Platform operators can face fines of up to 2 million RMB (approximately 290,000 USD) for property infringement associated with the sale of counterfeit goods in China.
What’s Next?
In 2009, the United States seized $230 million worth of counterfeit goods from China and Hong Kong, accounting for nearly 90% of the total value of all counterfeits intercepted that year. The situation is even more alarming in Europe, where customs officials reported close to 50,000 seizures in 2008—a tenfold increase compared to the previous decade.
European customs authorities estimate that two-thirds of all counterfeit items seized originated from China or Hong Kong. Among the seized goods, 57% were clothing or related accessories, while jewelry and watches made up 10%, and electrical devices constituted 7%.
The prevalence of counterfeit goods varies across the continent, with Germany, Spain, and particularly the Netherlands experiencing a significant number of seizures. The Chinese government has been under pressure to strengthen market regulatory measures and enhance intellectual property protections to combat the growing fake markets and black market activities.
For businesses looking to navigate these challenges, seeking legal advice is crucial to protect against counterfeit threats.
Bytescare offers tailored solutions that safeguard businesses from counterfeit scams, providing robust defenses that secure your brands integrity.
Contact us today and experience our solutions firsthand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
Why is it bad to buy replicas?
Buying replicas can support illegal activities and counterfeit markets, which often harm legitimate businesses and economies. Additionally, replicas may be of inferior quality, posing safety risks to consumers. Purchasing counterfeit goods can also lead to legal repercussions and contribute to the erosion of intellectual property rights.
Where do most fake goods come from?
The majority of counterfeit goods originate from countries with less stringent enforcement of intellectual property protections, particularly China and Hong Kong. These regions are known for producing a wide range of fake products that are distributed globally.
What brands are counterfeit in China?
In China, many luxury brands are frequently counterfeited, including Rolex, Gucci, Louis Vuitton, and Prada. Other common counterfeit items include popular consumer goods like Nike shoes, Apple electronics, and various cosmetics.
Is counterfeiting illegal in India?
Yes, counterfeiting is illegal in India. The country has laws in place to protect intellectual property rights, including the Trademark Act and the Copyright Act. However, enforcement can be inconsistent, leading to challenges in combating counterfeit goods.
What is the most common counterfeit item?
The most commonly counterfeited items include clothing and accessories, particularly branded apparel and handbags. Other prevalent counterfeit goods are electronics, pharmaceuticals, and luxury watches.
Why counterfeit products are gaining market?
Counterfeit products are gaining market share due to several factors, including increased consumer demand for affordable alternatives to luxury goods, the rise of e-commerce platforms that facilitate the sale of fake items, and insufficient enforcement of intellectual property laws. Additionally, the anonymity of online shopping makes it easier for counterfeiters to operate without detection.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.


