Key Takeaways:
- Fake fashion products undermine the integrity of brands, leading to huge costs in lost revenue and damaged reputation.
- The rise of counterfeit items negatively impacts clothing sales, threatening the business viability of legitimate fashion companies.
- Implementing an anti-counterfeiting solution serves as a crucial form of protection for brands against the pervasive threat of counterfeiting.
Counterfeiting in apparel is a ubiquitous issue with significant implications for brands, buyers, economies, and the environment. Whereas counterfeited goods have long been regarded as innocent copies of bestsellers, their impact extends a lot deeper than one purchase.
From financial loss and loss of integrity in a brand to loss of employment and unethical working environments, counterfeiting reaches into apparel and apparel-related industries in numerous sectors.
The worldwide counterfeit economy, extending to a variety of sectors, is valued at over $3 trillion a year.
Here, in this article, we will explore the impact of counterfeiting on the fashion industry and in what manner companies and buyers can make a contribution towards minimising its impact.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Why Fashion Businesses Should Be Concerned About Counterfeiters?
- The counterfeiting economy is a colossal worldwide issue. In terms of its financial impact, counterfeiting is costing the global economy between $1.7 trillion and $4.5 trillion annually.
- To put it in terms of an economy, counterfeiting is one of the largest economies on the planet, even larger than Canada and not much smaller than that of Germany.
- For fashion alone, loss through counterfeiting is enormous. Fashion companies alone forego over $50 billion in sales each year through counterfeit merchandise flooding the marketplace.
- The global counterfeiting of goods is worth over $500 billion a year, and one of its hardest-hit industries is fashion, claims the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
- Research has confirmed that 26% of purchasers who received counterfeit items discontinued buying at that store, and 27% notified others regarding the incident.
Consumer actions such as these illustrate how prevalent counterfeiting via cyberspace can destroy a brand name and margin of profit.
Aside from direct financial loss, counterfeit goods cause loss to the position in the marketplace for real brands, creating a causality circle.
The flood of counterfeit items in the marketplace makes it increasingly challenging for the actual brands to preserve their base of buyers.
In fact, counterfeited items can impact a brand’s marketplace presence to such an extent that many companies have to drop significant retail channels.
An example is Nike, whose sales via Amazon halted when Amazon gained notoriety for counterfeit goods. There is mounting pressure to counteract counterfeiting with an exponential growth in counterfeited apparel in the marketplace.
Why Do People Purchase Counterfeit Clothes?

People purchase counterfeit clothes for several reasons, often influenced by affordability, social status, and psychological factors.
Affordability: Cost is one of the prime reasons. Luxury apparel is pricey, and not everyone can afford high-class brands. Fashion counterfeiting then enters with a less expensive alternative that can mimic high-class trends at a much lesser price tag.
Desire for Status: Luxury brands have long been linked with wealth and status in many consumers’ minds. Fake clothes enable one to present an aura of wealth at a relatively cheap price, and that is most desired in social environments in which one’s looks matter most.
Lack of Awareness: Some buyers buy counterfeit apparel unaware, specifically when purchasing over the internet or in street stores. Most counterfeiters produce high-quality replicas that even a trained observer cannot discern with ease.
Ethical Indifference: Fewer and fewer consumers view counterfeiting as an issue of concern. Personal gain prevails when it comes to such an issue regarding intellectual property, fair labour, and its damaging impact on the fashion industry.
Impulsive Buying: Fast fashions encourage purchasing less expensive substitutes in preference to investing in high, short-term fashions. Copycat fashions offer a cheap alternative for emulating fashions at no financial expense.
Regardless of such motives, purchasing counterfeit apparel comes with legal and ethical consequences, both for buyers and for real brands.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Impact of Counterfeiting on the Fashion Industry
The Economic Impact of Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting takes a significant toll on the financials of the fashion sector.
Fashion companies lose an enormous amount of dollars in sales each year with counterfeit goods entering the marketplace in abundance. But financial loss doesn’t stop with sales—counterfeiting impacts the overall economy in a variety of fashions.
Financial Losses to Brands and Designers
The most direct impact of counterfeiting on luxury goods of fashion is financial loss for brands and designers.
By providing counterfeit items at a lesser price, counterfeiters steal competition and sales for real goods, taking potential buyers with them in the process.
For high-end brands including Gucci, Louis Vuitton, and Chanel, such loss can go into trillions of dollars. Fashion alone lost approximately $50 billion in sales in 2020 through sales of counterfeit goods.
The issue is even more critical for individual, freelance designers who cannot necessarily pay for effective counteracting counterfeiting in terms of dollars and cents.
For such designers, whose success and living depend in a considerable part on name and reputation, counterfeiters’ reproduction and resale in unauthorised form disproportionately hurt them.
Cost of Anti-Counterfeiting Measures
To protect their intellectual property, apparel companies must make an investment in anti-pirating technology.
Apparel companies produce high-tech security labels, including RFID labels, numbering, and holograms, and make an investment in legal expertise in an attempt to counteract counterfeiters.
All these investments have a high price, and, unfortunately, most often, cannot effectively hinder counterfeit merchandise entering into circulation.
Where big companies have deep pockets with which to fund battles over counterfeiting, smaller companies cannot possibly keep pace with such expense, putting them at peril of survival.
Job Losses in the Fashion Industry
The financial loss incurred through counterfeiting reaches out to employment in the apparel industry in a general way.
With reduced sales and earnings, companies can have to lay off, laying off jobs for employees, even shutting down stores in extreme cases.
It reaches out to a range of professionals, including producers, designers, retail workers, and even customer service representatives.
Small, high-end, and custom-made apparel companies suffer most. Undercutting the marketplace for real items, counterfeit goods, at a lesser price, makes them do a lot of work in competing and, therefore, in survival.
It brings about loss of jobs and a shrinking pool of craftsmen and artisans who depend on sales of real, high-quality apparel items.
Contribution to the Black Market
Counterfeit goods in the clothing industry are, in most cases, traded through networks that circumvent taxes and laws and therefore contribute to an expansion in the black economy, not only detrimental to the economy but also challenging to monitor and manage.
The black economy, in its turn, erodes legal companies through price competition and circumvention of laws, putting additional strain on the economy.
Damage to Brand Reputation and Consumer Trust
The financial loss is only one part of the problem. Loss of name can be irreparable.
Most counterfeited items are not of an equivalent quality to originals, and buyers purchasing fakes in innocence will become disbelieving when realising that they have been deceived. 52% of buyers become disbelieving in brands when buying counterfeit goods, and 64% become disbelieving in platforms through which such goods have been purchased, according to studies.
Consequently, many high-end apparel brands have ceased sales through third-part platforms altogether, in an attempt to save face and not have counterfeit goods sully their name.
Also, counterfeited goods sell at a much reduced price compared to originals, creating a perception in buyers that real goods must sell at a cheap price, too. That erodes pricing strategies for branded apparel companies, who can then be compelled to drop their price in an attempt to maintain competitiveness and, in turn, hurt their profitability even more.
The Role of Social Media in Amplifying the Problem
The social media platforms have spurred counterfeiting activity. Social media platforms, including Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok, have provided an easy platform for counterfeiters to promote and sell counterfeit items to innocent buyers.
Social media influencers, who desire to post high-value items, can promote counterfeit items inadvertently and, in most cases, blur the line between counterfeit items even more.
Also, counterfeiters utilise fake reviews and manipulative advertisements to deceive buyers into buying counterfeit items.
Misinformation spreads at a rapid rate over the web, and increasingly, buyers have difficulty distinguishing between real and counterfeit apparel and apparel-related items.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges
The anti-counterfeiting battle in the apparel industry is also challenged by legal and regulatory obstacles.
Intellectual property laws have been adopted in most countries to safeguard brands, but counterfeiting is a worldwide issue, and therefore, it is challenging to implement them effectively.
Global Nature of Counterfeiting
Counterfeited items are produced in one country, exported to a second, and then bought by consumers worldwide.
Cross-border counterfeiting forms an inextricable web that cannot simply be undone.
Anti-counterfeiting legislation must then depend on worldwide collaboration for effective application, but many countries lack political will and assets to effectively confront the problem.
For example, counterfeiting operations can have a presence in nations with poor intellectual property protection and poor capabilities for enforcement. As a result, counterfeit goods can simply enter the international marketplace undetected.
Inadequate Intellectual Property Protections
Notwithstanding laws protecting intellectual property, counterfeiters have continued to exploit loopholes in worldwide legislation.
In most instances, counterfeitors utilise complex techniques for evading detection, including changing labels and packaging of a product. Others lack severe penalties for counterfeiting in such jurisdictions, and therefore, it is less risky for them to indulge in such an activity.
Fashion companies face a long and expensive court battle when attempting to protect their intellectual property. Weak, strong protections and country-by-country disparate enforcement make most companies vulnerable to abuse.
Environmental and Ethical Impacts
Counterfeiting not only destroys economies and brand reputations, but it also brings with it dire environmental and moral consequences.
Environmental Harm Caused by Counterfeit Goods
Counterfeited goods use cheap, environmentally unkind processes and materials. As actual companies invest in environmentally kind processes, counterfeiters will skimp in an effort to gain a larger profit margin.
Toxic dyes, cheap plastic, and other unhealthy materials produce toxins and make trash. Products are not even designed to have a long life, and when cheap, shoddy counterfeits disintegrate, even more trash is produced when buyers discard them.
The counterfeiting of fashion items keeps driving the cycle of quick fashion, with bulk production and consumption of cheap, shoddy items, and then overproduction, and then degradation of the environment.
Exploitation of Labor in Counterfeit Supply Chains
The working environment in counterfeited production is often unethical and exploitative in character.
Most counterfeited goods are produced in countries with poor labour laws, and workers earn below minimum wage and work in unsanitary working environments.
There is no supervision in counterfeited apparel, and such workers can be exploited with impunity.
In some cases, counterfeiters may rely on child labor or other forms of human trafficking to manufacture their products. This highlights the darker side of the counterfeit fashion industry and the human cost associated with the trade.
Technological Solutions to Counterfeiting
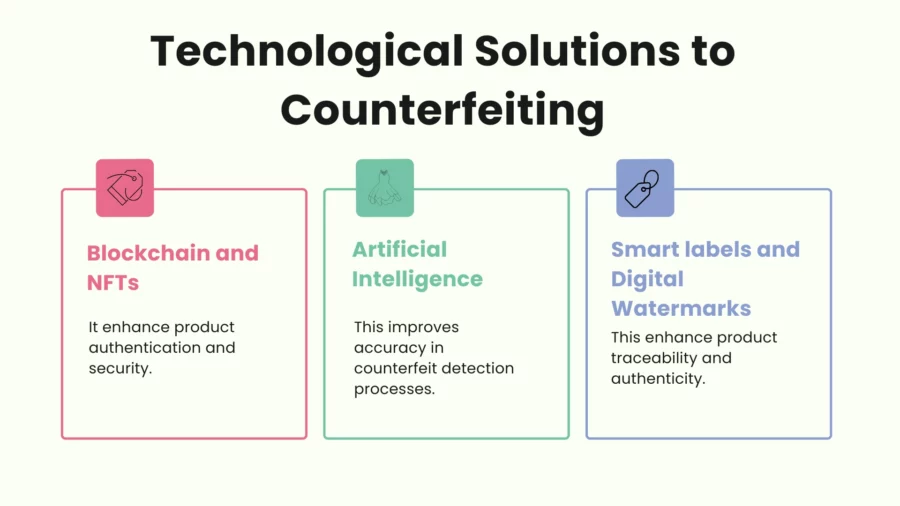
As counterfeiting becomes more sophisticated, so too must the solutions designed to combat it.
Technology is playing a significant role in identifying and preventing counterfeit goods from entering the market.
Role of Blockchain and NFTs in Authentication
Blockchain technology can transform the fashion industry with its transparent and unchangeable record of a product’s journey, beginning with its origin and concluding with its purchase.
Its use in clothes, for one, helps companies gain an invisible presence that validates a product’s legitimacy.
NFTs have even begun to authenticate and validate high-value clothes items’ legitimacy of ownership.
Artificial Intelligence and Counterfeit Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used in a quest to detect counterfeit goods.
AI photograph software can scan photographs of goods for resale in virtual shops and compare them with real-product photographs in an attempt to detect fakes. AI can scan for mismatches in emblems, seams, and materials that characterise counterfeit goods through its algorithms.
AI algorithms can even scan massive sets of sales channel data in an attempt to search for patterns of counterfeit activity, and allow brands to act in anticipation of counterfeit items entering circulation.
AI can even be utilised in buyer-facing apps in a manner that enables buyers to scan and authenticate items for purchase in advance. That is a convenient option for buyers concerned about buying counterfeit fashion goods over the web.
Smart Labels and Digital Watermarks
Other technology, such as smart labels, RFID tags, QR codes, and watermarks, is yet another technology tool that is being utilised in counterfeiting in apparel industries.
Labels can be inserted in items and then verified for legitimacy through a scan. RFID tags, for example, allow for ease in tracking items through a value chain, such that items arrive at buyers in their first, unaltered state.
Not seen with naked eyes, digital watermarks can be placed in labels or logos in apparel.
On a scan with a certain app or device, such watermarks can reveal significant information about a product’s origin, production, and authenticity.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Strategies to Combat Counterfeit Fashion
| Key Area | Description |
|---|---|
| The Role of Brands in Combating Counterfeiting | Brands have a responsibility to fight counterfeiting to protect revenue, maintain consumer trust, and preserve their reputation. Measures include legal action, collaboration with authorities, and technological solutions. |
| Collaboration with Customs and Law Enforcement | Fashion brands work with customs agencies and law enforcement to seize counterfeit goods before they reach consumers. Efforts include intelligence sharing, joint raids, and legal proceedings against counterfeiters. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Consumers should buy only from official brand websites and authorised retailers. Learning to spot fake items through signs like poor stitching, low-quality materials, and unusually low prices is crucial. |
| The Role of Consumers in Preventing Counterfeiting | Consumers play a key role by avoiding counterfeit products and purchasing from reputable sources. Educating themselves on counterfeit risks and ethical fashion choices helps reduce demand. |
| How Consumers Can Avoid Buying Counterfeit Products | Consumers should buy only from official brand websites and authorized retailers. Learning to spot fake items through signs like poor stitching, low-quality materials, and unusually low prices is crucial. |
| Supporting Anti-Counterfeit Initiatives | Consumers can report counterfeit sellers to brands or online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay. These platforms have dedicated teams to investigate and remove fake products, preventing further deception. |
What’s Next?
Counterfeiting significantly impacts the fashion industry, undermining the value of authentic products and harming original manufacturers.
Counterfeit fashion products often fail to meet safety standards, leading to issues such as skin irritation for unsuspecting consumers.
As online stores proliferate, the risk of purchasing counterfeit fashion items increases, often driven by social pressure to own copies of luxury fashion.
Negative reviews can tarnish the reputation of original products, making it crucial for brands to take proactive measures.
To further safeguard your brand from counterfeit products and misuse, consider brand protection service.
With advanced tools tailored to tackle the impact of counterfeiting, Bytescare empowers businesses to protect their reputation and revenue.
By ensuring that real images of original products are showcased, brands can help consumers make informed choices.
Ready to protect your brand? Book a demo today and experience Bytescare’s solutions firsthand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What are the most commonly counterfeited fashion products?
Luxury handbags, shoes, clothing, and accessories are the most commonly counterfeited items in the fashion industry. Brands like Louis Vuitton, Gucci, and Rolex are frequently targeted by counterfeiters due to their high demand and price points.
How can I tell if a fashion item is counterfeit?
Look for signs such as poor stitching, irregular logos, substandard materials, and packaging that doesn’t match the brand’s usual standards. Additionally, counterfeit products are often sold at prices much lower than the original retail price.
How does counterfeiting affect the environment?
Counterfeit products are often made from cheap, low-quality materials that can harm the environment. These goods are typically not built to last, leading to increased waste, and counterfeit manufacturers often avoid using sustainable or ethical production methods.
What legal measures can fashion brands take against counterfeiters?
Fashion brands can pursue legal action against counterfeiters through intellectual property laws, file complaints with customs authorities to seize counterfeit goods, and collaborate with law enforcement to investigate and prosecute counterfeit operations.
What role does consumer behavior play in the prevalence of counterfeiting?
Consumer demand for affordable luxury and a lack of awareness about the consequences of purchasing counterfeit goods contribute to the ongoing problem. By choosing to buy only from reputable sources and supporting ethical fashion brands, consumers can reduce the demand for counterfeit items.
How does counterfeiting affect the global economy?
Counterfeiting leads to significant financial losses, job cuts, and tax evasion, weakening economic stability worldwide.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

