Key Takeaways:
- Protected content in Chrome safeguards DRM-controlled content, ensuring secure streaming of videos and music.
- Navigate to Chrome’s settings, access “Site Settings,” and toggle “Protected Content” to allow media playback.
- Ensure Chrome is updated and reset permissions if media playback issues persist, ensuring seamless access to protected content.
Online media consumption has become an integral part of our daily lives. Whether it’s streaming your favorite show on Netflix or listening to premium audio content on Spotify, many platforms rely on protected content to ensure secure access to their media.
Protected content refers to digital media safeguarded using Digital Rights Management (DRM) or encryption technologies, designed to prevent unauthorised sharing or piracy.
Examples of protected content include DRM-protected videos on platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video, or encrypted audio files on premium music services. Without these measures, content creators and distributors could face financial losses and intellectual property theft.
However, to access such content seamlessly, users must enable specific settings in their browsers. On Chrome, this involves allowing protected content permissions, ensuring that media playback works as intended.
Let’s explore how to enable protected content in Chrome. Whether you’re troubleshooting playback issues or setting up Chrome on a new device, this guide provides easy-to-follow steps.
By the end, you will have smooth, unrestricted access while staying compliant with media platform requirements.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What Is Protected Content in Chrome?
Protected content in Chrome refers to digital media files safeguarded by technologies such as Digital Rights Management (DRM) or encryption.
These steps make sure that only authorised users can access media like videos, audio, or other digital content under specific conditions. This content protection plays a key role for content creators and distributors, as it helps prevent piracy, unauthorised sharing, and copyright violations.
For instance, streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ use DRM to restrict access to their shows and movies to paying subscribers. Similarly, music services like Spotify and Apple Music use encrypted audio files to provide secure playback for their users.
Chrome, one of the most widely used browsers, supports protected content playback through its built-in DRM settings called Widevine Content Decryption Module. This feature allows users to enjoy DRM-protected media seamlessly without requiring additional software.
However, for Chrome to play such content, the protected content feature must be enabled in the browser settings. When enabled, Chrome permits sites to check your device’s DRM capabilities and decrypt media files for playback. If this setting is disabled, users may encounter content errors such as videos not playing or media being blocked.
By knowing what protected content is and why it’s essential, users can ensure a secure and enjoyable experience when accessing premium digital media. Chrome’s support for protected content not only makes things easier for users but also protects the rights of content creators.
Why Is Protected Content Disabled in Chrome?
Chrome’s protected content can be turned off for a number of reasons, most of the time having to do with user preferences, system settings, or browser updates.
Chrome, by default, allows protected content playback. But this setting can turned off, either by manual or due to specific situations.
User Privacy Concerns
- Some users choose to disable protected content permissions in Chrome to prioritise privacy and control over their devices.
- By disabling this feature, they limit websites’ ability to access their system’s DRM capabilities, ensuring minimal data sharing and interaction with external services.
Browser or System Incompatibilities
Protected content settings may be disabled due to outdated browser versions or corrupted files.
- Chrome’s built-in DRM tool, the Widevine Content Decryption Module, needs to be up-to-date to function correctly.
- Any disruptions in its updates or installation can lead to the feature being turned off.
Device or Organisational Policies
- In some cases, protected content by default is disabled on devices managed by schools, workplaces, or other organisations.
- These restrictions are often implemented to comply with internal guidelines or security policies that limit DRM-protected content play.
What is Digital Rights Management (DRM)?

Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a set of technologies and protocols used to protect digital content from unauthorised access, copying, or distribution.
It ensures that only authorised users can access copyrighted materials, such as videos, music, eBooks, and software, under predefined terms and conditions.
DRM works by encrypting digital content with a license or specific permissions to decrypt and play content from streaming services.
For example, streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Spotify use DRM to ensure that only subscribers can access their content. Similarly, eBook platforms like Kindle restrict file sharing to prevent piracy.
The primary purpose of DRM is to protect intellectual property and ensure fair compensation for creators and distributors.
While it safeguards content, DRM also enables content providers to implement features like subscription models, rental periods, and device-specific access, ensuring a secure and controlled user experience.
What is the Importance of DRM for Digital Media?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) plays a vital role in the digital media ecosystem by safeguarding intellectual property and ensuring fair usage.
- With the rise of online platforms for streaming, downloading, and sharing content, protecting copyrighted material has become more important than ever.
- DRM helps content creators, distributors, and platforms prevent unauthorised access, piracy, and illegal distribution of digital media such as movies, music, software, and eBooks.
- This protection ensures that content owners are compensated fairly for their work and can continue producing high-quality content.
- Moreover, DRM enables content platforms to implement flexible business models, such as subscriptions, rentals, or one-time purchases, while controlling how the content is accessed and shared.
- For example, streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify rely on DRM to maintain the exclusivity of their content.
- By striking a balance between user accessibility and copyright protection, DRM is essential for sustaining the digital content industry.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
How to Enable Protected Content in Chrome?
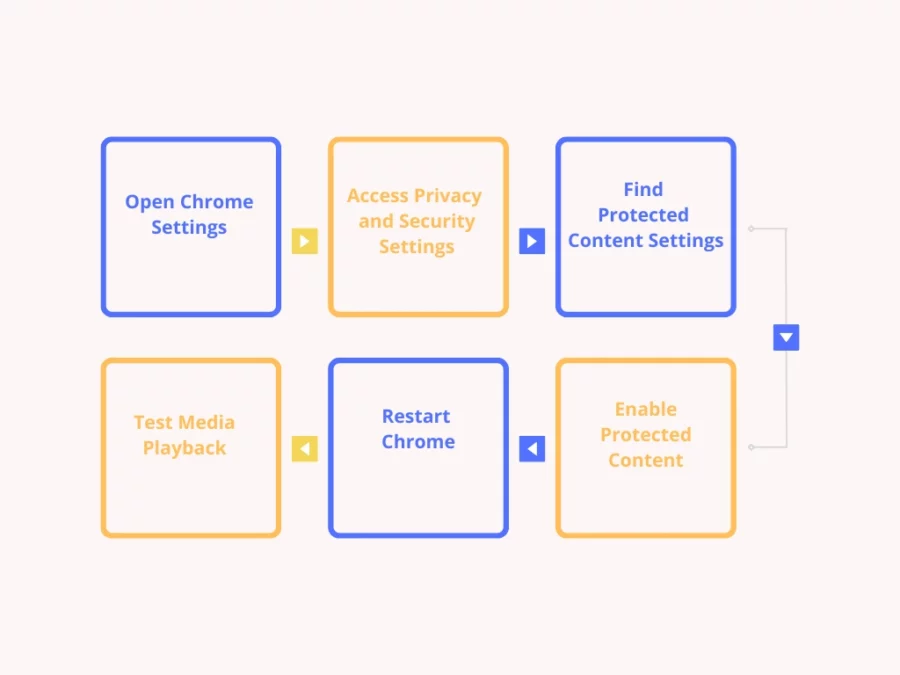
If you’re encountering issues with streaming services or encrypted media not playing in Chrome, enabling protected content can resolve the problem. Follow these simple steps:
Open Chrome Settings
- Launch Chrome and click the three-dot menu icon in the top-right corner of the browser window.
- From the dropdown menu, select Settings.
Access Privacy and Security Settings
- In the Settings menu, scroll down and click on Privacy and Security in the left-hand sidebar.
- Select Site Settings under this section.
Find Protected Content Settings
- Within Site Settings, scroll down to locate the Additional Content Settings section.
- Click on Protected Content IDs or Protected Content, depending on your Chrome version.
Enable Protected Content
- Toggle the switch next to “Allow sites to play protected content (recommended)” to the on position.
- If available, also enable the option for Protected Content IDs to ensure seamless playback of DRM-protected media.
Restart Chrome
Close and reopen Chrome to apply the changes.
Test Media Playback
Visit a streaming platform like Netflix or Spotify to confirm that protected content now plays without issues.
By following these steps, you can quickly enable protected content in Chrome and enjoy uninterrupted access to DRM-protected media. If playback issues persist, ensure that Chrome is updated to the latest version.
Troubleshooting Protected Content Issues in Chrome
| Common Issue | Cause | Quick Fixes |
| Media not playing on streaming sites | Protected content setting is disabled in Chrome. | Enable Protected Content under Chrome’s Site Settings. |
| Protected content playback error | Outdated Widevine Content Decryption Module. | Update Chrome to the latest version or reinstall the Widevine module. |
| Protected content still blocked | Device or browser restrictions (e.g., managed by an organisation). | Check for system policies or use a personal device if restrictions are in place. |
| Audio or video quality issues | Insufficient internet speed or outdated browser. | Ensure a stable internet connection and update Chrome to the latest version. |
| Content only works on certain devices | DRM compatibility issues with the current device. | Use a device that supports DRM and ensure DRM capabilities are enabled in Chrome. |
| Playback works intermittently | Corrupted Chrome profile or cache. | Clear Chrome’s cache and cookies or create a new Chrome user profile to resolve issues. |
| Pop-up asking for permission repeatedly | Misconfigured browser permissions. | Reset Chrome permissions for the website under Privacy and Security > Site Settings. |
Advanced Troubleshooting Tips
If you continue to experience issues with protected content despite following basic steps, try these advanced troubleshooting techniques:
Reinstall Widevine Content Decryption Module
- Open chrome://components in the address bar.
- Locate Widevine Content Decryption Module and click Check for Updates.
- If issues persist, click Uninstall, restart Chrome, and reinstall the module.
Clear Chrome’s Cache and Cookies
- Go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Clear Browsing Data.
- Choose Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files, then click Clear Data.
Disable Conflicting Extensions
- Some extensions, particularly ad-blockers or privacy tools, can interfere with media playback.
- Go to chrome://extensions and disable extensions one by one to identify the cause.
Reset Chrome Settings
If the issue persists, go to Settings > Advanced > Reset Settings and select Restore settings to their original defaults.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Best Practices for Privacy and Security
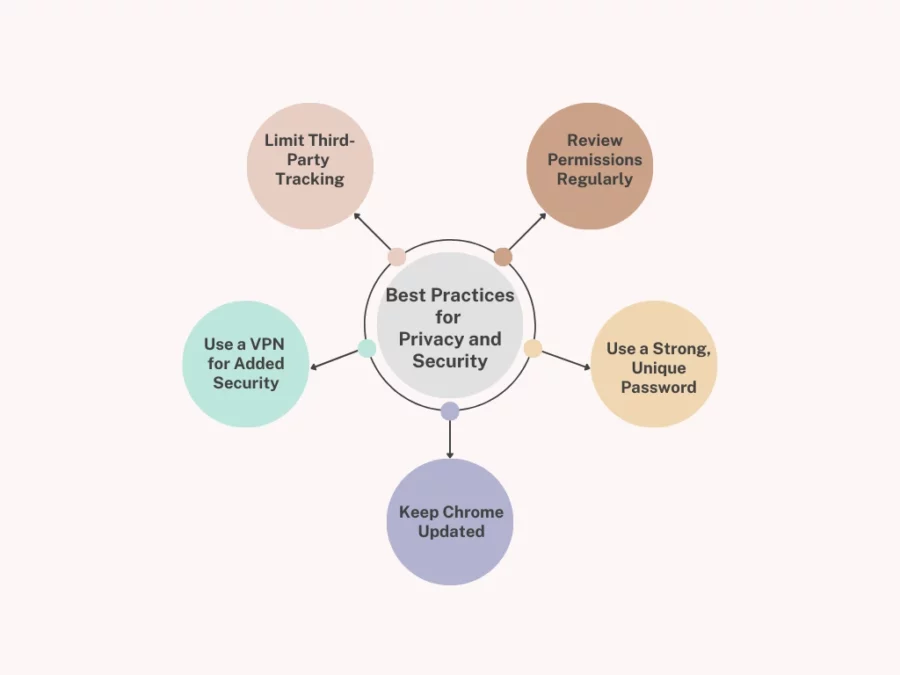
When enabling protected content in Chrome, it’s essential to maintain a balance between convenience and privacy matters. Here are some best practices to ensure your online activities are secure:
Limit Third-Party Tracking
Many streaming platforms and websites use cookies and tracking technologies to collect data. To maintain privacy, consider using Incognito Mode in Chrome for private browsing or install privacy-focused extensions like Privacy Badger or uBlock Origin to block trackers and ads.
Review Permissions Regularly
Periodically check the permissions granted to websites, including access to protected content. In Chrome’s Site Settings, you can manage which websites are allowed to access your DRM capabilities and other sensitive features, giving you better control over your browsing experience.
Use a Strong, Unique Password
For accounts where protected content is accessed, such as Netflix or Spotify, always use a strong, unique password. Consider enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added layer of security to protect your accounts from unauthorised access.
Keep Chrome Updated
Always ensure that your Chrome browser and related plugins, like the Widevine Content Decryption Module, are up-to-date. Updates often include critical security patches to protect you from vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Use a VPN for Added Security
If you’re concerned about potential data breaches or want to hide your online activity, consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). This will encrypt your connection, making it more difficult for anyone to intercept your personal data.
Alternatives to Chrome for Protected Content
While Google Chrome is a popular choice for accessing protected content, there are several other browsers that also support DRM (Digital Rights Management) and provide a secure, seamless experience for streaming and encrypted media.
Here are some alternatives to Chrome:
Mozilla Firefox
- Firefox supports protected content playback using the Widevine DRM plugin.
- It’s an excellent choice for users who prioritise privacy, as it offers robust security features and does not track your browsing activity by default.
- Firefox is a great alternative for those seeking to control permissions and customise their browsing experience.
Microsoft Edge
- Microsoft Edge is built on the Chromium engine, just like Chrome, but with additional security enhancements and integrated DRM support.
- It offers seamless streaming for platforms like Netflix, Disney+, and Hulu, and is highly optimised for Windows users, making it a reliable choice for accessing protected content.
Safari (for macOS and iOS users)
- Safari is the default browser for Apple devices, and it supports FairPlay, Apple’s DRM system, for streaming protected content.
- It works well with services like Apple TV+, iTunes, and other media platforms, offering high-quality video and audio playback.
- Safari is ideal for users in the Apple ecosystem.
Opera
- Opera supports DRM content via the Widevine plugin, just like Chrome and Firefox.
- It also features a built-in VPN and ad blocker, providing an extra layer of security and privacy while streaming.
- Opera is a great alternative for users seeking more privacy-focused browsing options.
These browsers offer strong DRM support, providing a secure environment for streaming protected content, each with unique features catering to different user needs.
What’s Next?
Enabling protected content in Chrome is a straightforward process that ensures a seamless and uninterrupted media streaming experience.
By following the simple steps outlined in this guide, you can easily enable DRM protection settings in Chrome and enjoy content from platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Spotify without issues.
However, if you encounter problems, troubleshooting steps like updating the Widevine module, clearing browser cache, or resetting permissions can help resolve most issues.
For a safer online experience, it’s essential to maintain browser security by using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping Chrome updated.
By properly configuring these settings, you ensure both smooth media playback and enhanced privacy while browsing.
Bytescare offers tailored strategies and digital piracy monitoring to ensure your assets are safe from unauthorised distribution. Focus on creating while we secure and safeguard your intellectual property.
Book a demo with Bytescare today for worry-free protection!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
How do I enable protected mode in Chrome?
To enable protected mode in Chrome, go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Tap Site Settings > Protected Content and toggle the option to allow sites to play protected content.
How do I turn off protection in Chrome?
To turn off protection in Chrome, go to Settings > Privacy and Security > Site Settings > Protected Content and toggle the switch to disable sites from playing protected content.
Can I enable protected content on mobile Chrome?
Yes, you can enable protected content on mobile Chrome by ensuring the Widevine DRM module is enabled in settings, but mobile devices may have limited content compatibility compared to desktops.
What is DRM and why does it restrict playback?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a technology that protects content from unauthorized copying or distribution. It restricts playback to authorised users to prevent piracy and ensure content creators are compensated fairly.
Is enabling protected content safe?
Yes, enabling protected content is generally safe. It allows DRM-protected content to play without compromising security, as long as you download updates from trusted sources and use up-to-date software.
Does enabling protected content affect browser performance?
Enabling protected content typically has little to no impact on browser performance. However, issues may arise if your device has outdated software or insufficient resources to handle DRM-controlled content.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

