Key Takeaways:
- Anti-piracy involves implementing strategies and technologies to enforce intellectual property laws, ensuring that creators and businesses retain control over their copyrighted works.
- Effective anti-piracy measures utilise tamper technology and integrated technology solutions such as digital rights management (DRM), watermarking, and monitoring systems.
- With the rise of Internet piracy, anti-piracy efforts are crucial in addressing the illegal downloading and distribution of media online.
The internet is a widespread platform for sharing and accessing content, but it also enables Internet piracy. This rampant issue undermines intellectual property laws designed to protect creators and their work. So, what is anti-piracy?
Anti-piracy encompasses a range of strategies and technologies aimed at combating illegal file sharing and safeguarding intellectual property.
Effective anti-piracy measures include tamper technology and integrated technology solutions that prevent unauthorised access and distribution of digital content.
Additionally, piracy prevention measures such as digital rights management (DRM) and watermarking play key role in deterring infringers.
This article will give you useful knowledge on “what is anti-piracy,” exploring the tools and techniques used to enforce intellectual property laws and maintain the integrity of creative works in the digital field.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Anti-Piracy?
Anti-piracy refers to the measures and efforts taken to prevent the unauthorised use, reproduction, and distribution of copyrighted material. This material can include software, movies, music, books, and other forms of digital and intellectual property.
The goal of anti-piracy is to protect the rights of creators and copyright holders, ensuring they receive the appropriate recognition and financial compensation for their work.
When we talk about piracy in this context, it’s the act of illegally copying, distributing, or using copyrighted material without permission from the rights holder. This can range from downloading movies from torrent sites to using pirated software.
Piracy is not just a legal issue; it’s also a moral one, as it involves taking someone else’s work without paying for it or obtaining proper authorisation.
Anti-piracy methods vary widely and can include technological solutions, legal actions, and public awareness campaigns.
Technological solutions might involve digital rights management (DRM) systems that control access to digital content, watermarking to trace the origin of content, or encryption to prevent unauthorised access.
Legal actions can include lawsuits against individuals or groups engaged in piracy, as well as lobbying for stricter laws and penalties against piracy.
Anti-Piracy Laws in India
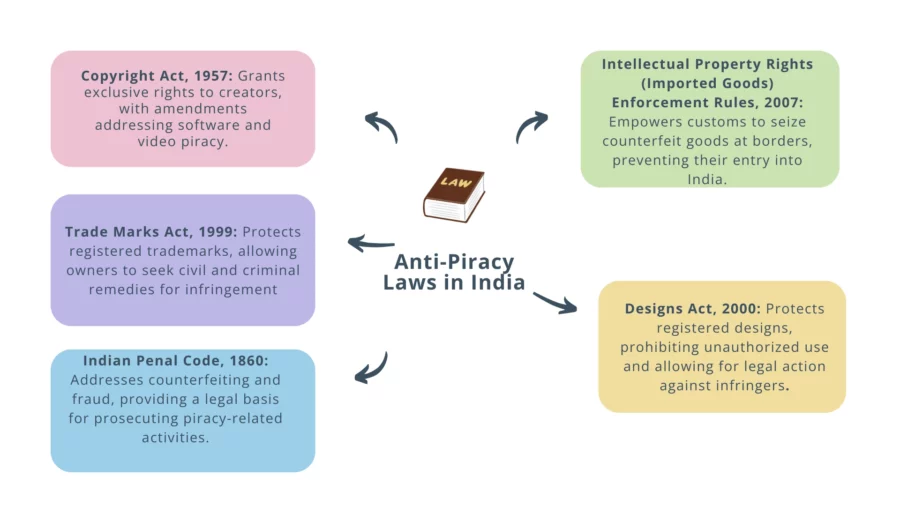
Anti-piracy laws in India play a crucial role in protecting intellectual property and combating the widespread issue of piracy and counterfeiting.
These laws are designed to safeguard the rights of creators and ensure that they receive due recognition and financial compensation for their work. Here’s an overview of the anti-piracy laws in India:
The Copyright Act, 1957
India’s anti-piracy laws are primarily governed by the Copyright Act of 1957, which serves as the foundation of the country’s efforts to protect intellectual property.
This legislation provides authors, musicians, filmmakers, and other creators exclusive rights over their work, giving them control over how their content is used, reproduced, or distributed.
The Act has undergone several amendments to stay relevant to modern challenges, with the 1995 Amendment being particularly significant in addressing software piracy.
This amendment clarified the rights of copyright holders, including the ability to make backup copies of software, restrictions on software rentals, and heavy penalties for copyright infringement.
The 1984 Amendment was also important, focusing on combating video piracy, as it introduced specific measures to tackle the growing issue of unauthorised copying and distribution of films.
Over time, the Copyright Act has evolved, extending its scope to address new forms of infringement as technology and piracy tactics have advanced.
Through these legal updates, India aims to safeguard the interests of content creators while imposing strict punishments, including fines and imprisonment, for those who violate copyright laws.
The Trade Marks Act, 1999
This Act plays a vital role in cases where there is a violation of trademarks or brand names.
Action against piracy involving registered brands and infringement of trademark rights must be initiated in appropriate courts for civil and criminal remedies.
The responsibility to take action lies with the owner of the registered trademark, who can approach both civil and criminal courts for redress.
Sections 101-105 of the Trade Marks Act, 1999, prescribe penalties for falsifying or falsely applying trademarks.
Offenses under Sections 103, 104, and 105 are cognizable, with imprisonment ranging from six months to three years, and fines from INR 50,000 to INR 2,00,000.
Additionally, under Section 135 of the Act, the court may issue an injunction, preventing or compelling specific actions, such as halting the sale of counterfeit goods or ordering their destruction. This provides comprehensive legal recourse to protect trademark owners’ rights.
Indian Penal Code, 1860
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) of 1860, though not directly aimed at piracy, contains provisions that can be applied to acts of counterfeiting, cheating, and fraud, which are often associated with piracy activities.
Sections dealing with forgery, cheating, and criminal breach of trust can be invoked in cases where piracy involves the use of counterfeit goods, falsified documents, or fraudulent transactions.
The IPC serves as a broad legal tool for prosecuting those engaged in piracy-related activities, ensuring they face criminal charges in addition to any civil liabilities. This multi-faceted approach helps in addressing both the intellectual property violations and the associated fraudulent actions.
Intellectual Property Rights (Imported Goods) Enforcement Rules, 2007
The Intellectual Property Rights (Imported Goods) Enforcement Rules, 2007, were introduced to prevent the cross-border movement of pirated or counterfeit goods.
These rules empower customs authorities to seize goods suspected of infringing intellectual property rights, ensuring they do not enter the Indian market. Right holders, including companies and individuals, can request the suspension of clearance for such goods, providing them with a vital tool to prevent piracy at its source.
These rules complement existing anti-piracy laws by addressing the global nature of piracy, ensuring that international trade channels are not used to import or export counterfeit or pirated goods.
Designs Act, 2000
Section 22 of the Designs Act, 2000 outlines the legal framework for addressing piracy of registered designs.
During the copyright period of a design, no person is allowed to apply or imitate the registered design for commercial purposes without the registered proprietor’s consent. This includes importing or selling articles that bear the design or its imitation.
If violated, the offender may be required to pay up to INR 25,000 for each offense, capped at INR 50,000 per design.
The registered proprietor can also file a lawsuit seeking damages and an injunction to stop further infringement. In such cases, grounds for canceling the design’s registration under Section 19 may be used as a defense. The court’s decree must be sent to the Controller for registration.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Key Aspects of Anti-Piracy
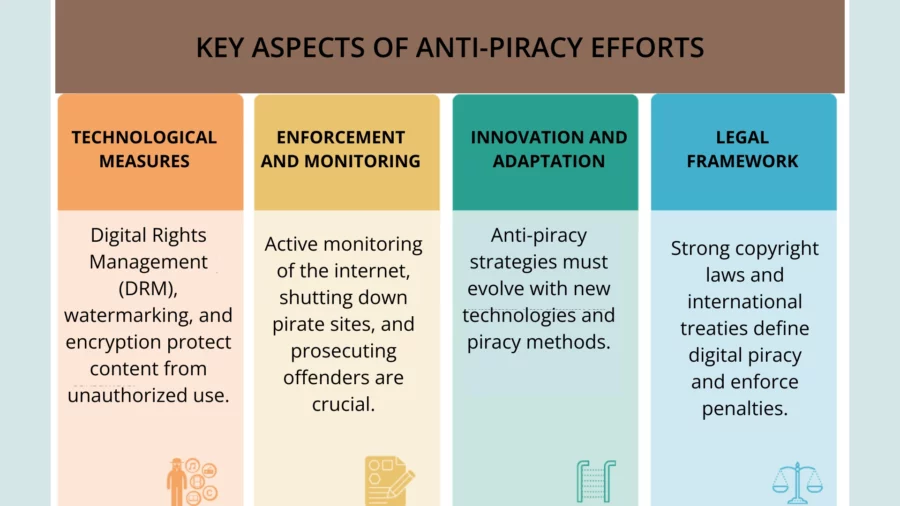
Anti-piracy efforts are essential these days, where the proliferation of online content and digital piracy pose significant challenges to content creators and producers.
These efforts encompass a range of strategies and measures designed to protect original content from unauthorised use and distribution.
Here’s a detailed look at the key aspects of anti-piracy:
Legal Framework
A robust legal framework is fundamental to anti-piracy efforts. This includes copyright laws and international treaties that define digital piracy and the penalties for engaging in it.
These laws are the backbone for legal action against entities involved in online piracy, ensuring that content theft is not only discouraged but also penalised.
Technological Measures
Technology plays a pivotal role in anti-piracy. Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems are crucial in controlling how digital content can be used, copied, and distributed.
These systems are a beacon for content creators, offering a way to safeguard their work.
Other technological measures like watermarking help trace the origin of pirated content, while encryption secures content against unauthorised access.
Enforcement and Monitoring
Effective enforcement is key to combating online piracy. This involves monitoring the internet, including P2P sites, for pirated content and taking action against those distributing it.
Shutting down pirate websites, removing pirated content from online platforms, and prosecuting individuals or groups responsible for piracy are part of these enforcement efforts.
Innovation and Adaptation
As technology evolves, so do the methods of piracy. Anti-piracy strategies must continually adapt and innovate to stay ahead of new piracy techniques.
Developing new anti-piracy software solutions and updating legal and enforcement approaches are crucial in this ongoing battle.
Consumer Access and Affordability
Making legal content more accessible and affordable addresses one of the key reasons why people turn to pirated content.
By reducing the incentive for consumers to seek out pirated alternatives, anti-piracy efforts can promote the use of original content through legitimate channels.
Global Cooperation
Piracy often crosses international borders, making global cooperation essential.
Sharing intelligence, conducting joint operations, and harmonising legal frameworks across countries are necessary to effectively tackle piracy on a global scale.
Anti-Piracy Content Protection
Anti-piracy content protection measures are vital to safeguarding the interests of content producers.
These measures ensure that the hard work and creativity invested in producing original content are not undermined by content theft.
Maintaining a Fair Marketplace
Piracy creates an unfair advantage for those who steal content, undermining legitimate businesses and creators who operate within the law.
Anti-piracy measures help level the playing field and promote a fair marketplace where original content is valued and protected.
What is the Need of Anti-Piracy Tools?

The need for anti-piracy tools in digital sphere is more critical than ever, especially with the rapid growth of the internet and digital media.
The ease of accessing and sharing content has led to a significant rise in online piracy, making these tools essential for a multitude of reasons, including:
Protecting Intellectual Property Rights
Anti-piracy tools safeguard the intellectual property rights of creators and producers, particularly in the realm of copyrighted audio-video content and other forms of content.
When content is pirated, it’s not just a violation of legal rights; it’s also an infringement on the creative efforts and investments of those who produce original content.
These tools ensure that creators maintain control over their work and receive the recognition and financial benefits they deserve.
Ensuring Revenue for Creators and Distributors
Piracy leads to significant revenue loss for both creators and distributors of content. Illegal content distribution means that the rightful owners do not receive the earnings they are entitled to.
Anti-piracy tools help in securing these revenue streams, ensuring that the profits from sales and distribution of software, audiovisual content, and other media go to the appropriate parties.
Maintaining Market Integrity
Piracy distorts the market by providing illegal access to premium content, which can unfairly compete with legal offerings. This not only affects market dynamics but also discourages future content investments.
Anti-piracy tools help maintain a level playing field in the market, ensuring that content safe from piracy is available for legitimate consumption.
Promoting Fair Competition
In a market where piracy is rampant, legitimate businesses that follow the law are at a disadvantage.
Anti-piracy tools promote fair competition by ensuring that all players in the market, from creators to service providers, operate under the same legal framework.
Enhancing User Security
Pirated content often comes with risks such as malware, viruses, and other security threats. Users who access pirated content may unknowingly expose their devices to these risks.
Anti-piracy tools help in reducing these security threats by discouraging the distribution and use of pirated content.
Upholding Quality and Integrity of Content
Pirated content can often be of inferior quality, and may even be incomplete or altered.
Anti-piracy tools ensure that consumers have access to high-quality, authentic content as intended by the creators, preventing content leaks and preserving the integrity of the content.
Supporting Legal Compliance
For businesses and individuals, using anti-piracy tools is part of complying with legal requirements. It helps in avoiding legal repercussions that can arise from unintentionally using or distributing pirated content.
Encouraging Creative Endeavors
By ensuring that creators can reap the benefits of their work, anti-piracy tools encourage continued innovation and creativity.
This support is essential for the growth and diversity of content across various media and is vital for the sustenance of creative industries.
Anti-Piracy Protection Service
These services play a crucial role in the ecosystem, providing robust protection against piracy.
They offer a comprehensive approach to keeping content from piracy, ensuring that the creative industries continue to thrive and that the rights of creators and distributors are protected.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Different Types of Anti-Piracy Measures

Anti-piracy measures are diverse and cater to different forms of media and distribution channels. Here are some of the key types:
- Digital Rights Management (DRM): DRM systems are used to control how digital content, like software, music, and movies, is used and distributed. They can restrict the copying, printing, and altering of digital files, and often require authentication for access.
- Watermarking: This involves embedding a unique code or marker in digital content (like images, videos, or documents) that can identify the original source or authorised user. It’s particularly useful in tracing the source of pirated content.
- Encryption: Encryption secures content by encoding it, making it inaccessible without the correct decryption key. This is commonly used in streaming services and software applications to prevent unauthorised access and copying.
- Copy Protection: In physical media like DVDs and Blu-rays, copy protection schemes prevent the disc content from being copied onto other devices or media. This can include encoding content in a way that is unreadable by standard copying software.
- Internet Monitoring and Takedowns: Companies and organisations often monitor the internet for pirated copies of their content. When found, they issue takedown notices to websites, ISPs, and search engines to remove or block access to the infringing material.
- Legal Action and Litigation: Pursuing legal action against individuals or entities involved in piracy is a direct approach to enforce anti-piracy laws. This can include lawsuits, fines, and in some cases, criminal charges.
- Software Activation and Licensing: Many software companies require users to activate their software through an online process, ensuring that each copy is legitimate. Licensing agreements also play a part, where users agree to terms that typically include non-distribution clauses.
- Geoblocking: This involves restricting access to content based on the user’s geographic location. It’s commonly used in streaming services to enforce regional licensing agreements.
- Collaboration with Payment Processors and Ad Networks: Anti-piracy efforts often involve working with payment processors and advertising networks to cut off revenue streams to websites hosting pirated content.
- Fingerprinting and Content Recognition: Advanced technologies can automatically detect copyrighted material in uploaded content (like on social media or video sharing platforms) using digital fingerprinting and content recognition algorithms.
These measures, often used in combination, form a comprehensive approach to combating piracy across various digital platforms and media types.
Which Industries Need Anti-Piracy Measures?
Anti-piracy measures are crucial across various industries, especially those that produce, distribute, or rely on intellectual property and digital content.
The rise of the internet and digital technologies has made it easier to copy and distribute content illegally, making anti-piracy measures essential for protecting the rights and revenues of creators and businesses.
Here are some key industries that need anti-piracy measures:
Film and Television Industry: This sector of the entertainment industry is significantly impacted by piracy. Movies and TV shows are often illegally downloaded or streamed on illegal platforms, including illegal websites and streaming sites.
Anti-piracy measures are essential to protect the investments in the film industry and ensure that creators and production companies are compensated.
Music Industry: Long battling with piracy, from illegal CD copying to unauthorised downloading and streaming, the music industry requires robust anti-piracy service to safeguard the earnings for content creators and those involved in music production and distribution.
Software and Gaming Industry: Software and video games are common targets for digital pirates, leading to substantial revenue loss. Anti-piracy technology like DRM and activation keys are vital to control the unauthorised distribution and use of these digital materials.
Publishing Industry: Both physical book piracy and digital e-books piracy affect authors and publishers. Copyright protection is necessary to ensure writers receive royalties and their intellectual property rights are respected.
Educational Content Providers: E-learning materials, online courses, textbooks, and research papers face piracy issues. Anti-piracy measures help protect these educational materials and sustain the business models of content providers.
Photography and Graphic Design: These fields often see creative materials used without permission. Watermarking and copyright notices are common anti-piracy measures to protect the work of photographers and graphic designers.
Fashion and Apparel: Dealing with design piracy and counterfeit products, the fashion industry needs to protect its design blueprints and marketing content from piracy.
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology: In these industries, piracy can manifest as patent infringement and unauthorised production of patented drugs or technology. Protecting research and development investments is crucial here.
Broadcasting and Streaming Services: The rise of online streaming has posed challenges in controlling unauthorised access and distribution of content. Anti-piracy measures are essential to protect revenue and content exclusivity for broadcasters and service providers.
Art and Cultural Industries: Digital reproductions of artworks and cultural artifacts are also prone to piracy. Protecting these works is crucial for both economic and cultural preservation reasons.
The Role of Anti-Piracy Measures
- Preventing Content Theft: Anti-piracy measures help prevent the theft of content from illegal file-sharing platforms and other unauthorised sources.
- Safeguarding Earnings: They ensure that earnings for content creators are protected, which is vital for the sustainability of creative industries.
- Promoting Legal Consumption: By combating illegal platforms, these measures promote the legal consumption of movies, music, and other digital content.
- Advancing Technology: The continuous advancement of anti-piracy technology is essential to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated piracy methods.
What’s Next?
Anti-piracy is a critical response to the advancement of technology, which has given rise to internet pirates and widespread copyright breaches.
As illegal streaming sites proliferate, threatening the integrity of creative content, Bytescare’s anti-piracy services emerge as a vital tool.
These services not only combat digital piracy effectively but also ensure that the rights of content creators are protected in this rapidly evolving digital field.
Don’t let digital piracy erode the value of your hard work. Book a demo with us today and secure your digital assets with us and move forward with confidence.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is the definition of anti-piracy technology?
Anti-piracy technology involves various tools and techniques designed to deter and detect unauthorised access or use of copyrighted content. Common examples include:
Digital Rights Management (DRM): Encrypts content and restricts its access to authorised users and devices.
Watermarking: Embeds invisible codes or marks within content to identify its origin and track unauthorised distribution.
Fingerprinting: Analyses unique characteristics of devices or software installations to identify and track individuals involved in piracy.
Monitoring and takedown systems: Scan online platforms for pirated content and initiate legal procedures for its removal.
What is anti-piracy in games?
In the gaming industry, anti-piracy measures aim to prevent unauthorised copying and distribution of video games. This can involve:
Activation codes: Unique codes required to install and play a game, often tied to specific accounts or platforms.
Online authentication: Games require verification with online servers to confirm legitimacy before allowing gameplay.
Anti-cheat software: Monitors player activity and system files to detect and prevent hacking, modifications, or unauthorised access.
Content encryption: Game files and assets are encoded to prevent unauthorised copying or manipulation.
Why piracy is bad?
Piracy harms creators and rights holders in several ways:
Lost revenue: Piracy deprives creators of income from their work, hindering their ability to sustain themselves and continue creating.
Reduced investment: Declining revenue due to piracy can dis-incentivise investments in new content creation.
Quality decline: Lower income can lead to budget cuts, impacting production quality and audience experience.
Copyright infringement: Piracy is illegal and violates the intellectual property rights of creators.
Security risks: Pirated content often harbors malware or viruses, posing security threats to users.
How does anti-piracy work?
Anti-piracy measures combat unauthorised content distribution using various strategies. Digital Rights Management (DRM) controls content usage, while watermarking helps track pirated material. Internet monitoring leads to takedown requests for illegal copies.
Legal actions, including lawsuits and fines, deter piracy. Public awareness campaigns educate about piracy’s ethical implications.
Geo-blocking restricts content access by location, and collaboration with ISPs helps monitor and restrict piracy. Secure distribution methods, like encrypted streaming, also play a crucial role. These evolving measures aim to reduce piracy’s prevalence and impact.
How can individuals support anti-piracy efforts?
Individuals can support anti-piracy by respecting intellectual property laws, using legal sources for downloading and purchasing content, and avoiding the distribution of copyrighted material without permission.
Additionally, staying informed about the importance of protecting creative works helps foster a culture that values and upholds anti-piracy principles.
What role do intellectual property laws play in anti-piracy?
Intellectual property laws provide the legal framework that supports anti-piracy efforts. These laws define and protect the rights of creators, allowing them to take legal action against individuals or organisations that engage in piracy.
Anti-piracy measures enforce these laws by preventing and addressing unauthorised use of protected works.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

