Key Takeaways:
- Counterfeiting leads to significant revenue losses for governments and legitimate businesses.
- Counterfeit products often lack quality control, posing health and safety hazards to consumers.
- Widespread counterfeiting undermines consumer confidence in brands and regulatory systems.
Counterfeiting, a practice of producing and distributing goods with an intention to replicate a legally branded counterpart in an unauthorised form, is an issue with long-reaching implications for economies, legal structures, and consumer trust in general worldwide.
Not only is counterfeiting a problem with grave implications for companies whose products are counterfeited, but for governments and consumers who must suffer its consequences, too.
With increased expansion in e-business and cheap production, counterfeiting is an issue governments, industries, and citizens must face at all times.
This article gives you a useful insight into the impact of counterfeiting on governments and consumers.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Scope and Definition of Counterfeiting
What is Counterfeiting?
Counterfeiting involves the illegal reproduction of merchandise, most frequently branded merchandise, with a view to convincing buyers that they are purchasing authentic merchandise.
All types of merchandise, both high-value merchandise such as watches, bags, and electronic merchandise, and general merchandise such as drugs, foods, and software, become a victim of counterfeiting.
Types of Counterfeit Goods
Counterfeit goods can be placed in two categories:
Designer Apparel, Handbags, and Luxury Products: Luxury items, including designer apparel, bags, watches, and such items, fall under this group. Copycat manufacturers produce them almost indistinguishably and sell them at a lesser price.
Consumer Products: Everyday items such as electronic items, drugs, foodstuffs, and even automotive parts. Consumer counterfeit goods are most perilous in terms of direct impact on consumers’ well-being and health.
The Global Scope of Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting reaches a range of industries, including apparel, electronic items, drugs, and even foodstuffs.
In 2019, pirated or fraudulent goods accounted for 3.3% of global trade, as per OECD. Also, this is equivalent in value in dollars in terms of loss for governments and companies in general terms.
E-business has compounded the problem, with counterfeiters having direct access to buyers through direct sales.
Impact of Counterfeiting on Governments and Consumers
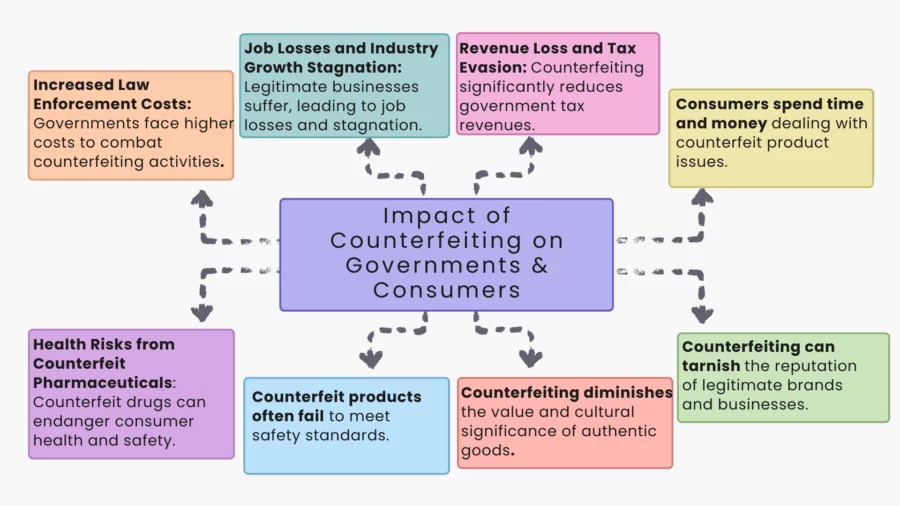
The Economic Impact on Governments
Revenue Loss and Tax Evasion
Counterfeiting robs governments of taxes through loss, with counterfeit goods being traded in the black economy, exempted from import taxes, sales taxes, and excise taxes.
Losses incurred in such cases form a colossal burden for government budgets, impacting public outlays for critical public goods and services.
The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) estimates counterfeit sales and piracy cost the global economy upto $1.7 trillion by 2015, with a significant portion reflecting lost tax revenue.
Job Losses and Industry Growth Stagnation
The impact of counterfeiting on the supply chain extends to job losses and stagnation in industry growth.
Counterfeit production undermines market competition, reducing the profitability of legitimate products and discouraging investment in research and development.
Sectors that rely on intellectual property rights, such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and fashion, suffer financial losses, leading to hundreds of thousands of job cuts worldwide.
The impact of counterfeiting on the fashion industry is particularly severe, as counterfeit luxury goods dilute brand exclusivity and devalue original products.
Increased Law Enforcement Costs
Governments allocate massive amounts of resources to combat illegal activities linked to counterfeiting.
Public awareness programs, court cases, and customs inspections require a significant amount of funding.
Trade in counterfeited goods is, in most cases, accompanied with organised crime, and therefore puts a strain not only on law enforcement but also takes funding out of other areas of commercial activity.
Impact on Consumer Health and Safety
Health Risks from Counterfeit Pharmaceuticals
The risks to consumers from counterfeit medicines are among the most alarming consequences of counterfeiting. These fake drugs often contain incorrect active ingredients, leading to ineffective treatment, severe side effects, or even death.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that 10% of medicines sold globally are counterfeit, with some regions reporting figures as high as 30%.
The counterfeit drug market is especially prevalent in developing countries where regulations may be lax or enforcement weak.
The impact of counterfeit products on global trade has included a surge in illicit medicines, particularly in countries with weak regulatory enforcement.
Unsafe and Substandard Consumer Goods
Counterfeit goods, including electronic items, computer software, automotive parts, and children’s toys, represent a significant danger.
Made with cheap materials, such goods have a poor compliance record with regard to requirements for safety. Deceptive electrical items can cause fires, and shoddy car parts can cost lives.
For children, toy goods with chemicals can have disastrous health repercussions. The consequences for the consumer range between minor annoyance and life-threatening complications.
Erosion of Trust in Brands
Counterfeiting erodes trust in companies and brands in terms of consumption amongst buyers.
Consumers become disillusioned with companies and brands whose products have been bought in innocence, under a wrong presumption of genuineness.
Consumers, even with full awareness of purchasing fakes, will have less desire to purchase real goods in the future.
Over a long period, such behaviour can demolish a real company’s goodwill, especially when counterfeiting is widespread in a particular industry.
Cultural Devaluation of Original Products
The impact of counterfeit luxury goods is evident in the luxury fashion industry, where high-end brands symbolise status and exclusivity.
A marketplace filled with counterfeit goods brings down real goods’ value, altering consumption behavior and affecting global brand value. It transforms cultural values in terms of price over value, redefining demand in a marketplace.
Customs and Border Protection Issues
The governments face a significant challenge in intercepting counterfeit goods at borders.
Customs departments face an issue with volumes of goods entering borders, and it is not easy for them to differentiate between real and counterfeit goods.
As a result, most counterfeit goods pass through and enter consumption, undermining the purpose of efforts in law enforcement.
Weakening of Intellectual Property Rights Enforcement
The impact of counterfeiting on intellectual property rights is considerable.
Counterfeiters replicate patented goods, trademarks, and copyrighted items in an illicit form, discouraging companies from producing new items and disincentivising them from investing in new items.
In the long run, it discourages long-term development and disincentivises foreign investment in national industries.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Measures to Combat Counterfeiting
| Measure | Description | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stronger Intellectual Property Laws | Governments should enact stricter laws to protect intellectual property (IP) rights and enforce these laws rigorously. | Enacting tougher IP laws like the TRIPS Agreement (Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights). | Helps businesses protect their products and IP from being copied. |
| Improved Customs and Border Control | Customs agencies must strengthen their inspections and cooperation to intercept counterfeit goods at borders. | Increasing the number of customs officers and training them to spot counterfeit items. | Reduces the entry of fake goods into the market. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Educating consumers about the risks and dangers of counterfeit goods through media and educational programs. | Government-backed campaigns that highlight the dangers of fake medicines and electronics. | Increases consumer vigilance and reduces demand for counterfeit products. |
| Collaboration Between Industry and Government | Public-private partnerships can be formed to share intelligence and enhance enforcement against counterfeiters. | Industry groups (of medicines) are working with national authorities to crack down on fake drugs. | Increases the efficiency of enforcement and strengthens deterrents against counterfeiting. |
| Digital Authentication Technologies | The use of blockchain, QR codes, and other digital tools to verify the authenticity of products. | Using blockchain to track the origins of luxury goods like watches and handbags. | Provides consumers and businesses with a reliable way to check if a product is genuine. |
| Online Market Monitoring | E-commerce platforms must take responsibility for monitoring and removing counterfeit listings. | Major platforms like Amazon and eBay partnering with brands to detect and remove fake products. | Reduces the availability of counterfeit goods on online marketplaces. |
| International Cooperation | Countries must cooperate internationally to enforce IP rights, share data, and track cross-border counterfeit trade. | Collaboration through INTERPOL, World Customs Organisation (WCO), and other international bodies. | Provides a global solution to the transnational nature of counterfeiting. |
| Stronger Penalties for Counterfeiters | Increasing fines and prison sentences for individuals and organisations involved in counterfeiting. | Countries like the U.S. and EU implementing severe penalties for those caught distributing counterfeit goods. | Deters potential counterfeiters due to the higher risk of severe punishment. |
| Consumer Protection Laws | Enforcing laws that hold manufacturers, importers, and retailers accountable for selling counterfeit products. | Legislation that mandates refunds or replacements for consumers who unknowingly purchase counterfeit goods. | Empowers consumers and encourages businesses to ensure the authenticity of their products. |
| Product Serialisation and Tracking | Manufacturers can implement serialisation to track the production and distribution of genuine products. | Using unique codes on packaging or products to verify their authenticity at each stage of distribution. | Enhances traceability and accountability of products throughout the supply chain. |
These measures, when combined, can significantly reduce the impact of counterfeiting, protecting both consumers and legitimate businesses while supporting global economic integrity.
What’s Next?
Counterfeiting has wide-ranging consequences for both governments and consumers.
It causes financial losses, compromises safety, disrupts industries, and weakens economic activity. Governments must implement stricter laws, enhance enforcement, and collaborate with businesses to protect intellectual property rights.
Consumers, on the other hand, must remain vigilant to avoid counterfeit products and ensure their safety.
The fight against counterfeiting requires global cooperation to minimise its illicit industry and preserve market integrity.
To further safeguard your brand from counterfeit products and misuse, consider brand protection service.
With advanced tools tailored to tackle the impact of counterfeiting, Bytescare empowers businesses to protect their reputation and revenue.
Ready to protect your brand? Book a demo today and experience Bytescare’s solutions firsthand!
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What are the main types of counterfeit goods?
Counterfeit goods include luxury items like watches, handbags, and designer clothes, as well as everyday consumer products like food, medicine, electronics, and automobile parts.
How does counterfeiting affect government revenue?
Counterfeiting results in lost tax revenue for governments because counterfeit goods are typically sold without proper taxation, and import duties are evaded.
Can counterfeit products harm consumers?
Yes, counterfeit products, particularly medicines, electronics, and food, can be harmful to consumers’ health and safety due to the use of substandard materials or harmful ingredients.
How can I identify counterfeit products?
Check for authenticity markers such as serial numbers, holograms, and official brand packaging. Purchase from authorised dealers and be cautious of unusually low prices.
What role does e-commerce play in counterfeiting?
E-commerce platforms enable counterfeiters to easily reach global markets, often with little oversight, making it harder for authorities to identify and remove counterfeit listings.
How can consumers avoid buying counterfeit products?
Consumers should buy goods from trusted sources, look for authenticity verification, avoid suspiciously low prices, and educate themselves about the risks of counterfeiting.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

