Key Takeaways:
- Copyright protects original works like art, music, and writing, granting creators exclusive rights to use, reproduce, and distribute them.
- Unauthorised use of copyrighted content without permission may lead to legal consequences, including fines or copyright removal requests from online platforms.
- Protecting your creative content ensures ownership while respecting others’ copyrights fosters ethical creativity and compliance with intellectual property laws.
There is more creativity than ever before. Millions of people are getting ideas from other creators who share their work on different platforms.
How do you make sure that your work stays yours? To save your hard work from being used without your permission copyright protection steps in.
Copyright laws are your safety net whether you’re a young artist selling prints online or a writer publishing your latest blog. Your exclusive rights to use in addition to make money off of your works are granted by them.
They also teach people to value other people’s intellectual property which leads to more creative thinking in a world where people work together.
But a lot of people still don’t know what copyright covers or what might happen if they don’t follow it.
Knowing these basics is vital, not just to protect your content but to avoid unintentionally infringing on someone else’s rights.
Let’s explore the essentials of copyright protected content, unraveling the complexities with practical insights and tips.
Let’s explore how you can safeguard your creative assets and foster a culture of respect for intellectual property!
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal protection that protects original works of creativity, ensuring that creators have control over how their work is used.
Think of it as a do-not-copy sign for your individual images, writing, music, photography, or even software license. It’s automatically copyright-protected material when you create something unique and put it in a tangible form—like writing it down or uploading it online.
You have exclusive rights to make money off of your work because you are the author. No one else can use it without your permission for business or personal reasons.
Copyright doesn’t just keep people safe. It makes sure that artists credited for their work. It’s important to remember that ideas aren’t protected on their own. But only the way they’re presented is protected.
You can protect your work by preventing accidentally violating the fundamental rights of others by knowing the questions about copyright.
Types of Works Protected Under Copyright
| Type of Work | Examples |
| Literary Works | Novels Poems Articles Blogs Scripts |
| Artistic Works | Paintings Drawings Sculptures Graphic designs |
| Musical Works | Songs Compositions Sheet music |
| Audio-Visual Works | Films TV shows Videos Motion Pictures |
| Sound Recordings | Podcasts Musical compositions Audiobooks Audio recordings |
| Software | Computer programs Apps Websites |
| Dramatic Works | Plays Choreography Screenplays |
| Architectural Works | Building designs Blueprints |
What Does Copyright Protected Content Mean?

Copyright-protected content refers to original works of creativity that are legally safeguarded against unauthorised use, reproduction, or distribution.
When someone creates something unique—whether it’s a sound recordings, painting, blog post, or video—and expresses it in a tangible form, copyright laws automatically cover. This protection gives the individual creator exclusive rights to decide how their work is used.
Let’s say you’ve put all of your heart into writing a book. Copyright makes sure that no one else can use your work without your permission. To say This is mine you choose how to share it.
But copyright isn’t just about keeping things safe. It shows appreciation for the work that go into making creative works. Copyright laws give artists a reason to produce meaningful work by protecting material.
Using someone else’s copyright-protected works without their permission can result in serious repercussions. That’s why copyright is important for everyone who uses content online, not just people who make content.
Why Is Copyright Important?
Copyright is vital because it safeguards intellectual property, giving creators control over their work. Original ideas that are expressed in tangible medium are protected so they can’t be used without permission.
It’s a way to honor the hard work that went into making something unique. Along with protecting people copyright encourages creativity. Creators who know their work is protected by the law are more likely to try new things.
Copyright also helps the economy in big ways. It lets artists make money off of their work. This makes sure they get paid for their work. Copyright lets creative people make a sustainable livelihood from selling books to software license.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
The Scope of Copyright Protection
Copyright protection covers a lot of ground but it has clear limits to keep things fair. Creators can better handle the legal system if they know what it covers.
The duration of copyright protection is an important factor.
The copyright lasts as long as the author does along with a certain number of years after they die ( This is often 70 years).
This makes sure that the person who created the work can continue to make money from it. This duration can change depending on the type of work in addition to the local laws.
The geographic limitations of copyright laws.
Copyright protection isn’t the same everywhere; it depends on the federal copyright laws of each country. International agreements like the Berne Convention help to make copyright laws more consistent.
But implementation depends on where the infringement happens. These differences should be known by content creators when they share their work around the world.
There are limitations on what copyright protects.
While it covers tangible medium of expression—like a written book, a song, or a painting—it doesn’t protect the ideas themselves. For example, the concept of a magical school isn’t copyrighted, but the specific way it’s portrayed in a book or movie is.
What Are the Rights Granted Under Copyright?
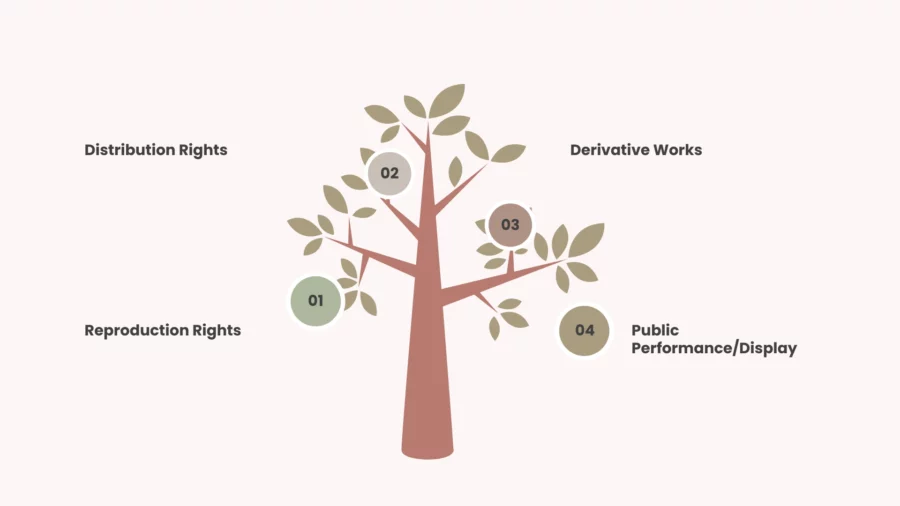
When you create an original work, copyright grants you exclusive rights to control how others use it. These rights ensure that your creation remains protected and that you, as the creator, have the final say in sharing or using your work. There are several key rights granted under copyright protection:
Reproduction Rights
This is the right to make copies of your work. Whether it’s printing your book, duplicating a song, or reproducing an artwork, no one can copy your creation without permission. This right is fundamental in controlling how your work is distributed.
Distribution Rights
With distribution rights, you have the power to decide how your work is made available to the public. This includes selling, renting, or lending copies of your work. For example, only you can decide to sell your book or album to the public.
Derivative Works
You have the exclusive right to create adaptations of your work, such as turning your novel into a movie or remixing your music. This right ensures that no one can transform your work into something new without your consent.
Public Performance/Display
This right allows you to control where and how your work is shown in public. Whether it’s performing a play, displaying artwork in a gallery, or screening a film, no one can use your work for public viewing without permission.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What Does Not Qualify for Copyright Protection?
| Ideas | Copyright doesn’t protect ideas, concepts, or methods, only their specific expression or form. |
| Facts | Facts, discoveries, or simple data cannot be copyrighted, as they are considered public domain. |
| Short Phrases | Titles, names, and short phrases (like slogans or catchphrases) are not eligible for copyright. |
| Processes | Methods of operation, procedures, or systems (like business methods) are not covered by copyright. |
| Works Not Fixed in a Tangible Form | Unwritten or unfixed works, such as impromptu performances, aren’t protected until recorded. |
| Public Domain Works | Works already in the public domain cannot be copyrighted, as they’re free for anyone to use. |
| Government Works | In many countries, works created by government employees or agencies are not eligible for copyright. |
How Does Copyright Protection Work?
Copyright protection automatically applies as soon as you create an original work and fix it in a tangible form, like writing it down or recording it. No formal registration is required to copyright claims, and your work is protected from the moment of creation.
However, registering your work with the relevant copyright office is optional but highly beneficial. Registration provides a public record of your work and strengthens your ability to enforce your rights in court if needed. It also allows you to claim statutory damages and attorney fees in case of willful infringement.
You might also notice the copyright symbol (©) used alongside works. While not required, it serves as a proper copyright notice that the work is copyrighted and indicates that the creator claims rights to it.
The symbol is followed by the year of first publication and the creator’s name (e.g., © 2025 John Doe). This acts as a deterrent to potential infringers.
Navigating Copyright Laws
What Is Fair Use?
Fair dealing is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission, under certain circumstances. Fair use factor is designed to balance the rights of the creator with the need for public access to ideas and information.
While copyright protects creative works, fair use enables society to use those works for purposes like education, commentary, or criticism.
Examples of fair dealing include:
- Teachers using brief excerpts of books or videos in teaching activities.
- Quoting parts of a book in a Commentary or Criticism.
- Creating a humorous or satirical version of an existing work for entertainment purposes.
To determine whether a use qualifies as factor fair use, courts consider several aspects:
Purpose and Character
Is the use for commercial or non-commercial purposes? Non-profit educational uses are more likely to be fair.
Nature of the Work
Is the work factual or creative? Factual works are more likely to be used under fair use.
Amount Used
How much of the original work is being used? Using only a small portion favors fair use.
Effect on the Market
Does the use harm the market value of the original work? If it does, it’s less likely to be fair use.
Public Domain & Copyright
Public domain content refers to works that are no longer protected by copyright laws and can be freely used by anyone for any purpose. This could happen because the copyright has expired, or the creator has explicitly released the work into the public domain.
Once a work enters the public domain, it can be reproduced, distributed, adapted, or performed without seeking permission or paying royalties.
To determine if a work is in the public domain, you need to consider several factors, including:
Copyright expiration
In many countries, works enter the public domain after a certain period, typically 70 years after the author’s death. For works created by corporations, the duration can be different.
Creation date
Works created before a certain year (e.g., before 1923 in the U.S.) are often in the public domain.
Explicit release
Some creators voluntarily place their work in the public domain, making it free to use.
Examples of works in the public domain include:
- Classic literature like Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen or Moby-Dick by Herman Melville.
- Classical music compositions by Mozart or Beethoven.
- Old films and artworks, such as those by Vincent van Gogh.
Creative Commons & Open Licensing
Creative Commons (CC) licenses offer a flexible way for creators to share their work while still maintaining some control over how it’s used. These licenses allow others to use, remix, and share content, but with specific terms of service outlined by the creator.
Unlike traditional copyright, Creative Commons licenses are designed to make sharing easier and more accessible, with clear rules about what is and isn’t allowed.
There are several types of Creative Commons licenses, each with varying levels of permissions:
CC BY (Attribution)
Allows anyone to use, modify, and distribute the work as long as they give credit to the creator.
CC BY-SA (Attribution-ShareAlike)
Similar to CC BY, but derivative works must be licensed materials under the same terms.
CC BY-ND (Attribution-NoDerivs)
Allows sharing of the work but not modifications.
CC BY-NC (Attribution-NonCommercial)
Allows use and modification for non-commercial purposes only.
CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike)
Allows non-commercial use and modification, with the same license applied to derivatives.
CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs)
The most restrictive; allows only sharing for non-commercial purposes without modifications.
Websites like Wikimedia Commons, Flickr, and Creative Commons Search offer vast libraries of full-size images, music, and other media to find Creative Commons content. Always check the specific license for each work to ensure you’re following the terms correctly.
What Are the Consequences of Copyright Infringement?
Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses a copyrighted work without permission, and it can have serious consequences for both individuals and businesses.
Legal consequences can be severe for acts of copyright infringement.
Copyright holders have the right to take legal action against infringers, which may result in hefty fines, lawsuits, and even court orders for takedown notices.
In some cases, violators can be required to pay statutory damages, which can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars, depending on the severity of the infringement. The cost of defending against a copyright lawsuit can also be significant, even if the infringement was unintentional.
Beyond the legal risks, there are ethical implications for creators and businesses.
Using someone else’s work without permission undermines the value of intellectual property rights. It also damages trust with audiences and can tarnish a brand’s reputation. For businesses, infringement can result in a loss of customer loyalty and potentially alienate partners or clients who value ethical practices.
Some of the notable copyright infringement cases highlight the serious impact of copyright infringement. For instance, the lawsuit between Napster and record companies in the early 2000s showed how large-scale piracy can lead to the shutdown of a platform.
More recently, Google faced a copyright dispute with Oracle over the use of Java in Android, which led to a lengthy legal battle.
How to Use Content Legally?
Using content legally is essential to avoid copyright infringement and respect the rights of creators. Here are three key ways to ensure you’re using content the right way:
Always seek permission for copyrighted works
If you want to use someone else’s work—whether it’s a photo, song, or article—always ask for permission first. This is the safest way to ensure you’re legally allowed to use it. Often, creators are happy to grant permission, sometimes for a fee or with specific conditions attached.
If you can’t get permission, look for alternative ways to use the content, like finding works with open licenses or those in the public domain.
Use licensed or public domain content
Another great option is to use content that’s either licensed for free use or already in the public domain. Creative Commons licenses, for example, allow creators to share their work with specific permissions, such as non-commercial use or attribution.
Public domain works, like many classic books and old films, are free to use without restrictions. Make sure to verify the license or public domain status before using any content.
Utilise fair use responsibly
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted works without permission for purposes like commentary, criticism, or education.
However, it’s essential to apply fair use carefully and consider factors like the amount of the work used and its impact on the market. When in doubt, consult a legal expert to ensure you’re staying within fair use guidelines.
Tools & Resources for Copyright Compliance
| Creative Commons Search | A search tool that helps find works with Creative Commons licenses. |
| Wikimedia Commons | A repository of free-use images, sounds, and videos. |
| Google Copyright Removal Tool | A tool for submitting copyright infringement notices to Google. |
| Copyright.gov | The United States Copyright Office’s official website. |
| Plagiarism Checkers | Tools like Copyscape or Turnitin that check for duplicate content online. |
| Royalty-Free Image Websites | Websites like Unsplash, Pexels, and Pixabay offer free-to-use images. |
| License Agreements | Platforms like Artlist and Audiojungle provide clear licensing for music and images. |
| Fair Use Evaluators | Online tools that help assess whether a particular use qualifies as fair use. |
What’s Next?
Knowing copyright protection is essential for both creators and users of content. It not only safeguards the hard work and creativity of individuals but also ensures a fair and respectful environment for sharing and using intellectual property.
Whether you’re a content creator, business owner, or simply someone who enjoys using digital media, it’s essential to respect copyright laws. By seeking permission, using licensed or public domain content, and applying fair use responsibly, you can avoid legal risks and contribute to a culture of ethical content use.
With the right tools and resources, staying compliant with copyright is easier than ever. From Creative Commons licenses to fair use evaluators, there are numerous ways to ensure you’re using content legally.
Respecting copyright not only protects you legally but also helps foster creativity, innovation, and a thriving digital ecosystem. Always be mindful of copyright to avoid unintended consequences and support the work of others.
Your content is constantly at risk in today’s world. Bytescare digital piracy monitoring uses AI to detect, remove, and monitor unauthorised distribution of your work.
Our digital piracy monitoring service protects your intellectual property, so you can focus on creativity. Secure your intellectual property rights with Bytescare—book a demo today!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What does it mean copyright protected content found?
Copyright-protected content refers to original works like text, images, music, or videos that are legally protected by copyright law. The copyright owner has exclusive rights to use, distribute, and modify the work.
How do I check if something is copyright-protected?
You can check if content is copyright-protected content by reviewing the source for copyright notices, researching through copyright databases, or confirming whether the content is under a Creative Commons or public domain license.
What are the 5 main copyright protections?
The five main copyright protections include the rights to reproduce, distribute, perform publicly, display publicly, and create derivative works based on the original content.
How do you write a copyright disclaimer?
A copyright disclaimer typically includes the copyright symbol (©), the year of creation, and the copyright owner name. Example: “© 2025 John Doe. All rights reserved.”
Can I use copyrighted content if I credit the creator?
Simply crediting the creator does not always grant permission. You must ensure the material in question is licensed for use, fall under factor fair use, or obtain explicit permission from the copyright owner.
How can I protect my content from copyright infringement?
To protect your content, register it with a copyright office, add proper copyright notices, use watermarks, and monitor the web for unauthorised use. Legal action may also be necessary if copyright-protected material infringement occurs.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

