Key Takeaways:
- The DMCA is a crucial law that protects online content from copyright infringement, including music, videos, images, software, and written works.
- It establishes a process for copyright holders to report infringement and for service providers to respond, with safe harbor provisions for compliant providers.
- Copyright infringement can lead to significant fines and legal consequences, making DMCA compliance essential.
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a key U.S. law from 1998. The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is an important piece of legislation that helps protect digital content creators from copyright infringement.
Knowing what DMCA content protection entails and how it can safeguard your intellectual property is essential for any business or individual operating online. This outline will explore the key aspects of DMCA content protection, its importance, and the practical steps you can take to leverage it.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Historical Context and Legislative Purpose
The DMCA was signed into law on October 28, 1998, during a time when the internet was rapidly changing how information was disseminated and consumed.
Traditional copyright laws, designed in an era dominated by physical media like books and vinyl records, were ill-equipped to handle the scale and speed at which digital copies could be made and shared.
As personal computers, the World Wide Web, and digital storage solutions became more accessible, copyright holders found themselves scrambling to keep pace with the explosive rate of online distribution.
Two international treaties from the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)—the WIPO Copyright Treaty (WCT) and the WIPO Performances and Phonograms Treaty (WPPT)—helped pave the way for the DMCA by laying out updated protections for creative works in the digital realm.
The DMCA was the United States’ mechanism for implementing these treaties into national law.
The legislative intent behind the DMCA was twofold.
First, it aimed to encourage the development and use of technological measures to prevent unauthorised access to and copying of copyrighted works. Second, it sought to clarify the responsibilities and liabilities of internet service providers (ISPs) and online platforms regarding user-generated content.
By limiting the liability of service providers that followed specific procedures (notably, the “safe harbor” provisions), the DMCA created a framework that simultaneously protected rights holders and promoted the growth of the internet as a platform for free speech and innovation.
From a historical standpoint, the DMCA marked a turning point in how the U.S. government addressed the challenges of piracy in a digital context.
It catalysed the creation of digital rights management (DRM) technologies, shaped the policies of major online platforms, and compelled businesses to develop systems for responding to copyright infringement notices.
Despite being over two decades old, the DMCA remains the cornerstone of online copyright law in the United States.
Digital Millennium Copyright Act
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) was passed in 1998. It was made to fight online piracy and protect copyrights. It helps copyright owners and online services by setting rules for them.
The DMCA was created because digital technology made copying and sharing easy. It aimed to balance the rights of copyright holders with the needs of online users and services.
Key components of copyright protection are:
- The DMCA has “safe harbor” rules. These protect online services from copyright lawsuits if they follow certain steps, like removing content when asked.
- It also makes it illegal to break digital locks on copyrighted works.
- The DMCA sets up a process for copyright holders to ask for content removal from online sites.
The DMCA covers many types of digital content, like text, images, and videos. It guides online services in the U.S. on how to handle copyright claims.
This legal structure helps protect copyrights. It also lets the digital world grow and information flow freely online.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Protected by DMCA?
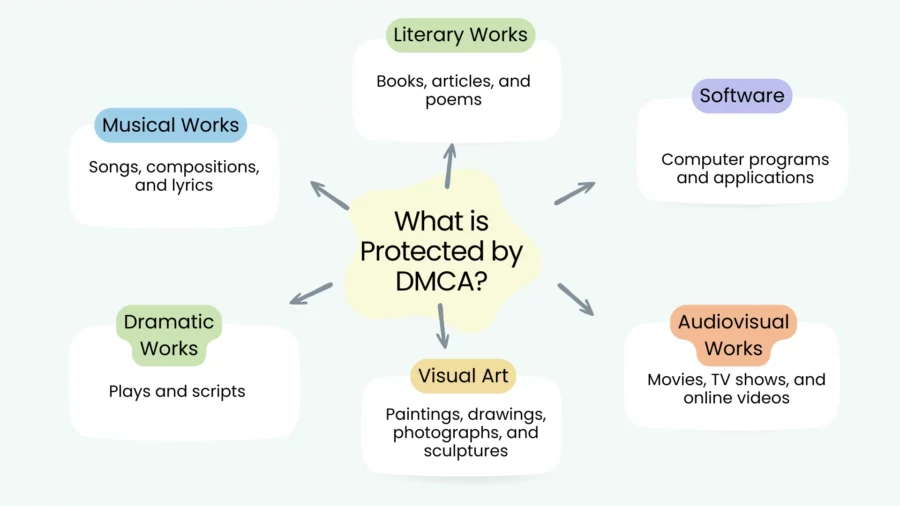
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) protects a wide range of original works that fall under copyright law. Here are the primary categories of content that are protected by the DMCA:
Literary Works: This includes books, articles, poems, and any other written content. Copyright protection applies to both published and unpublished works.
Musical Works: This category encompasses songs, musical compositions, and lyrics. Both the sound recordings and the underlying compositions are protected.
Dramatic Works: Plays, scripts, and other forms of dramatic literature are protected under the DMCA, including any accompanying music.
Visual Art: This includes paintings, drawings, sculptures, photographs, and other visual artworks. Copyright protection extends to both the original works and reproductions.
Audiovisual Works: Movies, television shows, online videos, and other multimedia content are protected. This includes both the visual and audio components.
Software and Computer Programs: Source code and object code for software applications, as well as video games, are protected under the DMCA.
Databases and Compilations: Original databases and compilations of data that exhibit creativity in their selection or arrangement are also protected.
Architectural Works: The design of buildings and structures is protected, including architectural plans and drawings.
Digital Content: Any content distributed online, such as e-books, digital music, and streaming media, is also covered under the DMCA.
Why DMCA Protection Matters?
Upholding Creative Industries
From music and movies to software and digital art, the DMCA’s provisions help shield creative industries from the financial and reputational harm caused by piracy.
By discouraging the unauthorised copying and redistribution of copyrighted material, DMCA enforcement supports content creators in monetising their efforts.
In the absence of such laws, piracy would be more rampant, undermining the incentive to produce new and original works. When creators feel protected, innovation and creativity flourish.
Encouraging Online Service Growth
The DMCA’s safe harbor provisions have been pivotal in spurring the growth of online platforms.
Sites like YouTube, for instance, handle vast amounts of user-uploaded content every second. Without safe harbor protections, YouTube could have faced crushing liability for any copyright infringement perpetrated by its millions of users.
Safe harbor has allowed platforms to exist and thrive, provided they follow reasonable procedures for responding to infringement claims. This has enabled the creation of an entire ecosystem of digital distribution channels where legitimate uses of copyrighted material can flourish, such as transformative works (e.g., remixes, commentary videos) and community-driven content.
Consumer Protection and Fair Use
The DMCA also matters because it helps protect consumers from pirated or malicious content.
While critics argue that DRM can sometimes be overly restrictive, legitimate DRM measures can help ensure the safety of users and the reliability of the content they purchase.
Moreover, the DMCA, in conjunction with broader copyright law, makes room for the concept of “fair use”—allowing uses of copyrighted materials for criticism, commentary, scholarship, research, or other socially valuable forms of expression.
Although navigating fair use in a DMCA context can be complicated, the legal structure does attempt to balance the interests of content owners with the public’s right to engage in free speech.
International Implications
The internet is global, and so is digital piracy. While the DMCA is U.S. legislation, its influence extends internationally.
Many countries have similar laws or interpret the DMCA to guide their own approach to online copyright enforcement.
For U.S.-based companies operating internationally, comprehending the DMCA is often the first step toward navigating a range of international treaties and regulations.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
DMCA Protection Badges and Their Significance

A DMCA protection badge is a small graphic displayed on web pages alongside copyrighted content that is not available for public use without explicit permission.
Although the DMCA does not mandate the use of these badges, they serve as a useful deterrent against potential copyright infringement.
By clearly indicating that certain resources require permission for use, content owners strengthen their position when requesting takedowns of unauthorized content. This clarity also aids service providers in swiftly verifying ownership claims.
There is no standardized design or format for DMCA badges, allowing content owners the flexibility to create their own unique versions or utilize pre-made templates available online.
These badges can enhance the visibility of copyright claims and reinforce the message that the content is protected.
By incorporating a DMCA protection badge, creators can effectively communicate their rights and discourage misuse of their intellectual property. Ultimately, while not a legal requirement, these badges can play a significant role in safeguarding creative works and facilitating the enforcement of copyright protections.
How DMCA Content Protection Works?
Technological Protection Measures (DRM)
When you buy or stream a movie from a legitimate online source, you might have noticed limitations on how and where you can watch it. This is an example of a technological protection measure, often called Digital Rights Management (DRM).
It can involve everything from encryption to watermarking to licensing keys that unlock content. By enforcing these technological controls, the DMCA aims to reduce unauthorised distribution.
- Encryption: An encrypted music or video file requires a decryption key to be accessed. Services like iTunes or Amazon Prime Video keep those keys under strict control so that only authorised users can play the files.
- Watermarking: Some businesses embed a unique, invisible watermark in their digital content, linking it to the individual purchaser. If the content is illegally shared, the watermark can sometimes lead investigators to the original source of the leak.
- License Management: Many software applications check licenses online to verify that the software is properly purchased and registered before granting full access.
Title I of the DMCA makes it illegal to circumvent these protective measures. For example, creating a tool that strips DRM from eBooks or streaming video files for resale or distribution is typically a violation. This anti-circumvention rule helps preserve the market for legitimately acquired content and software.
Takedown Notices
Perhaps the most visible mechanism of DMCA enforcement is the DMCA Takedown Notice.
When a rights holder discovers infringing content on a website or platform, they can issue a formal notice to the platform’s designated DMCA agent. The notice should include:
- A physical or electronic signature of the person authorised to act on behalf of the copyright owner.
- Identification of the copyrighted work(s) allegedly infringed.
- Identification of the infringing material and information reasonably sufficient to locate it (e.g., a specific URL).
- Contact information of the complaining party.
- A statement of good faith belief that the use of the material is not authorised by the copyright owner, its agent, or the law.
- A statement that the complaint is accurate, and under penalty of perjury, that the complaining party is authorised to act on behalf of the copyright owner.
Once the platform receives a valid DMCA takedown notice, the service provider is obligated to act “expeditiously” to remove or disable access to the infringing material. If they do so, they retain their safe harbor protection; if they fail to comply, they could be held liable for the infringement.
Counter-Notification and Restoration
The DMCA also includes provisions for an alleged infringer to file a counter-notification.
If the user whose content was removed believes that their use is fair or that the notice was otherwise mistaken, they can submit a counter-notice to the service provider, asserting their rights to use the content. This counter-notice must include:
- The user’s physical or electronic signature.
- Identification of the material removed and its location prior to removal.
- A statement under penalty of perjury that the user has a good faith belief the material was removed as a result of mistake or misidentification.
- The user’s contact information and consent to the jurisdiction of the federal district court in their region (if in the U.S.).
If the original claimant does not file a lawsuit within 10 to 14 business days (depending on jurisdiction), the platform may restore the content, effectively resolving the dispute in favor of the user.
Repeat Infringer Policy
To preserve safe harbor status, service providers must adopt and implement policies to address repeat infringers. This often includes permanent account termination for users who rack up multiple valid takedown notices.
The exact thresholds for what counts as “repeat” infringement vary among platforms, but the overarching requirement is that platforms cannot simply ignore or allow systematic misuse.
Essential Tools for DMCA Content Protection
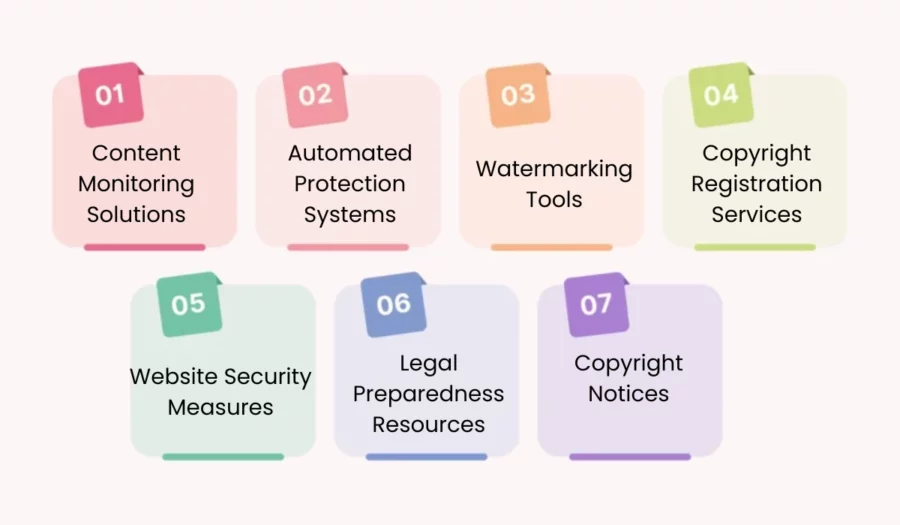
Protecting your digital content from unauthorised use is key today. Luckily, many tools and services help creators and copyright holders. They work under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA).
Content Monitoring Solutions
Monitoring the web for copyright infringement is vital. One such tool is provided by Bytescare that helps find duplicate content online. This ensures your work is not used without permission. Their premium plan offers more features like batch search and automated scanning.
Reverse image search focus on plagiarism and image protection. Such tool checks billions of web sources for copied content. They can finds duplicate images online as well.
Automated Protection Systems
Automated protection systems are software solutions or platform-based tools that streamline the process of detecting and responding to copyright infringement.
Rather than manually searching for infringing material or sending takedown notices one at a time, these systems use rule-based algorithms, machine learning, or direct integration with content platforms to automate most of the enforcement workflow.
Copyright Registration Services
While copyright protection is automatic the moment a work is “fixed in a tangible medium of expression,” formal registration with the U.S. Copyright Office provides additional legal advantages.
Copyright registration services assist creators in officially registering their works with the U.S. Copyright Office or equivalent organizations in other countries.
While copyright protection is automatic upon creation, registration provides additional legal benefits, such as the ability to sue for statutory damages and attorney fees in case of infringement.
By registering your content, you enhance your legal standing and make it easier to enforce your rights under DMCA regulations.
Best Practices for Protecting Digital Content
Given the complexity of the DMCA, individuals and businesses need to be proactive in managing and protecting their copyrighted works while also respecting others’ rights. Below are some best practices:
Register Your Copyrights: Although copyright protection is automatic in the U.S. the moment a creative work is “fixed in a tangible medium,” registering with the U.S. Copyright Office offers additional legal benefits. Should you need to file a lawsuit, a registered copyright can enable you to claim statutory damages and attorney’s fees.
Implement Robust DRM (If Applicable): If you are distributing digital content such as software, eBooks, or multimedia, consider implementing a balanced DRM solution that protects your IP without overly inconveniencing legitimate users. Tools like encryption, watermarking, and license checks can deter casual piracy.
Designate a DMCA Agent: For online platforms or businesses that allow user-generated content, you must designate a DMCA agent and publicly post the agent’s contact information. This is crucial for receiving notices in a timely fashion.
Maintain Clear Internal Processes: Outline the steps your company or team will take if you receive a DMCA takedown notice or counter-notification. This might include designating roles for reviewing claims, deciding whether to remove content, and determining if and how to notify the user.
Develop a Repeat Infringer Policy: Clarify the criteria under which you will suspend or terminate user accounts for repeat violations. Make sure this policy is clearly stated in your terms of service.
Use Screening Tools Wisely: Content identification tools, such as YouTube’s Content ID, can help rights holders flag unauthorised usage. However, they can also generate false positives, so it’s wise to monitor these tools carefully.
Educate Your Team: Employees, moderators, and community managers should understand the basics of the DMCA. Regular training on fair use, takedown notice procedures, and repeat infringer policies helps prevent costly legal action.
The Difference Between Copyright and DMCA Protection
Content creators face a complex world of intellectual property rights. It’s key to know the difference between copyright law and the DMCA. Both protect original content, but in different ways.
Legal Distinctions
Copyright law automatically protects original works like text, images, music, and videos. This protection starts when the work is created, even if it’s not registered. Copyright law gives creators many ways to fight against infringement, like suing for damages.
The DMCA deals with copyright infringement online. It makes it illegal to bypass the protection measures on digital works. It also has a process for taking down infringing content from websites.
Enforcement Methods
- Copyright enforcement often means going to court, which can be expensive and take a long time. The average case costs about $300,000 and takes over a year.
- DMCA enforcement is faster. It focuses on taking down infringing content quickly. Rights holders can ask service providers to remove infringing content.
- Copyright law offers broad protection, but the DMCA is better for quick action against digital piracy.
Creators need to know copyright law and the DMCA to protect their work online. Using both can help keep their content safe on different platforms.
The Future of DMCA Content Protection
As technology advances and the ways we consume and create content continue to evolve, the DMCA faces new challenges:
- Streaming and Live Content: The rise of platforms like Twitch and the popularity of live events (sports, concerts, etc.) present unique infringement scenarios. Real-time monitoring of live streams is far more complex than static content, raising questions about how DMCA enforcement should adapt.
- Blockchain and NFTs: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a new way to represent digital ownership. However, the underlying content can still be copied or infringed. Questions persist about how DMCA takedown notices apply to content residing on decentralised networks.
- Automated Takedown Systems: Artificial intelligence and machine learning tools can detect infringing material at scale. However, these automated systems also risk overreach, potentially blocking fair use and other legitimate forms of content. Ensuring human review and more nuanced processes could be crucial.
- Global Enforcement: The DMCA is U.S.-based, but the internet is global. Countries worldwide are reconsidering or implementing their own versions of notice-and-takedown frameworks. Harmonising these diverse systems remains a significant legal and logistical challenge for multinational corporations.
Though the DMCA’s core principles—protecting copyrights and balancing them with platform innovation—are likely to remain, incremental reforms and judicial interpretations will reshape it in the coming years.
Keeping abreast of these developments is essential for businesses, creators, and consumers alike.
What’s Next?
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is key in protecting digital content and intellectual property online.
It sets up a strong system for enforcing copyrights, balancing the needs of creators, service providers, and users. It’s important to use DMCA protection strategies well to keep digital assets safe and create a respectful online space.
As the digital world keeps growing, knowing and using DMCA rules is crucial for everyone. The DMCA helps deal with online copyright issues worldwide and encourages countries to work together. It lets content creators quickly act against infringement and get their work back online.
The DMCA is also used by service providers around the world to fight copyright and trademark issues. This shows how flexible the DMCA is in protecting digital content. It’s a vital tool in the fast-changing online world.
Bytescare prevents copyright violation through its innovative solution, which is designed to protect digital content using advanced technologies.
By knowing the core functionality of content protection and respecting the rights of creators, you can ethically use online resources. Book a demo to explore how Bytescare can safeguard your digital content.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is DMCA content protection and how does it work?
DMCA content protection refers to the legal framework established by the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, which safeguards original works of authorship in the digital environment.
It works by providing copyright holders with the ability to issue takedown notices to online service providers (OSPs) when their content is used without permission.
The DMCA also includes anti-circumvention provisions that prohibit the bypassing of technological measures designed to protect copyrighted works. By facilitating a streamlined process for reporting and removing infringing content, the DMCA helps creators maintain control over their intellectual property.
What are DMCA protected content?
DMCA protected content refers to any original work that is safeguarded under the provisions of the DMCA. This includes a wide range of creative expressions, such as music, films, literature, software, photographs, and visual art.
The DMCA provides copyright holders with the legal tools necessary to protect their intellectual property from unauthorized use, reproduction, or distribution in the digital realm.
How can I file a DMCA takedown notice if my content is being used without permission?
To file a DMCA takedown notice, you should follow these steps:
a. Identify the infringing content and the location (URL) where it is hosted.
b. Prepare a written notice that includes: your contact information, a description of the copyrighted work, of the infringing material, a statement of good faith belief that the use is unauthorised, and a declaration under penalty of perjury that the information is accurate.
c. Send the notice to the designated agent of the OSP hosting the infringing content. Most platforms have a specific process for submitting DMCA notices, often found in their terms of service or copyright policy.
What are the consequences for violating DMCA content protection laws?
Violating DMCA content protection laws can lead to several consequences, including:
Legal Action: Copyright holders can pursue legal action against infringers, which may result in monetary damages, statutory damages, and attorney fees.
Account Suspension: Online platforms may suspend or terminate accounts of users who repeatedly infringe copyright, as part of their compliance with the DMCA.
Criminal Penalties: In severe cases, willful infringement can lead to criminal charges, resulting in fines or imprisonment.
How does DMCA content protection apply to user-generated content on social media platforms?
DMCA content protection applies to user-generated content on social media platforms by holding both users and platforms accountable for copyright infringement.
When users post content that includes copyrighted material without permission, copyright holders can issue takedown notices to the platform.
Social media companies benefit from safe harbor provisions, which protect them from liability for user-generated content as long as they act promptly to remove infringing material upon receiving a valid DMCA notice. However, users are still responsible for ensuring that the content they share does not violate copyright laws.
What are the best practices for ensuring my content is protected under DMCA regulations?
To ensure your content is protected under DMCA regulations, follow these best practices:
Register Your Copyright: Officially register your work for stronger legal protection.
Use Watermarks: Add watermarks to visual content to deter unauthorized use.
Monitor Your Content: Regularly check for unauthorized use online.
Educate Your Audience: Inform users about your copyright policies.
Utilise Licensing Agreements: Create clear agreements if you allow others to use your work.
These steps help safeguard your intellectual property effectively.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

