Key Takeaways:
- Information rights management is essential for protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access.
- Content protection is a critical aspect of digital security, and information rights management plays a key role in this effort.
- Information rights management enables organisations to control access to sensitive information, preventing unauthorised users from viewing, printing, or forwarding confidential documents.
Information rights management is key to keeping digital data safe. It stops unauthorised access, printing, or copying of sensitive info. With cyber attacks on the rise, strong content protection is vital. It helps keep valuable digital assets safe.
This method is essential for effective data security today. It helps prevent sensitive info from falling into the wrong hands. This way, organisations can protect their intellectual property and stay ahead in the market.
Content protection is a major concern for companies. Information rights management helps control who can see or share sensitive documents. This boosts digital security and keeps companies in line with laws, reducing the risk of data breaches.
So, information rights management is a must for any business wanting to keep its data safe. It’s a powerful tool for protecting sensitive information and ensuring a secure digital space.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What are Information Rights Management Protected Content
Information Rights Management (IRM) systems are key for keeping sensitive data safe. They help businesses protect their content from start to finish.
IRM-protected content refers to digital information that has been secured using IRM technologies to control how it can be accessed, shared, and used. This protection is applied to various types of content, including documents, emails, spreadsheets, presentations, and multimedia files.
The primary goal of IRM is to ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and is only accessible to authorised users.
Core Components of IRM Systems
IRM systems have several important parts that work together:
- Policy Servers: These define and enforce access rules based on company policies.
- Encryption Mechanisms: They make files unreadable without the right access.
- Authentication Protocols: These check who is accessing the content.
Key Protection Features
IRM has strong features to control how content is used and shared:
- Access Control: It decides who can see or change documents.
- Usage Restrictions: It stops actions like copying, printing, or forwarding.
- Content Expiration: It sets a time limit after which content is no longer accessible.
Common Use Cases for IRM-Protected Content
- Corporate Documents: Protecting sensitive corporate documents, such as financial reports, contracts, and strategic plans, from unauthorised access and sharing.
- Legal and Compliance: Ensuring that legal documents and compliance-related information are only accessible to authorised personnel, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Healthcare Records: Safeguarding patient records and sensitive health information to comply with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
- Intellectual Property: Protecting proprietary information, trade secrets, and research data from being accessed or copied by unauthorised individuals.
Key Features of IRM-Protected Content
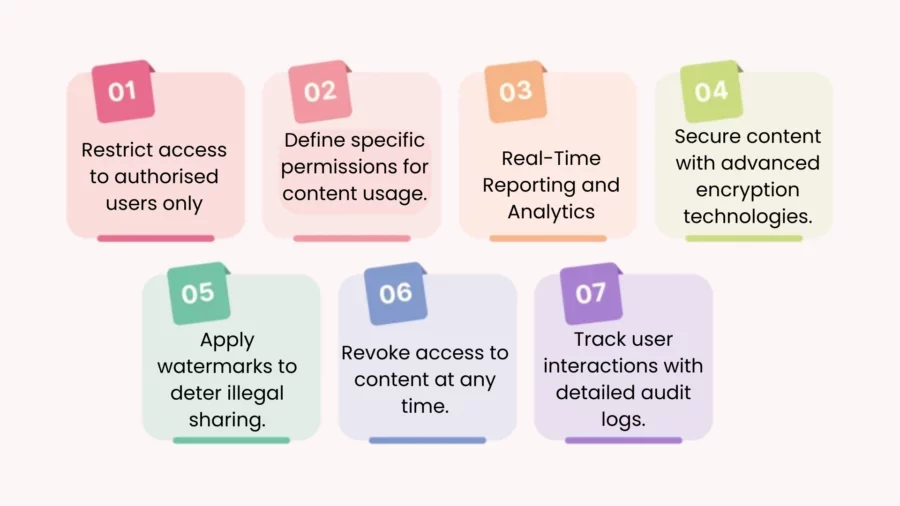
Access Control: IRM allows content owners to define who can access the information and what actions they can perform. This includes permissions such as view, edit, print, or forward. Access can be restricted based on user roles, groups, or specific individuals.
Persistent Protection: Unlike traditional security measures that may only protect content while it is stored or transmitted, IRM provides persistent protection. This means that the content remains protected even when it is shared outside the organisation or saved on local devices.
Encryption: IRM typically employs encryption to secure the content. This ensures that even if unauthorised users gain access to the file, they cannot read or use it without the appropriate decryption keys.
Usage Tracking and Auditing: IRM solutions often include features that allow organisations to track how their content is being used. This can include monitoring who accessed the content, what actions they took, and when they accessed it. This auditing capability is essential for compliance and security purposes.
Revocation of Access: One of the significant advantages of IRM is the ability to revoke access to content even after it has been shared. If a user’s access needs to be removed, the content owner can do so, ensuring that the information is no longer accessible to that user.
Policy Enforcement: Organisations can enforce specific policies regarding how content is handled. For example, they can set rules that prevent users from printing or forwarding sensitive documents, thereby reducing the risk of data leaks.
Integration with Existing Systems: Many IRM solutions can integrate with existing document management systems, email clients, and collaboration tools, making it easier to apply protection to content without disrupting workflows.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Digital Rights vs Information Rights Management
DRM and IRM both protect digital content, but they have different goals. DRM mainly controls access to media like music and videos. It helps creators keep their work safe. IRM, on the other hand, focuses on protecting internal documents and data. It gives companies the tools to manage and safeguard their own information.
| Feature | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | Determines who can view or edit content | Read, Change, Full Control permissions |
| Usage Restrictions | Limits what users can do with the content | No copying, printing, or forwarding |
| Content Expiration | Sets a timeframe for content accessibility | Documents expire after a set date |
| Encryption | Secures content by encoding it | Protected Word and Excel files |
| Authentication | Verifies user identities | Integration with Active Directory |
The Critical Role of Content Protection in Modern Business
In digital world, content protection is key to keeping sensitive info safe. Companies face many threats like data breaches and digital piracy. These can harm intellectual property and damage a company’s reputation and finances.
A Yubico report from 2019 shows that many people share passwords, making them vulnerable. Using online content protection tools helps businesses control who sees their content. It lets you set rules for when and where content can be accessed.
Good IRM solutions protect intellectual property and keep businesses ahead. They also help meet legal standards. By tracking who views content, companies can stop unauthorised access and leaks.
Groups like non-profits can also use DRM to stop money loss. It ensures only the right people see premium content. DRM also fights digital piracy by managing how content is shared.
Without strong content protection, companies face big risks. They must invest in good IRM to keep their data safe and their intellectual property secure.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Who Can Use IRM for Content Protection?
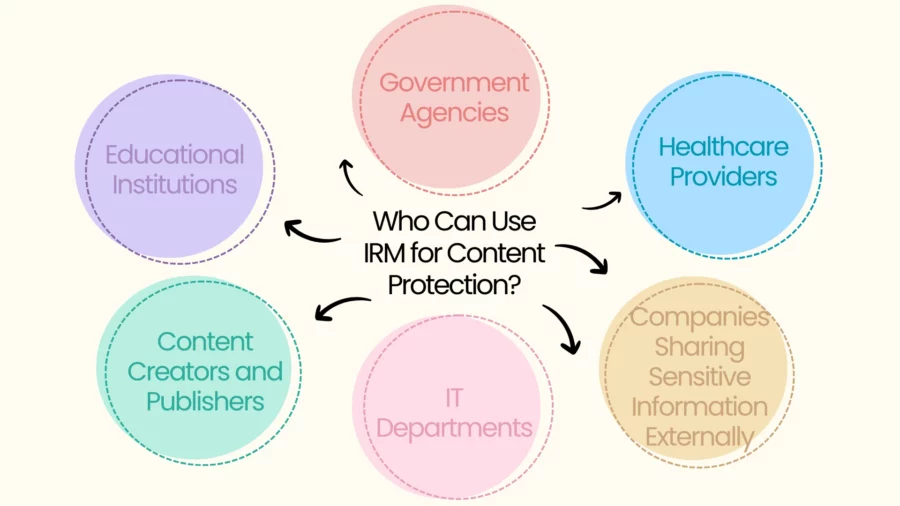
Virtually anyone handling sensitive information can use IRM for content protection. While large organisations with dedicated IT departments are common users, IRM’s accessibility is broadening thanks to cloud-based services and integration with popular software. Here’s a breakdown:
Large Enterprises: These organisations often have robust IT infrastructure and dedicated security teams to implement and manage complex IRM solutions across the enterprise. They typically utilise server-based or cloud-based IRM systems for comprehensive data protection.
Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs): SMBs can benefit significantly from IRM, even without extensive IT resources. Cloud-based IRM services offer a cost-effective and easy-to-deploy solution for protecting sensitive data. Integration with commonly used platforms like Microsoft 365 makes implementation simpler.
Individuals: Individuals can utilise IRM features integrated into cloud-based email services (like Gmail’s confidential mode) or file-sharing platforms. They can also subscribe to standalone IRM services for protecting personal sensitive documents.
Specific Departments/Teams: Within organisations, specific departments or teams dealing with highly sensitive information, like legal, HR, or R&D, can implement IRM even if it’s not deployed enterprise-wide.
Anyone with access to IRM-enabled platforms: If an organisation uses a platform with integrated IRM capabilities (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace), authorised users within that organisation can utilise the IRM features to protect their documents and emails.
Essentially, anyone who needs to control access and usage of sensitive information can leverage IRM, regardless of technical expertise or organisation size.
The availability of cloud-based services and integration with widely used software has democratised access to IRM, making it a practical solution for a broader range of users.
How IRM Works?
Policy Definition: Administrators establish usage policies tailored to specific documents or data types. These policies act as blueprints, outlining permissible actions and restrictions for the protected content.
They define who can access the information, what they can do with it (e.g., read, edit, print), and for how long. This granular control forms the foundation of IRM’s protective framework.
Content Encryption: The sensitive information is encrypted using a unique cryptographic key, rendering it unreadable without proper authorisation. This encryption safeguards the data even if it’s intercepted or accessed without permission.
The encryption key is linked to the defined usage policies, ensuring only authorised users can decrypt and access the content.
Rights Management Application: This software acts as the enforcer of the defined policies.
It interacts with a central rights management server to authenticate users and validate their access permissions against the document’s policies. This application mediates all interactions with the protected content, ensuring adherence to the established rules.
User Access: When a user attempts to open IRM-protected content, the rights management application springs into action.
It verifies the user’s identity and consults the rights management server to confirm their access rights according to the applicable policies for that specific document.
Policy Enforcement: Based on the policy evaluation, the application either grants or denies access. If granted, the application decrypts the content, enabling the user to view it.
Simultaneously, the application actively enforces usage restrictions, preventing actions prohibited by the policy, like printing or copying.
Implementing IRM Solutions Across Your Organisation
Starting with IRM implementation means first checking your current security setup. Look at what you already have to see where IRM can help protect your data better.
Choosing the right IRM solution is key; for example, using IRM with Microsoft 365 needs Windows Rights Management Services (RMS) Client Service Pack 1 (SP1).
The steps to implement IRM are important:
- Make sure computers can use IRM features.
- Download and apply the right permissions for your documents and data.
- Use strong user authentication to keep sensitive info safe from unauthorised access.
Getting everyone on board with IRM is easier with good training and change management. It’s vital for all departments to grasp IRM’s benefits and how it works. This way, IRM fits well with your security goals and meets compliance needs, making your environment safer and more secure.
In SharePoint Online, IRM can protect documents at the list and library levels. This limits actions like copying or printing, making documents safer.
- Boosts data security across all departments.
- Helps meet regulatory standards.
- Lessens the chance of unauthorised data access.
With careful planning and execution of IRM implementation, organisations can greatly improve their security. This ensures that sensitive information stays safe from unauthorised access and breaches.
Best Practices for Content Security Management
Effective content security management needs a strategic plan to protect valuable information. Strong policies keep sensitive data safe while letting authorised users access it.
Policy Development Guidelines
Creating detailed policies is key for content security. Set up clear access levels and editing permissions that fit your organisation’s needs. For instance, a “Company Confidential” policy limits document access to internal users, boosting security.
User Authentication Protocols
Strong user authentication is vital to confirm identities and block unauthorised access. Use multi-factor authentication and Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions for secure access. These steps make sure only real users can get to sensitive content.
Monitoring and Reporting Strategies
Keeping an eye on security is important to catch and handle threats fast. Use security monitoring tools to watch content access and use. Regular reports show user behavior and spot any odd activities.
| Best Practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Policy Development | Establish clear guidelines for access and permissions. | Ensures data is protected and accessible only to authorised personnel. |
| User Authentication | Implement multi-factor authentication and SSO. | Enhances security by verifying user identities effectively. |
| Security Monitoring | Use tools to track and report on content access. | Enables early detection of unauthorised activities and threats. |
| Regular Policy Reviews | Update security policies to address evolving threats. | Maintains the effectiveness of security measures over time. |
| Employee Training | Educate staff on security best practices. | Fosters a security-conscious culture within the organisation. |
Measuring the ROI of Information Rights Management
Comprehending the IRM ROI is key to seeing the value of your security investment.
Good rights management systems control who can see your documents. This stops unauthorised access and brings big data protection benefits.
There are many ways to measure IRM ROI:
- Reduced Data Breaches: Fewer breaches mean less financial loss.
- Compliance Improvement: Staying in line with rules saves you from big fines.
- Operational Efficiency: Faster, smoother processes save time and money.
Doing a cost-benefit analysis means looking at setup costs, upkeep, and savings from avoiding security issues. Both real savings and the good your brand gets from being secure add up to your ROI.
Here’s a table to help you see the ROI factors:
| ROI Factor | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Cost of starting IRM solutions | High |
| Maintenance Costs | Costs for keeping the system running | Moderate |
| Cost Savings | Money saved from avoiding breaches and fines | Significant |
| Efficiency Gains | Time saved with automated tasks | High |
| Reputation Enhancement | More trust from clients and partners | Intangible |
By looking at these points, companies can figure out the real value of their security. This helps them make smart choices about protecting their data.
Common Challenges and Solutions in IRM Implementation
Setting up Information Rights Management (IRM) can be tough. Companies face many hurdles to protect their content well.
Technical Integration Issues
Making IRM work with current systems is hard. It’s key to make sure it fits with what you already have. Choosing the right tech is also important.
For example, linking to licensing servers and setting up software can mess up your work flow if not done right.
User Adoption Hurdles
Getting people to use IRM can be a big challenge. Many workers don’t want to change how they work, fearing it will be harder. Giving them good training and clear info can help them accept it better.
Compliance Considerations
It’s vital to follow rules when using IRM. Companies need to make sure their IRM plans match up with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and FISMA. Good IRM use can lower risks and keep you in line with the law.
| Approach | Compliance Violation Rate |
|---|---|
| Integrated Risk Management | 40% |
| Rule Enforcer Approach | 71% |
Limitations of IRM
Despite its advantages, IRM also has some limitations that organisations should consider:
User Experience: IRM can introduce friction for users, requiring extra software installations, logins, or application-specific configurations to access protected files. This added complexity can hinder productivity and frustrate users accustomed to seamless access.
Compatibility Issues: IRM solutions might not function flawlessly with all software or devices. Older applications, specialised operating systems, or uncommon file formats could present compatibility challenges, limiting accessibility for some users and potentially disrupting workflows.
Complexity: Deploying and administering an IRM system can be intricate, demanding careful planning, configuration, and ongoing maintenance.
Integrating IRM with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging, requiring specialised expertise and potentially impacting other systems.
Cost: Implementing and maintaining IRM solutions, including software licenses, server infrastructure, and administrative overhead, can be expensive, especially for large organisations with vast amounts of data requiring protection.
Dependence on IRM Provider: Organisations opting for cloud-based IRM solutions relinquish some control over security and availability to the third-party provider.
Service outages or security breaches at the provider’s end could impact access to protected content and compromise data security.
Potential for Circumvention: While IRM significantly strengthens security, determined attackers can potentially bypass restrictions.
Exploiting vulnerabilities in user devices, obtaining compromised credentials, or employing sophisticated techniques like screen recording could allow unauthorised access to protected information.
Future Trends in Content Protection Technology
The world of content protection is changing fast, thanks to new tech. New trends are helping businesses keep their digital stuff safe.
AI is making a big difference in security. It helps predict threats and catch odd behavior. This makes security better and stronger.
Blockchain is also changing things. It makes sure content access logs are safe and can’t be changed. This builds trust and keeps things secure.
- Data-centric security models protect data at its core, no matter where it is.
- Improving user experience makes IRM easier and less annoying for users.
- Active Rights Management lets access rights change quickly, giving more control over content.
The Digital Rights Management (DRM) market is expected to grow a lot. It’s going to hit USD 7.9 billion by 2027, with a 13.0% CAGR. This growth comes from more streaming services and the need to protect digital content.
Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure
It’s key to add Information Rights Management (IRM) smoothly to your current security setup. This ensures all your sensitive info stays safe on every device and platform.
Cloud Security Integration
IRM tools like Azure Rights Management Service (RMS) are great for cloud use. They work well on Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android. Setting up Azure RMS is easy, just a few clicks or simple PowerShell commands.
RMS also keeps an eye on how your documents are used. It tracks who’s accessing them and if anyone’s trying to get in without permission. This keeps your cloud storage safe.
Enterprise Software Compatibility
IRM systems need to work well with your company’s software. They fit right in with Microsoft 365 apps, Oracle Information Rights Management, and other CRM and document management tools. This helps keep your data safe across different systems.
Mobile Device Management
With more people working from home, keeping mobile devices secure is a big deal. IRM solutions protect your data on phones and tablets. They work with Mobile Device Management (MDM) to enforce security rules and keep an eye on device health.
| IRM Solution | Compliance Certifications |
|---|---|
| Azure Rights Management | ISO/IEC 27001:2013SOC 2 SSAE 16/ISAE 3402HIPAA BAAEU Model ClauseFedRAMPPCI DSS Level 1 |
| Oracle Information Rights Management | ISO/IEC 27001:2013SOC 2HIPAAFedRAMP |
What’s Next?
Information Rights Management (IRM) is a crucial component of modern document security practices.
It empowers organisations to control access content to restricted contents such as critical files across various file types.
By leveraging an RMS server, IRM enables granular control over authoring permissions, allowing administrators to define precise level of access for different users and groups. This prevents unwanted access and the potential spread of malicious programs through compromised IRM-protected files.
Furthermore, IRM solutions are comprehensive security solution beyond basic access control.
Bytescare prevents copyright violation through its innovative solution, which is designed to protect digital content using advanced technologies.
By knowing the core functionality of content protection and respecting the rights of creators, you can ethically use online resources.
Key requirements for successful IRM implementation include identifying and classifying sensitive data, establishing clear usage policies, and regularly reviewing and updating rights-managed content settings.
Additional file protection measures, such as encryption and watermarking, can further enhance the security of target files and deter unauthorised distribution.
By adopting a robust IRM strategy, organisations can effectively safeguard their valuable intellectual property while ensuring the appropriate use of sensitive information.
Book a demo to explore how Bytescare can safeguard your digital content.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is information rights management (IRM) and how does it protect content?
Information Rights Management (IRM) is a technology that helps organisations protect sensitive digital content by controlling access and usage rights. It encrypts files and applies policies that dictate how users can interact with the content, such as viewing, editing, or sharing. This ensures that only authorised individuals can access the information, thereby preventing unauthorised use or distribution.
What types of content can be protected using information rights management?
IRM can protect a variety of content types, including documents (e.g., PDFs, Word files), spreadsheets, presentations, images, and multimedia files. Essentially, any digital file that requires controlled access and usage can be managed through IRM.
How do I implement information rights management for my documents and media?
To implement IRM, organisations typically need to deploy an IRM solution or software that integrates with existing systems. This involves setting up a Rights Management Server (RMS), defining access policies, and applying IRM protection to the desired files. Training users on how to use the system is also crucial for effective implementation.
How can I manage user access and permissions for IRM-protected content?
User access and permissions for IRM-protected content can be managed through the IRM software’s administrative interface. Administrators can assign specific rights to users or groups, such as view, edit, or print permissions. This allows for granular control over who can access the content and how they can interact with it.
How can organisations implement information rights management to safeguard sensitive information?
Organisations can implement IRM by first assessing their sensitive information and identifying key areas that require protection. They should then choose an appropriate IRM solution, configure it to meet their specific needs, and train employees on best practices for using IRM. Regular audits and updates to access policies are also essential to maintain security.
Can users share information rights management protected content, and if so, how is this managed?
Yes, users can share IRM-protected content, but sharing is controlled by the permissions set by the content owner. When sharing, the owner can specify which rights the recipient has, such as whether they can view, edit, or forward the content. This ensures that even when shared, the content remains protected according to the established policies.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

