Key Takeaways:
- Fraudulent websites can severely damage a brand’s image, customer base, and intellectual property.
- Report domain fraud to the appropriate authorities, and registrars can help take down these malicious sites quickly.
- Continuously monitoring your online presence and using domain monitoring tools can aid in the early detection of fraudulent activities.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Domain Fraud and Its Impact on Businesses
Domain fraud includes fake websites that trick users into harmful actions. These scams can harm businesses in many ways. They can lead to phishing, malware, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Types of Domain Fraud
- The sale of fake domains is a common type of domain fraud, where scammers pressurise buyers with a sense of urgency and claims of multiple interested parties.
- Identity theft is another frequent method used in domain fraud, where criminals impersonate legitimate entities to steal personal or financial information.
- Phishing and deceptive websites are alarmingly common tactics in domain fraud, where scammers create copycat sites to lure unsuspecting victims.
Common Business Threats
Domain fraud can lead to serious threats for businesses. These include phishing attacks, impersonation and intellectual property theft. Scammers often use cryptocurrencies to hide their tracks and make it hard for victims to get their money back.
- Reputation Damage: Domain fraud can severely damage a company’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in a brand if they fall victim to phishing scams or encounter spoofed websites.
- Data Breaches: Successful phishing attacks can lead to data breaches, exposing sensitive customer information and potentially resulting in legal consequences and regulatory fines.
- Loss of Customer Trust: If customers are misled by fraudulent domains, they may hesitate to engage with the legitimate business, leading to a decline in customer loyalty and retention.
- Operational Disruption: Domain hijacking can disrupt business operations, as companies may lose access to their websites and email services, impacting communication and sales.
- Legal Issues: Businesses may face legal challenges if their brand is misused in fraudulent activities, leading to costly litigation and settlements.
Financial Impact and Brand Damage
The financial losses from domain fraud can be huge, with billions lost worldwide. In 2017, a fake Financial Times site made $1.3 million a month. This not only costs money but also harms a company’s reputation. Fake sites can steal customers and damage a brand’s value.
| Types | Impact |
|---|---|
| The sale of fake domains is a common type of domain fraud. | Scammers often pressure buyers with urgency and claim multiple interested parties. |
| Identity theft is another frequent method used in domain fraud. | Criminals impersonate legitimate entities to steal personal or financial information. |
| Phishing and deceptive websites are alarmingly common tactics in domain fraud. | Scammers create copycat sites to lure unsuspecting victims. |
| Scammers often insist on payment methods like cryptocurrencies. | To evade detection and make it difficult for victims to recover their losses. |
Key Indicators of Fraudulent Websites
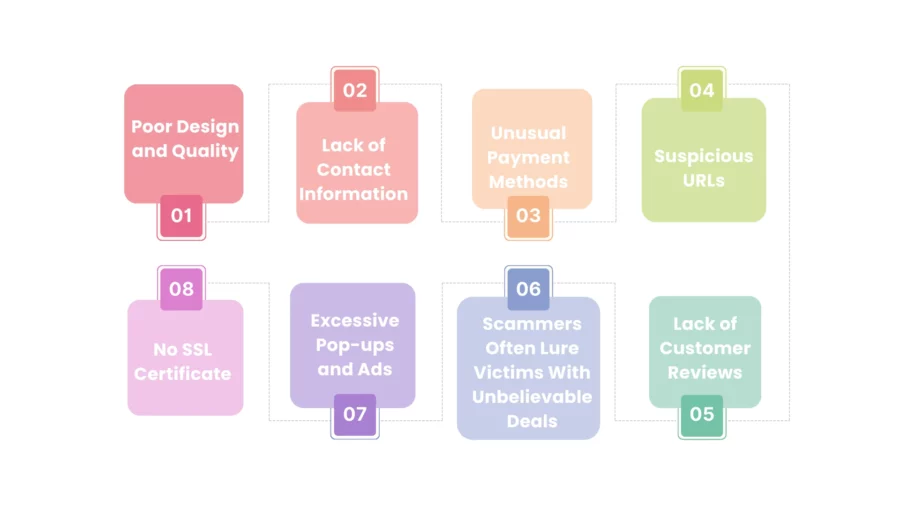
Spotting suspicious domain names, checking for website security, and watching out for fake reviews are key steps. These actions help businesses avoid the harm caused by domain fraud.
Scammers often use domain names that look similar to real businesses but have tiny mistakes. These suspicious domain names can trick people into falling for scams or phishing.
It’s also important to look for website security indicators. Good websites use SSL/TLS certificates for a secure connection. But, fake sites can also have these, so it’s not a sure sign of safety.
Fake reviews are another red flag. Scammers use fake reviews to make their sites seem trustworthy. If you see many similar positive reviews, it might be a scam.
| Common Indicators of Fraudulent Websites | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Suspicious domain names | Domain names that are similar to legitimate businesses, with small misspellings or variations |
| Lack of website security indicators | Absence of SSL/TLS certificates or other security measures |
| Fake reviews | An abundance of suspiciously similar positive reviews |
| Poor website design | Low-quality images, graphics, and logos, as well as spelling, grammar, or formatting issues |
| Unrealistic offers | Deals or promotions that seem too good to be true |
By being alert and knowing these signs, businesses can shield themselves from domain fraud. This helps avoid the risks it brings.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Essential Steps to Identify Domain Ownership
Stopping domain fraud begins with knowing who owns a suspicious site. Using WHOIS lookup services is key. These databases give info on the domain’s registrar, owner, and technical details. This helps spot fraud.
Using WHOIS Lookup Services
WHOIS lookup services give lots of info on a domain. They show who owns it, their contact info, and when it was registered. By checking this info, you can find oddities that might mean fraud.
Analysing Domain Registration Details
Looking closely at domain registration details can give you clues. Watch for odd email addresses, phone numbers, or addresses. If the domain’s ownership or registrar changes suddenly, it could be fraud.
Verifying Website Hosting Information
Checking the website’s hosting info is also important. By looking at the domain’s name servers, you can find the host. Then, compare this with WHOIS data. If they don’t match, it might be fraud.
Look for Brand Presence
- Social Media: Search for the domain name on social media platforms. Many businesses maintain a presence on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, which can provide additional context about the domain owner.
- Business Listings: Check business directories such as Google My Business, Yelp, or industry-specific directories to find more information about the entity associated with the domain.
Check for SSL Certificates
If the website uses HTTPS, you can view the SSL certificate details by clicking on the padlock icon in the address bar of your browser. This may provide information about the organisation that owns the domain.
Use Domain Name Appraisal Services
Some online services offer domain name appraisal tools that can provide insights into the ownership and value of a domain. While these may not always provide direct ownership information, they can give context about the domain’s history and market value.
It’s key to know the difference between domain registrars and hosting providers. Registrars handle domain ownership and details. Hosting providers manage the site’s online presence. Both need to be checked to fight domain fraud well.
How to Report Domain Fraud to Authorities
Reporting domain fraud is key to fighting it. To report domain fraud, you can follow these steps:
Identify the Registrar: Use a WHOIS lookup service to find the domain registrar for the fraudulent site.
Contact the Registrar: Reach out to the registrar directly, providing them with details about the fraudulent activity. Most registrars have a specific process for reporting abuse or fraud. Look for a “report abuse” link on their website.
Gather Evidence: Collect relevant evidence to support your claim, including:
- Screenshots of the
- fraudulent website
- URLs of the site
- Descriptions of the fraudulent activity
- Any contact information associated with the site
Report to Hosting Provider: If the fraudulent content is hosted elsewhere, identify the hosting provider using the WHOIS information and report the site to them as well.
Notify Search Engines: Report the fraudulent website to search engines like Google or Bing. For Google, you can use the Google Safe Browsing page to report phishing sites.
Contact Law Enforcement: If the fraud is severe, consider reporting it to law enforcement agencies. In the U.S., you can report to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Educate Others: Inform your customers or community about the fraudulent site to prevent them from falling victim to scams.
Consider Legal Action: If necessary, consult with a legal professional about sending a cease and desist letter to the fraudster.
By following these steps, you can effectively report domain fraud and help protect yourself and others from potential scams.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Legal Actions and Cease and Desist Letters
Dealing with domain fraud might mean taking legal steps. This includes sending cease and desist letters to those behind fake websites. These letters ask the person to stop their illegal actions. They should be sent to the scammer, site admin, or domain registrar.
If needed, businesses might have to go further to protect their brand and ideas. A good cease and desist letter has important details. It should include contact info, a clear explanation of the problem, a deadline for a response, and what could happen if they don’t stop.
Using online or legal services can make these requests more effective. It makes the process smoother and boosts success chances.
If hosting providers ignore your requests, you might need a lawyer. In the U.S., DMCA notices are often used to fight copyright issues and take down websites. But, dealing with sites from other countries can be more complicated.
“Securing key domain names including a company’s name and its variations can help reduce the likelihood of domain name fraud or cybersquatting.”
Legal actions and cease and desist letters are key in fighting domain fraud. By acting quickly to protect their brand and ideas, businesses can avoid big financial and reputation losses.
Preventive Measures to Protect Your Domain
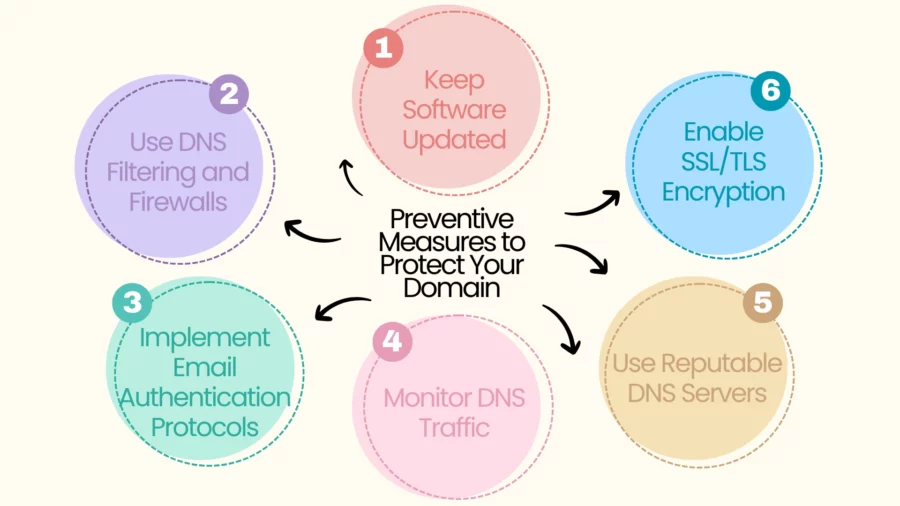
Keeping your domain safe is key to avoid domain fraud and keep your online presence strong. By being proactive, you can shield your brand and assets from cyber threats.
To protect your domain from fraud or spoofing, consider implementing the following preventive measures:
Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your website software and security protocols to close vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Use DNS Filtering and Firewalls: Implement DNS filtering services and configure firewall rules to block access to known malicious or spoofed domains. This helps in controlling access to specific domains through whitelisting and blacklisting.
Implement Email Authentication Protocols:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Specify which IP addresses are authorised to send emails on behalf of your domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Digitally sign outgoing emails to verify their authenticity.
- DMARC: Set policies to instruct email servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF or DKIM checks.
Monitor DNS Traffic: Use network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems to detect unusual or unauthorised DNS activities. Regularly check DNS logs for signs of suspicious behavior.
Educate Users: Conduct training sessions to raise awareness about phishing and spoofing tactics. Teach users how to recognise suspicious emails and websites.
Use Reputable DNS Servers: Configure your systems to use DNS servers from trusted and reputable sources to minimise the risk of DNS manipulation.
Enable SSL/TLS Encryption: Secure communication channels by enabling SSL/TLS encryption on your website to protect sensitive data during transmission.
Regularly Review Domain Records: Frequently check and update your domain records to ensure they are accurate and secure.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification steps for accessing sensitive accounts.
By adopting these measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of domain spoofing and fraud, thereby enhancing your overall cybersecurity posture.
How to Prevent Your Customers From Falling Victim to Fraudulent Websites?
To prevent customers from falling victim to fraudulent websites, consider implementing the following strategies:
Educate Customers: Provide resources and information on how to identify legitimate websites. Share tips on recognising red flags, such as poor website design, misspellings, and suspicious URLs.
Secure your website: Ensure that your website uses HTTPS to encrypt data and build trust with customers. Display security badges and certifications prominently.
Monitor for Phishing Attempts: Regularly check for phishing emails or messages that may impersonate your business. Inform customers about these attempts and how to recognise them.
Encourage Strong Passwords: Advise customers to use strong, unique passwords for their accounts and to change them regularly. Consider implementing two-factor authentication for added security.
Provide Clear Contact Information: Make it easy for customers to contact you with questions or concerns. Display your customer service phone number and email address prominently on your website.
Use Trusted Payment Processors: Partner with reputable payment processors to handle transactions securely. This can help protect customer financial information.
Regularly Update Software: Keep your website and any associated software up to date to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by scammers.
Monitor Online Presence: Keep an eye on social media and online platforms for any impersonation or fraudulent accounts that may be targeting your customers.
Report Fraudulent Sites: Encourage customers to report any suspicious websites or emails that claim to be associated with your business. Provide them with a clear process for reporting.
Create Awareness Campaigns: Run campaigns to raise awareness about online scams, especially during peak shopping seasons. Use newsletters, social media, and your website to share information.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of your customers falling victim to fraudulent websites and enhance their overall online shopping experience.
What’s Next?
Domain fraud is a growing threat that poses massive issues for businesses and individuals alike.
Fraudsters exploit vulnerabilities to create abusive websites that host malicious content, mislead users, or damage brand reputation. These threats encompass various types of abuse, including phishing, counterfeit sites, and spam, all designed to deceive users and harm legitimate domain name owners.
Recognising signs of fraud websites, such as suspicious URLs, poor design, or misleading claims, is vital for early detection. Employing a comprehensive Domain Monitoring solution helps businesses track and manage their domains, identifying threats before they escalate.
When fraud is detected, a Domain Takedown Service provides the swift action needed to remove harmful online content, safeguarding the business and its customers.
Protecting your digital presence requires vigilance and robust tools to combat these evolving threats.
Safeguard your digital identity with Bytescare Brand Protection servicce, ensuring comprehensive protection against cyber threats. Ready to secure your digital environment? Contact us today and experience Bytescare’s solutions firsthand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What steps should I take to report domain fraud?
To report domain fraud, gather all relevant details such as URLs, screenshots of fraudulent activity, and email headers if phishing emails are involved. Submit these details to the hosting provider, domain registrar, or a cybersecurity organisation for further investigation and takedown.
How can I identify if a domain is fraudulent?
Fraudulent domains often have slight misspellings of legitimate websites, lack SSL certificates (no HTTPS), feature poor design, or promote unrealistic offers. If the content or URL feels suspicious, avoid engaging and verify its authenticity.
What information is needed when reporting domain fraud?
Provide the suspicious domain name, examples of fraudulent activity (e.g., phishing emails or fake pages), timestamps, and any supporting evidence such as communications or transaction details when reporting domain fraud.
Are there specific organisations or authorities to contact for domain fraud cases?
Yes, you can report domain fraud to ICANN, national cybersecurity agencies, or online fraud prevention organisations. Many domain registrars also have dedicated abuse teams to handle such cases.
What are the potential consequences for individuals involved in domain fraud?
Individuals engaging in domain fraud can face legal action, hefty fines, loss of internet privileges, and even imprisonment, depending on the jurisdiction.
How to stop fraudulent websites at scale?
Deploy domain monitoring solutions and partner with domain takedown services to identify and remove abusive websites quickly. Use automated tools to flag and address fraudulent domains across your portfolio.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

