Key Takeaways:
- The DMCA provides essential protection for copyright owners, ensuring their exclusive rights are upheld in the digital landscape.
- Cooperation between content creators and online platforms is vital for effective copyright enforcement and compliance with copyright laws.
- The DMCA addresses both copyright infringement claims and the circumvention of copyright protections, balancing the interests of copyright holders and users.
The DMCA is one of the most important laws in America. The goal of this law is to revise and reorganise the copyright laws of the US to better deal with the age of the internet, content management systems, and the copyrighting and licensing of works on the web.
In the last twenty years the DMCA has greatly shaped the enforcement of copyright online for the benefit of copyright proprietors, Internet service providers, and the general public.
This article offers a comprehensive analysis of DMCA copyright protection, and its key provisions.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA)?
Definition and purpose of the DMCA
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), which came into effect on the 28th of October, 1998, is an important modification in United States of America copyright law.
This DMCA was created to solve copyright issues because of emerging new technologies and the Internet.
The DMCA was meant to comply with World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) treaties of 1996 by making them part of American law.
Key objectives of the DMCA include:
- Criminalising the production and distribution of technology that circumvents copyright protection measures
- Establishing heightened penalties for online copyright infringement
- Providing a legal framework for digital rights management (DRM)
- Encouraging the growth of online services through “safe harbor” provisions
Implementation of WIPO treaties
The implementation of the WIPO Copyright Treaty of 1996 through DMCA marked an important milestone in updating America’s copyright laws. This implementation:
- Dealt with issues brought about by distributing online content.
- Introduced a framework for digital rights management (DRM).
- Provided for punitive measures against the bypassing of technological protective measures.
- Provided for penalties against the sale of the devices which aid in circumvention.
The repercussions are visible for DMCA compliance with the WIPO treaties when considering copyright protection and enforcement in the cyberspace context. It provided a middle ground on protecting intellectual property rights and online content distribution.
What is DMCA Copyright Protection?
DMCA copyright protection is the safeguard provided by the Digital Millennium Copyright Act for copyrighted works and provides a legal framework to restrict unauthorised exploitation of the material.
It gives the copyright owner an opportunity to defend their rights against illegal usage, sharing, or copying.
Key Components of DMCA Protection
- Anti-circumvention provisions
- Safe harbor for online service providers
- Takedown notice procedures
- Criminal penalties for copyright infringement
Example of DMCA Copyright Protection in Action
Unauthorised Image Use on a Website
Imagine you are a photographer, and you find that a blog has used your original photo without permission.
You can file a DMCA Takedown Notice to the blog owner or the hosting provider, requesting them to remove the image. If they do not comply, legal actions can be taken.
Pirated Movies on a Streaming Platform
A movie studio discovers that its newly released film is illegally uploaded on a video streaming website. The studio can submit a DMCA takedown request, and the platform is legally required to remove the pirated content to avoid penalties.
Stolen Blog Content
You write an SEO blog article, and another website copies it word-for-word without giving you credit. You can file a DMCA complaint with Google to remove the copied page from search results and notify the site’s hosting provider to take down the infringing content.
How DMCA Protection Helps?
- Protects creators from content theft
- Ensures fair use of digital content
- Allows businesses to maintain their brand reputation
- Gives website owners a way to handle copyright claims legally
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is Protected by DMCA?
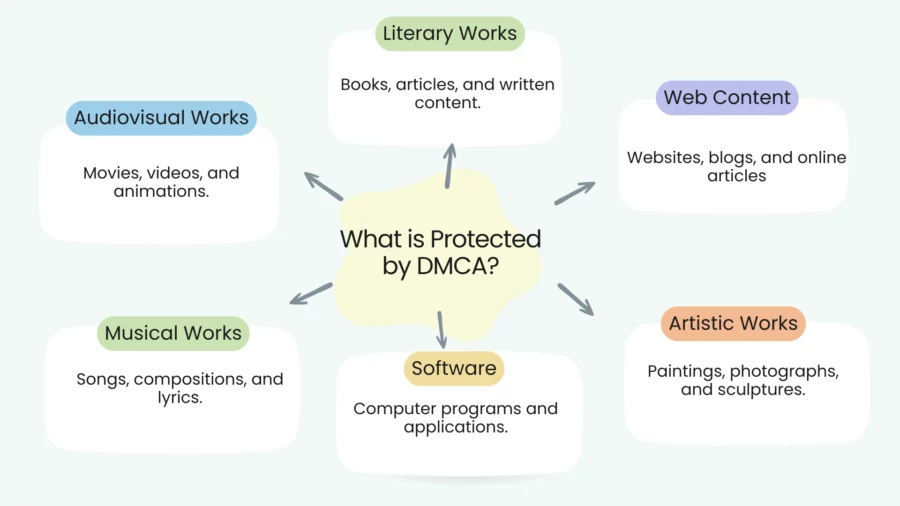
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act, also known as DMCA, deals with a variety of creative works that qualify for copyright protection. Outlined below are the major classes of works that the DMCA safeguards:
- Literary Works: This includes books, articles, poems, and other written content.
- Musical Works: This category includes compositions, songs, and the lyrics.
- Dramatic Works: These include scripts, plays, and other works performed.
- Artistic Works: Visual art such as paintings, drawings, sculptures, photographs, and graphic designs are protected.
- Audiovisual Works: These include Television shows, movies, videos, and other multimedia content.
- Sound Recordings: This includes music recordings that contain sounds other than music.
- Software and Computer Programs: Computer code, applications, and software are protected as literary works.
- Databases and Compilations: Original databases and compilations of data that involve creativity in their selection or arrangement can be protected.
- Web Content: Websites, blogs, and other online content, including text, images, and videos, are also protected.
- Digital Rights Management (DRM) Technologies: The DMCA protects the technological measures that control access to copyrighted works, making it illegal to circumvent these protections.
The DMCA does not protect the ideas, facts, and concepts per se but the expression of the ideas in a particular form. Further, DMCA mostly applies to works that are fixed in a medium of expression, which means they have to be captured or documented in one way or another.
It’s important to note that while the DMCA provides a framework for protecting these works in the digital environment, the underlying copyright laws still apply, and the DMCA is not the sole source of copyright protection.
DMCA Protection – Limitations and Shortcomings
Even though the DMCA was designed to protect digital content, it falls short in ferreting out infringements at times.
Here are some reasons why DMCA protection does not work effectively:
Jurisdiction Challenges: As the DMCA is a United States law, it primarily focuses on American citizens. To add on, infringers have the opportunity to ignore the DMCA because other countries do not practice the same or any copyright law, thus making the perpetrators’ task easier within the previously mentioned borders. Enforcing laws can get problematic.
Bypass of Protected Zones: Many unauthorised resellers and pirates use diverse techniques to go around DMCA protection. For example, they can lift restrictions and host infringing material under a cloak of anonymity.
Irregular Compliance: The lack of willingness to comply by IP hosts renders DMCA takedown notices useless. This puts a challenge to copyright owners who want to safeguard their work because a lot of websites and platforms do not abide by these orders.
Private Network Piracy: Such perpetrators constantly circulate within private networks. This makes them difficult to spot as well as control. So great is the restriction on circulating DMCA takedown requests that pirated material in closed circuits goes unchecked.
Re-uploading Challenges: Even if infringing content is successfully removed through a DMCA takedown, it can be quickly re-uploaded to other platforms, creating a frustrating cycle that resembles a never-ending game of whack-a-mole.
What DMCA Does Not Protect?
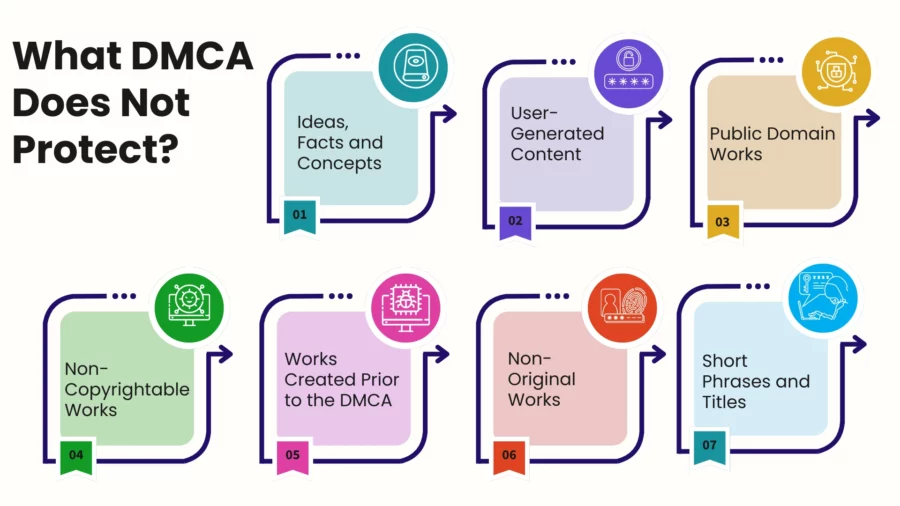
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) outlines provisions for copyright protection within the digital environment, yet there are several categories of works and situations that it overlooks.
Here are some specific areas that the DMCA is lacking in:
Ideas, Facts and Concepts: The DMCA only protects the expression of ideas and not the ideas themselves, which creates an allowance of misuse of facts and concepts. This means that while a certain work of literature or piece of art is protected, the motifs, ideas, facts, and concepts aimlessly is provided to others.
Public Domain Works: DMCA does not protect works that are in the public domain. This includes works whose copyright has expired or works that have never qualified to reception copyrighted protection.
Fair Use: The DMCA does not cover uses of copyrighted works that fall within the fair use doctrine, including certain educational, commentary, criticism, and changeable uses which require no authorisation from the copyright owner.
Non-Copyrightable Works: The types of works to which copyright protection is not granted, such as government works, ideas, procedures, methods, systems, and facts. These are not covered by DMCA.
User-Generated Content: The DMCA has a procedure for copyright infringement, yet it does little to protect content made by an individual or a group that infringes someone else’s copyright. Every individual is obligated to ensure that the content he or she creates does not violate copyrights.
Works Created Prior to the DMCA: Any works created before the construction of the law in 1998 are not subject to its protections. However, in all cases, the protection of existing laws on copyright still applies.
International Works: The DMCA was originated as a law of U.S. and has its primary geographical scope in the U.S. Content created and shared outside the United States is not under the DMCA protection, and its enforcement is difficult in other places.
Technological Measures: The DMCA does not protect against use of technologies that do not infringe the copyright. For instance, reverse engineering to allow two different software systems to interoperate may not be covered under the DMCA.
Moral Rights: The DMCA does not address moral rights, which include rights to protect the personality and reputation of the author within his work. Some countries provide these rights but it is neither recognised by the U.S. copyright law nor the DMCA.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
How the DMCA Protects Copyrighted Works?
Takedown Notices: There are several DMCA guidelines established for holders who own copyrighted content. They can issue takedown notices to the service providers hosting the infringing content.
The DMCA enables the service provider to take down or block the hosting of the materials without any form of legal fighting. This helps a copyright holder to take legal control over their work.
Criminalises Circumvention: Under DMCA, the legal creation, distribution, and use of technologies solely meant to block copy protection systems are illegal. This law helps in protecting a copyright holder’s work from being accessed or used unlicense.
It also helps in securing the functionality of digital rights management systems (DRM) where the work of a copyright holder is maintained dominantly.
Safe Harbor for ISPs: The DMCA provides a safe harbor clause which protects Internet Service Providers (ISPs) from that infringing copyright claim has been made by any of its users.
Since the ISPs systems are targeted towards protecting data and everything, their legal responsibility is greatly reduced.
Limits Liability for Service Providers: The DMCA eases the responsibility burden placed upon ISPs by protecting them from being liable for the forwarded infringement acts of their clients, as long as they attempt to control all compliant actions in accordance to takedown request and don’t actively know about the infringing activity.
What’s Next?
The DMCA copyright protection framework plays a critical role in safeguarding the rights of copyright owners in the digital age.
It establishes key elements that provide protection for content creators and content owners against copyright infringement.
By facilitating cooperation between copyright owners and online platforms, the DMCA aims to balance copyright enforcement with the principles of copyright protection. This includes addressing allegations of copyright infringement through a structured legal process, which can involve financial penalties for copyright infringers.
The DMCA also addresses the circumvention of copyright protections, ensuring that content providers maintain control over their original content. However, the alteration of copyright management practices and compliance with copyright laws remains essential for effective enforcement.
With Bytescare digital piracy monitoring service, your intellectual property stays secure, allowing you to focus on innovation and business growth.
Don’t let digital piracy undermine the value of your creations. Safeguard your digital assets with Bytescare and move forward confidently. Ready to protect your content? Book a demo with us today!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is the DMCA copyright protection law?
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) is a U.S. law that provides copyright protection for digital content. It establishes a framework for copyright holders to enforce their rights, including the ability to send takedown notices to online platforms hosting infringing material.
How do content creators enforce their rights under the DMCA?
Content creators can enforce their rights under the DMCA by submitting formal takedown notices to online service providers (OSPs) when they identify infringing content. These notices prompt OSPs to remove or disable access to the infringing material, helping protect the creators’ original works from unauthorised use.
What happens if online platforms ignore copyright notices?
If online platforms ignore copyright notices, they may lose their safe harbor protections under the DMCA, exposing them to potential liability for copyright infringement. Copyright holders can then pursue legal action against the infringing party or the service provider for failing to comply with the notice.
Can DMCA protect all types of digital content?
The DMCA primarily protects original works of authorship fixed in a tangible medium, including literary, musical, audiovisual, and software content. However, it does not cover ideas, facts, or works in the public domain. The law is designed to address the unique challenges of digital content.
What financial penalties exist for copyright infringers?
Copyright infringers may face lawsuits, monetary damages, and removal of content from platforms.
How does DMCA ensure balance between copyright protection and online access?
The DMCA aims to balance copyright protection and online access by providing safe harbor provisions for service providers, allowing them to avoid liability if they comply with takedown requests. This encourages cooperation between copyright holders and online platforms while allowing users to access content responsibly.
What are the key aspects of DMCA enforcement?
Key aspects of DMCA enforcement include the takedown notice process, safe harbor provisions for service providers, and the counter-notice mechanism for users. The law also criminalises the circumvention of copyright protections, ensuring that copyright holders can effectively protect their rights in the digital environment.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

