Key Takeaways:
- Counterfeit detection systems equip business owners with the tools needed to protect their usual product offerings, ensuring that only genuine items reach consumers and maintaining brand integrity.
- Utilising automatic detectors streamlines the identification process, allowing businesses to quickly and accurately differentiate between authentic products and counterfeits, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
- Implementing a robust program for banks that includes counterfeit detection technologies strengthens the financial ecosystem, helping to safeguard against counterfeit currency and protect both businesses and consumers.
Counterfeiting has been around for centuries, it evolved with monetary systems and consumer goods. Since coins were minted, counterfeiters have found ways to copy them for profit.
In modern times, counterfeiting has gone beyond currency; luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, electronics and even official documents are being forged by sophisticated criminal networks. As counterfeits have become more advanced, so have the technologies to detect and prevent them.
A counterfeit detection system can be defined as any methodological or technological framework to identify inauthentic items – from fake currency to forged documents and beyond.
Today’s systems include high-tech solutions using artificial intelligence and machine learning, specialised sensors, unique identifiers (holograms or RFID chips) and more. This article will give you an overview of counterfeit detection systems, importance, methods, challenges and future prospects.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is a Counterfeit Detection System?
The Counterfeit Detection System is a kind of tool, technique, and technology that may be employed in detecting counterfeit products, which are replicas of some genuine products made either to deceive or infringe on the intellectual property rights of others.
Counterfeit goods can be physical, which includes currencies, electronics, medicines, and others; or digital, such as software and media files.
The counterfeit detection systems, through various means-optical recognition, RFID tags, UV light scanning, chemical testing, and machine learning algorithms-have been used to make the much-needed line of demarcation between a genuine and a spurious product.
These are important across many industries for tackling counterfeiting-a serious threat both to consumer safety and corporate revenues.
Importance of Counterfeit Detection Systems
Economic Implications
Counterfeiting has very wide economic motivating factors:
Fake products take business away from real ones, reduce brand value, and make the playing field uneven for competitors.
Where the currency is concerned, a large amount of counterfeiting will break the trust of the public in that currency, result in inflationary pressure, and make it really expensive for the government to print new banknotes and upgrade security features.
Safety and Health Risks
Counterfeit pharmaceuticals and automotive or aerospace parts can have life-threatening consequences if these items fail or do not meet regulatory standards.
Because consumers depend on the safety and authenticity of essential parts and pharmaceuticals, strong detection methods are necessary to protect public health and safety.
Maintaining Trust
Whether it involves banknotes, official documents, or consumer products, authenticity is the foundation of trust upon which society has relied.
Indeed, confidence in currency underlines whole economies; and for trust in official documents-whether it’s a passport or a driver’s license-law enforcement and governance are seriously at stake.
Correspondingly, the protection of brand authenticity through the consumer’s trusting it preserves a brand’s equity in general.
The Growing Problem of Counterfeiting

Counterfeiting has grown to become an international problem since it affects many sectors, several economies, and a number of consumers.
With the advancement in manufacturing and distribution technologies, these counterfeits are not only increasingly easier to make but also difficult to identify. Their production is estimated to account for more than $500 billion annually in global economic loss.
In this respect, the industries most vulnerable to counterfeiting are those of luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and consumer products.
Adulterated pharmaceuticals are dangerous to health, while fake electronics can pose a safety risk leading to fire or device malfunction.
When counterfeits become rampant in the market, aside from the problems that individual customers face, companies will also experience legal issues, lost revenue, and damage to their brand reputation.
E-commerce platforms have worsened the problem of counterfeiting because they give counterfeiters a global reach.
Counterfeit goods regularly evade detection by taking advantage of weaknesses in enforcement systems, even in the face of efforts to enforce more stringent seller verification and product authenticity checks.
Counterfeits also stifle innovation: counterfeiters steal the intellectual property of others and avoid the costs associated with research and development.
Most counterfeit operations are also linked to organised crime, fueling broader illegal activities.
The issue that keeps on growing like this requires an overall controlling approach with the involvement of tougher regulations, advanced anti-counterfeit technologies using blockchain, AI-powered detection systems, and high consumer awareness.
The effort to reduce the economic, social, and safety risks of counterfeiting must be collaborative globally.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Core Methods of Counterfeit Detection
Visual Inspection
- Watermarks and Holograms: Many modern currencies and official documents include visible and hidden watermarks, micro-printing, or holographic strips. Trained individuals or devices can verify these features quickly.
- Color-Shifting Ink: Under certain angles or lighting conditions, color-shifting ink changes appearance. This feature is commonly integrated into high-denomination banknotes.
- Security Threads: Embedded security threads visible under strong light or ultraviolet (UV) light are common in many currencies.
Although traditional, visual inspection remains a critical component of most detection systems, particularly because it is cost-effective and can be deployed in nearly any environment.
Ultraviolet (UV) Detection
UV detection utilises fluorescent and phosphorescent materials that are embedded within currency or product packaging.
Most legitimate items, therefore, have embedded UV-reactive inks or strips which fluoresce at certain colors when viewed under UV light.
Often, these are impossible to be exactly reproduced in terms of the wavelength or color intensity, which makes this one of the more robust first-level checks for authenticity.
Infrared (IR) and Magnetic Detection
Infrared: Most of the security features now are made with various types of ink that react to infrared and are not visible to the naked eye. Special detectors look for these IR markings in order to authenticate them.
Magnetic Inks: Banknotes and various other official papers have magnetic inks in them, many of which display very specific magnetic properties. These are picked up by magnetic sensors, providing another layer of security.
Machine Vision and Automated Detection
The ability of the industrial cameras, scanners, and advanced optics to analyse a number of security features in just seconds makes them indispensable.
Automatic machines, employing algorithms, check observed features against a database of known authentic patterns.
Machine vision works well where large volumes have to be checked, such as retail or banking, where high throughput with great accuracy is imperative.
Spectroscopy and Chemical Analysis
Spectral Analysis: The technology involves instruments known as spectrometers, which analyse the chemical composition of inks, papers, or packaging materials. Such a device will show any anomaly in the spectral signature compared to the known authentic item as indicative of counterfeiting.
FTIR stands for Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy that determines the chemical bond present in the material. Any variation in the normal composition serves as an indication of the potential forgery.
Blockchain and Digital Authentication
In the field of digital goods and transactions, blockchain technology is increasingly being used to ensure authenticity.
Each product or item can be tagged with a unique identifier (such as a cryptographic token), creating an immutable record of its origin and ownership.
When coupled with physical goods, blockchain entries can be used to verify that a product is genuine throughout the supply chain.
Counterfeit Detection in Different Industries
| Industry | Common Counterfeited Items | Primary Detection Methods | Key Security Features/Technologies | Key Concerns/Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Currency | Banknotes, coins | – Visual inspection (watermarks, micro-printing, holograms) – UV/IR scanning – Magnetic ink detection – Machine vision (automated scanners) | – Color-shifting ink – Micro-text and raised printing – Transparent windows – Embedded security threads | – Economic losses – Undermines trust in monetary system – Inflationary pressures |
| Luxury Goods | Designer handbags, watches, clothing, perfumes | – RFID or NFC tag scanning – Holograms and QR codes – Micro-engravings – Visual/tactile inspections | – Serialised labels or tags – Unique holographic seals – Blockchain-based supply chain tracking | – Brand reputation damage – Revenue loss for legitimate manufacturers |
| Pharmaceuticals | Medications (pills, injectables), medical devices | – Serialised barcodes & traceability – Spectroscopic analysis (Raman, FTIR) – Tamper-evident packaging | – Unique serial numbers for each package – Tamper-proof labels & seals – RFID solutions in high-value or critical drugs | – Public health risks- Regulatory non-compliance – High potential for legal liabilities |
| Electronics & Components | Microchips, mobile phones, automotive and aerospace parts | – Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) – Unique laser-engraved serial numbers – Machine vision and AI pattern matching | – Secure supply chain management – Blockchain or cloud-based product tracking – Specialised labeling or etching | – Product failures & safety hazards – Warranty and service cost increases |
| Official Documents | Passports, driver’s licenses, ID cards, birth certificates | – Biometric verification (fingerprints, facial recognition) – UV/IR features & micro-print – Laser-perforated images | – Embedded microchips (e-passports) – Watermarks & holograms – Biometric data encryption | – National security risks – Identity theft & fraud – Undermines public trust |
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
How Counterfeit Detection System Works?
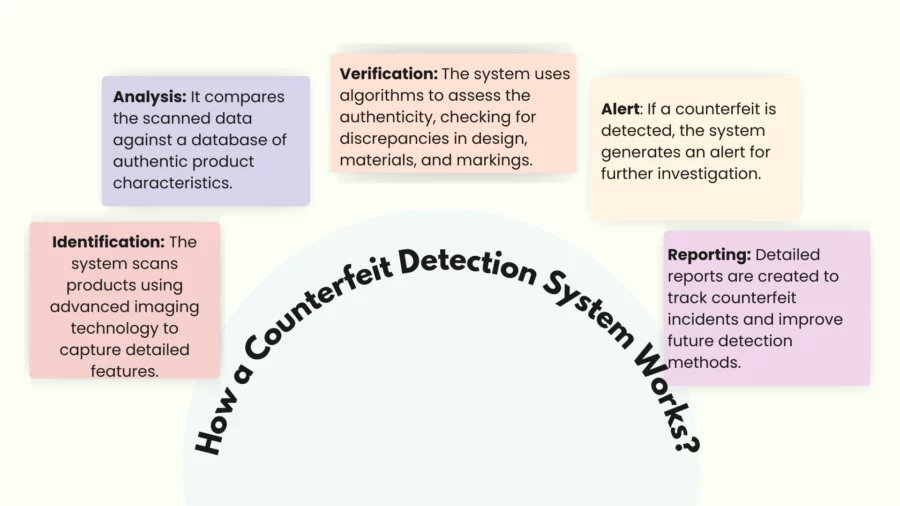
The system of the counterfeit detection works by the utilisation of various methods and technologies that make a difference between a real product and its fake version.
The precise functionality depends on the system being implemented, but in general, the suspect product gets compared to known characteristics of its genuine article. Here’s a breakdown of the common approaches:
Authentication Techniques:
- Taggants and Markers: These unique physical or chemical identifiers are embedded within the product or packaging. A detection device or specialised reader analyses the presence and type of taggant to confirm authenticity. This could involve:
- Covert Taggants: The taggants are invisible; however, their detection needs specific readers like UV light, portable scanners.
- Overt Taggants: Visible security features, easily checked by consumers (e.g., holograms, special inks).
- RFID and NFC Tags: These will hold unique digital information of any given product. Any wireless tag reader will therefore have an easy time scanning and retrieving data in a database.
- Barcodes and QR Codes: These are codes carrying information about a product. A smartphone or scanner would show the details, which could be verified against a database or the website of a given manufacturer, after scanning.
- Serial Numbers and Holograms: Unique serial numbers are printed on the product or packaging and can be verified through a database. Holograms are difficult to replicate and provide a visual authentication feature.
Data Analysis and Verification:
- Product Authentication Software/Apps: Consumers or retailers use apps to scan codes, take pictures, or input product information. The app compares this data with a database or uses AI to analyse for inconsistencies.
- Track-and-Trace Systems: It provides insight into how goods have moved along their complete supply chain from manufacturing through the retail level. Therefore, there could be developed certain verifiable histories that can verify points of a counterfeiting attack. To record the movement of products in detail, blockchain technology offers unparalleled fit, as it works simply by moving along an immutable record of goods.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI algorithms analyse product images, packaging details, or other data for subtle anomalies indicative of counterfeiting. This can involve:
- Image Recognition: Identifying discrepancies in logos, fonts, or other visual elements.
- Anomaly Detection: Detecting unusual patterns in sales data or product characteristics.
Material Analysis:
- Spectroscopy and Chemical Analysis: These include Raman scattered spectroscopy or mass spectrometry, which works on the principle of analysing the chemical composition of the product. These techniques are actually very accurate and can detect slight changes in materials used.
- Microscopy: Inspecting the product’s micro-structure may define the difference between manufacturing processes, suggesting material quality-which may evidence potential counterfeiting.
Human Inspection:
- Visual Inspection: Trained personnel observe the product for anomalies in specific packaging, labeling, and general quality compared to authentic samples. Most of the time, this method is applied with other techniques.
- Forensic Analysis: Detailed product component and material examination, which is generally performed in a laboratory. It is usually applied in the most complex cases or high-value items.
Example Workflow:
Suppose a customer is buying a designer purse.
This product has a means to contain within itself an NFC tag. In that respect, a customer uses their smartphone and hovers above that tag to scan for the details regarding that handbag. A Smartphone extracts data from it and compares its authenticity against the manufacturer database through an Internet link.
The product should be authentic or may be genuine carrying a serial number printed on any tag, for instance. Using an on-screen interface in this context could include using this serial number in entering on a related manufacturer website as confirmation.
Key Considerations for Effective Counterfeit Detection:
- Integration: The counterfeit detection measures have to be implemented across the entire supply chain.
- Data Management: To store and manage product information in a secure way, along with authentication data.
- Collaboration: Working with the partners, suppliers, and law enforcement agencies.
- Continuous Improvement: Change with increasingly sophisticated tactics that counterfeiters put into play; adopt new technologies.
With these combined techniques, the detection of counterfeits by various systems can effectively identify and block spurious products from flowing into the business and consumption spheres.
Counterfeit Detection Systems: Integration with Existing Business Operations
| Business Area | Integration Points | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Management & Supply Chain | – Supplier Onboarding & Verification – Inventory Management & Tracking – Quality Control Checks | – Reduced risk of counterfeit goods entering the supply chain – Improved product quality and customer satisfaction – Enhanced brand reputation | – Requires thorough supplier vetting and ongoing monitoring – May increase costs associated with inspections and testing |
| E-commerce & Online Marketplaces | – Product Listing & Monitoring – Customer Service Support (Reporting suspected counterfeits, Trained representatives) – Brand Protection & Enforcement | – Reduced number of counterfeit listings – Improved customer trust and loyalty – Enhanced brand image and customer experience | – Requires constant monitoring and adaptation to evolving online marketplaces – May require collaboration with online platforms |
| Legal & Brand Protection | – Evidence Gathering & Documentation – Investigation Support – Enforcement & Takedown Actions | – Stronger legal cases against counterfeiters – Improved ability to disrupt counterfeiting networks – Enhanced brand protection and enforcement capabilities | – Requires legal expertise and compliance with relevant laws – May involve complex legal procedures |
| Data Analysis & Business Intelligence | – Trend Analysis & Forecasting – Performance Measurement & Tracking – Predictive Modeling & Risk Assessment | – Data-driven insights to inform business decisions – Improved resource allocation and budget planning – Proactive identification and mitigation of risks | – Requires robust data collection, analysis, and interpretation capabilities – May require specialised data science expertise |
| Marketing & Sales | – Integrate counterfeit detection capabilities into product listing and advertising platforms – Educate customers about counterfeit risks and how to identify authentic products | – Proactive identification of counterfeit listings and takedown – Increased customer awareness and brand protection | – Requires coordination between marketing, sales, and legal teams – May involve changes to marketing materials and sales strategies |
Future Outlook
Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials
State-of-the-art solutions involve the incorporation of nano-scale features on the currency, product labels, and official documents. These can range from nano-optic security threads to high-resolution microprints observable under an electron microscope.
Current solutions based on nanotechnology are expensive, but their usage is liable to be widespread once costs decrease.
Quantum Dots and Photonic Security
Quantum dots are small semiconductor particles with special optical properties, which emit light at a specific wavelength upon the occurrence of a specific stimulus. When these quantum dots are embedded in inks or papers, very unique optical signatures can be provided that would be practically impossible for any counterfeiter to copy. The other avenue is photonic crystals, offering color-shifting properties beyond the capability of current inks.
Wider Adoption of Blockchain
In the future, as blockchain continues to mature, many companies would use distributed ledgers to verify products and then track them through the supply chain.
Consumers might have apps that are checking the blockchain record and instantly verify a product’s provenance with less reliance on even physical security features.
Advances in AI
These machine learning models will keep on improving because of:
- Bigger Datasets: Larger datasets mean that the more images and data about counterfeits collected make the models stronger.
- Faster Processing: Cloud computing and special hardware for AI enable real-time processing.
- Edge AI: Running AI models on-device (such as smartphones) to perform counterfeit checks without needing an internet connection.
These improvements will further democratise access to powerful detection tools, potentially making it nearly impossible for unsophisticated counterfeiters to operate successfully.
Cross-Border Collaboration
Globalisation demands that multinational collaboration should be there for effective curbing of counterfeiting.
Some of the probable future measures could be standardisation of international norms related to product authentication, shared databases of illicit networks, and treaties on extradition and prosecution of counterfeiters.
Organisations like the WCO, Interpol, and WTO might hold important positions in bringing governments and businesses together.
What’s Next?
Counterfeit detection systems are essential in combating the widespread issue of counterfeit currency and fake bills that threaten economies, businesses, and consumers.
With advances in technology, counterfeit detectors now leverage automatic detection and advanced scanning technologies to identify counterfeit bills and protect against security issues. These systems, combined with Visual-AI solutions, offer businesses and central banks high-end solutions to distinguish genuine items from fake ones.
Efforts by counterfeiters continue to evolve, targeting popular products and product types with counterfeit branding and unrelated products.
Business brands and central banks can enhance their defenses by implementing counterfeit detection technologies and additional security features like security strips, layers of security, and product setup tailored to specific product details.
Programs for banks and recourse to businesses ensure broader protection against counterfeits.
By safeguarding branding on products, businesses can maintain their reputation and trust. Investing in a counterfeit detection system not only addresses security issues but also protects business brands from becoming targets for counterfeiters.
Safeguard your brand from counterfeit products and misuse with Bytescare brand protection service. Ready to protect your brand? Book a demo today and experience Bytescare’s solutions firsthand!
By taking proactive measures, businesses can ensure their integrity and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What types of products can benefit from counterfeit detection systems?
Counterfeit detection systems can benefit a wide range of products, including luxury goods, electronics, pharmaceuticals, fashion items, and consumer packaged goods. High-value items and popular products are particularly vulnerable to counterfeiting, making them prime candidates for these systems.
What are some common challenges faced when implementing counterfeit detection systems?
Common challenges include the high cost of advanced technology, the need for continuous updates to keep up with evolving counterfeiting techniques, and the integration of detection systems into existing business processes. Additionally, training staff to effectively use these systems can be a hurdle.
How can businesses stay ahead of counterfeiters by adopting emerging technologies in counterfeit detection?
Businesses can leverage Visual-AI solutions, blockchain for supply chain transparency, and advanced scanning technologies to enhance detection accuracy, automate processes, and stay ahead of counterfeiters’ evolving tactics.
How effective are counterfeit detection systems in preventing financial losses?
Counterfeit detection systems can be highly effective in preventing financial losses by identifying fake products before they reach consumers. By reducing the incidence of counterfeit goods, businesses can protect their revenue, brand reputation, and customer trust.
How do counterfeit detection systems differentiate between genuine and fake currencies or products?
Counterfeit detection systems utilise various methods, including advanced scanning technology, visual recognition, and security features embedded in genuine products, such as holograms, watermarks, and security strips. These systems analyze specific characteristics to determine authenticity.
What are the limitations of current counterfeit detection systems?
Limitations include reliance on pre-set databases, potential false positives, difficulty in detecting highly sophisticated counterfeits, and the need for regular updates to keep up with new counterfeiting techniques.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

