Key Takeaways:
- HDCP protects copyright-protected content for display by encrypting data, ensuring secure transmission between digital device types like TVs and players.
- HDCP requires compatible devices; non-compliant connection between devices may block content, impacting user experience in digital media setups.
- Anti-piracy technology deters unauthorised copying of content and redistribution of digital content, safeguarding intellectual property for creators and distributors.
Digital content flows seamlessly across devices, and protecting intellectual property has become more important than ever.
Consider you are streaming your favorite content on a high-definition TV or playing a advanced video game on a top-notch console.
Behind the scenes, an unsung hero ensures that the high-quality visuals you enjoy remain secure from unauthorised access or copying. That hero is High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP)!
Developed by Intel Corporation, HDCP is a security feature that works silently yet effectively to protect copyrighted digital content.
Whether it is a blockbuster movie, an engaging TV series, or live sports, HDCP ensures that the digital data transmitted between your devices—like Blu-ray players, streaming devices, and monitors—remains encrypted and out of reach for prying eyes.
But HDCP is more than just a fancy tech acronym; it’s the backbone of trust in the digital content protection system.
It reassures content creators, distributors, and viewers alike that the media we consume is safe from piracy. However, HDCP also comes with its quirks, like the need for compatible device types to work seamlessly.
Here, we will break down the essence of HDCP, exploring its role in securing digital content, its challenges, and why it matters in today’s connected world!
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection?
High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection is a technology designed to safeguard digital content as it moves between device to device.
Think of it as a digital lock that ensures copyrighted material, like movies, TV shows, or games, is transmitted securely from your streaming device, Blu-ray player, or gaming console to your TV or monitor without being intercepted or copied along the way.
It is created by Intel, HDCP plays a vital role in protecting the intellectual property of content creators and distributors.
When you are watching your favorite movie in stunning high definition or streaming a live event, HDCP ensures that the digital data stays HDCP-encrypted content, making it nearly impossible for hackers or pirates to steal or duplicate the content.
Here’s how it works: HDCP-enabled devices communicate with each other through a process called “handshaking.” If both devices—say your streaming box and your TV—are HDCP-compliant, the content flows smoothly.
If one device isn’t compatible, you may encounter a frustrating error or a blank screen. This successfully blocks illegal access to make sure that only authorised devices can play the video content.
While HDCP-restricted content is a great way to keep content safe. Users may have trouble connecting older devices to modern devices because of compatibility issues.
However, its role in maintaining the integrity of digital content is undeniable. HDCP-protected content is the unsung hero quietly working behind the scenes to ensure that your favorite entertainment stays secure.
How Does High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection Works?
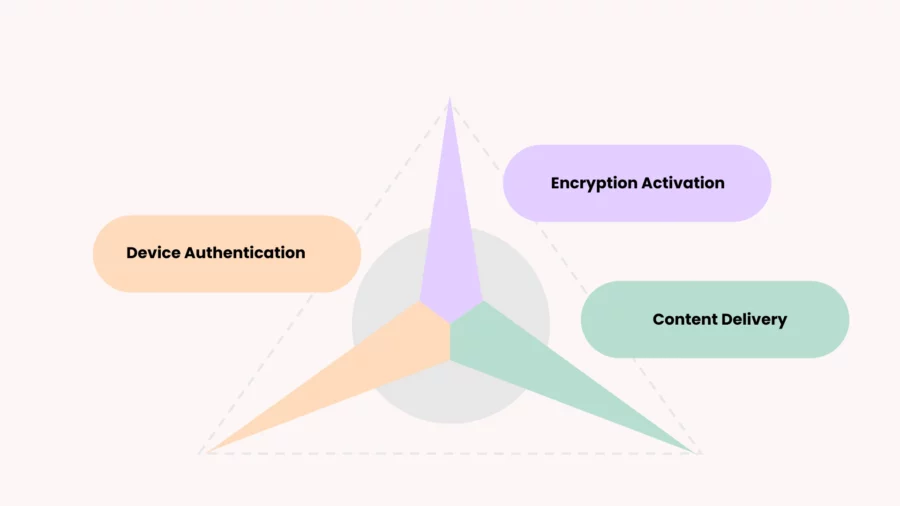
High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection works like a security guard for your digital entertainment.
It ensures that copyrighted content—like movies, TV shows, and games—travels securely between devices without being intercepted, copied, or tampered with. But how does it pull this off?
HDCP creates a encrypted connection between two devices (such as a Blu-ray player and a TV or a streaming device and a monitor). This process also known as handshaking. It starts the moment you hit play.
Here is what happens:
- Device Authentication: Both devices check if the other is HDCP-compliant. This is like asking, Are you authorised to receive this content? If the answer is yes, the connection proceeds.
- Encryption Activation: Once the devices trust each other, HDCP encrypts the digital data being transmitted. This stronger encryption acts like a digital lock, making the content unreadable to any unauthorised device trying to intercept it.
- Content Delivery: The encrypted data travels securely between the devices, ensuring that the content remains intact and piracy-free.
If one of the devices in the chain isn’t HDCP-compatible, the system blocks the content. This is why you might see a blank screen or an error message if you use older or non-compliant devices.
HDCP works silently behind the scenes, ensuring that your digital entertainment remains secure while preserving the rights of content creators. It is a critical component of the digital ecosystem that keeps your viewing experience smooth.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Evolution of High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection Versions
| HDCP Version | Release Year | Key Features | Limitations |
| HDCP 1.0 | 2001 | Initial version for DVI and HDMI connections. | Basic protection; vulnerable to hacking attempts. |
| HDCP 1.1 | 2002 | Improved security features. | Limited compatibility with newer devices. |
| HDCP 1.2 | 2005 | Added support for DisplayPort. | Still susceptible to some piracy methods. |
| HDCP 1.3 | 2006 | Stronger encryption algorithms for better security. | Backward compatibility issues with older devices. |
| HDCP 2.0 | 2008 | Designed for wireless content transmission. | Vulnerable to certain security breaches. |
| HDCP 2.1 | 2009 | Improved protection for wireless streaming. | Limited adoption by manufacturers. |
| HDCP 2.2 | 2013 | Standardised for 4K UHD content protection. | Requires all devices in the chain to be 2.2 compliant. |
| HDCP 2.3 | 2018 | Further enhanced security for 4K and HDR content. | Compatibility issues with older HDCP versions. |
Significance of HDCP in 4K Content Protection
As the demand for ultra-high-definition (UHD) content grows, 4K has become the gold standard for visual entertainment.
The stunning clarity of 4K makes it a favorite for movies, gaming, or streaming.
This technological leap also brings a heightened risk of piracy. This is where High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection plays a pivotal role.
HDCP, particularly its 2.2 and 2.3 versions, is specifically designed to secure 4K content during transmission between devices like streaming boxes, gaming consoles, and 4K TVs.
It ensures that the digital data remains encrypted, preventing unauthorised copying or interception.
For content creators and distributors, HDCP is essential for protecting their intellectual property. With production costs for 4K content significantly higher than standard HD, piracy could lead to substantial financial losses.
By requiring HDCP compliance, content providers can ensure that only authorised devices display their work, maintaining the integrity of their creations.
From a consumer’s perspective, HDCP guarantees a seamless and secure viewing experience. When all devices in the chain—such as a 4K Blu-ray player, AV devices, and TV—are HDCP 2.2 compliant, users can enjoy their content without interruptions.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Common Applications of HDCP
| Application | Importance |
| Digital streaming devices like Roku, Apple TV, and Amazon Fire Stick use HDCP to protect 4K content during streaming. | Ensures that premium content, such as Netflix and Amazon Prime, is securely transmitted. |
| HDCP ensures that 4K Ultra HD Blu-ray discs are transmitted securely to 4K TVs. | Protects high-definition movies from being copied or pirated. |
| PlayStation, Xbox, and other gaming systems use HDCP to secure 4K game content and streaming services. | Prevents unauthorised copying of games and secure gameplay experiences. |
| HDCP-enabled TVs and monitors receive protected content from compatible devices. | Ensures that users can enjoy premium content like 4K UHD movies and games. |
| AV receivers and home theater setups with HDMI connections use HDCP for secure content transfer. | Keeps movies and TV shows safe from piracy while delivering high-quality audio content and video. |
| Cable and satellite boxes use HDCP to prevent illegal recording of HD and 4K channels. | Ensures that live TV and on-demand content are protected from unauthorised redistribution. |
| Digital Signage is Used in commercial displays to secure digital advertising content. | Safeguards copyrighted advertising content in public spaces and retail environments. |
| HDCP secures confidential content to videoconferencing and presentations over HDMI connections. | Protects sensitive business information from being intercepted or recorded. |
Common Issues and Troubleshooting HDCP Errors
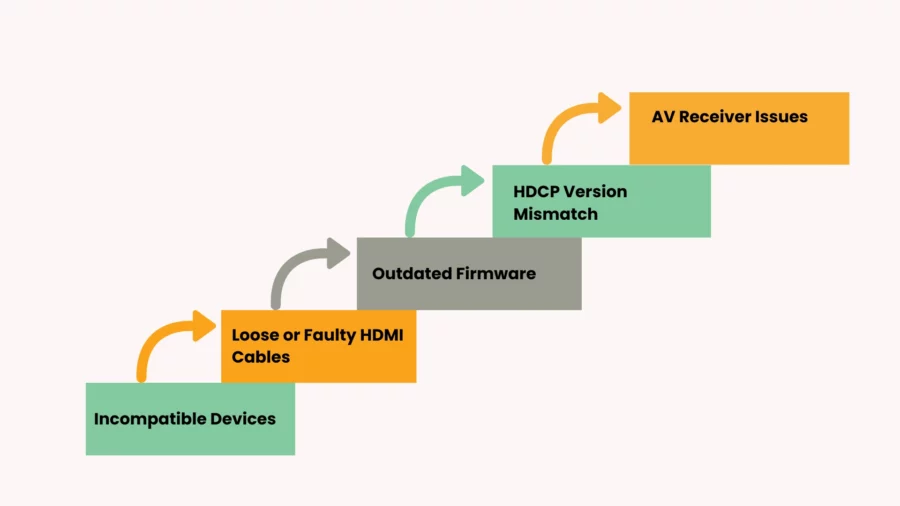
While HDCP is essential for securing digital content, it’s not without its frustrations. Many users encounter HDCP errors, especially when connecting devices like Blu-ray players, gaming consoles, or streaming devices to 4K TVs or monitors.
These errors typically manifest as a blank screen, an error message, or a signal loss. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
Incompatible Devices
HDCP errors often occur when one or more devices in the connection chain are not HDCP-compliant, especially with the latest HDCP 2.2 standard.
Here is a Quick Solution
For 4K content, make sure that all of your devices are HDCP 2.2 compatible. See the device specification to discover if it works with your device.
Loose or Faulty HDMI Cables
Sometimes, the problem is as simple as a poor HDMI connection. A damaged or loose HDMI cable can cause signal loss and HDCP errors.
Here is a Quick Solution
Replace the HDMI cable with a high-quality cable designed for 4K.
Outdated Firmware
Outdated firmware on any device in the chain (TV, console, Blu-ray player, etc.) can cause HDCP compatibility issues.
Here is a Quick Solution
Check for firmware updates on all connected devices and install them to ensure proper HDCP functionality.
HDCP Version Mismatch
An error may occur if a device uses an older HDCP version (like 1.4) while another device requires HDCP 2.2.
Here is a Quick Solution
Use devices that support the same HDCP version or ensure all devices are updated to support HDCP 2.2.
AV Receiver Issues
Sometimes, AV receivers can block or disrupt HDCP signals, especially if they are older models.
Here is a Quick Solution
Directly connect the source device (like a Blu-ray player or gaming console) to the TV, bypassing the receiver, to see if the issue resolves.
What is HDCP Content Protection Standards?
High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection is a set of content protection standards developed to prevent unauthorised copying and piracy of digital content as it’s transmitted over HDMI, DisplayPort, and other digital interfaces.
The primary goal of HDCP is to ensure that high-quality media—like 4K movies, TV shows, and games—remains secure from interception or duplication as it travels between devices.
The HDCP standard works by encrypting the content being sent from a source device (like a Blu-ray player or gaming console) to a display device (like a TV or monitor).
This advanced encryption methods ensures that only HDCP-compliant devices can decrypt as well as display the content. This makes it nearly impossible for hackers to steal the media.
There are different versions of HDCP, each made to meet the needs of higher-quality content:
- HDCP 1.0 – 1.4: These versions were designed to protect HD content over HDMI and DVI connections. HDCP 1.4, for example, introduced support for 1080p HD content.
- HDCP 2.0 – 2.2: These later versions were developed to protect 4K UHD content in addition to ensure secure transmission for higher resolutions, HDR (High Dynamic Range), and wider color gamuts. HDCP 2.2 is the current standard for 4K content protection.
- HDCP 2.3: The most recent version, designed to enhance security for 4K and beyond, and prevent newer types of digital piracy.
HDCP’s Role in Modern Digital Rights Management
High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection plays a key role in modern Digital Rights Management (DRM) by ensuring that high-definition and 4K content remains secure during transmission between devices.
As digital media consumption grows, especially with the rise of streaming services, digital piracy has become a major concern for content creators, distributors, and rights holders.
This is where HDCP steps in to protect intellectual property and enforce content usage rights!
HDCP functions as a form of encryption standards by securing digital signals sent over HDMI, DisplayPort, or other digital interfaces.
HDCP ensures that the data is encrypted when you watch a movie or stream content in high definition. So it cannot be intercepted by unauthorised devices.
Only HDCP-compliant devices—such as TVs, Blu-ray players, or gaming consoles—are allowed to decrypt and display the content.
In modern DRM systems, HDCP serves as a gatekeeper, ensuring that only authorised devices can access premium content.
For example, in the case of 4K streaming, HDCP 2.2 is required to ensure that UHD content is securely transmitted without the risk of illegal copying or redistribution.
Without HDCP, it would be much easier for pirates to intercept, record, and distribute high-quality digital media, undermining the financial viability of content creators & distributors.
HDCP protects the rights of creators while letting users enjoy high-quality digital content. This makes sure that DRM systems work well.
Challenges and Criticisms of HDCP

While High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection plays a vital role in securing digital content. It is not without its challenges.
Many industry professionals have pointed out several issues that can arise from the use of HDCP.
Compatibility Issues
One of the most common complaints about HDCP is compatibility. Devices from different manufacturers may not fully support the latest versions of HDCP.
This can result in error messages, a blank screen, or no signal at all when trying to view content. Users may face frustration when upgrading their TVs or devices and discover that their older components are not HDCP-compliant.
HDCP Enforcement
HDCP’s strict enforcement can sometimes lead to a negative user experience. For instance, when a device in the connection chain isn’t HDCP-compliant, the entire content stream can be blocked.
This can be inconvenient for users who have a mix of old and new devices, as they might not be able to watch high-definition content on their setup, even though their TV or display is capable.
Piracy Workarounds
Despite its strong protection, HDCP is not foolproof. Hackers have found ways to circumvent the industry-standard encryption algorithms which leads to illegal piracy.
This undermines the effectiveness of HDCP in some cases by leaving content creators & distributors vulnerable.
Cost & Complexity
The need for HDCP-compliant devices adds extra costs to both consumers as well as manufacturers. Devices must be specially designed & licensed to support HDCP. This can make the overall system more expensive.
How to Ensure HDCP Compliance?
Ensuring HDCP compliance is essential for users who want to enjoy high-quality, protected content without interruptions.
Whether you are setting up a home theater system, upgrading to 4K devices, or troubleshooting HDCP errors, here are some key steps to ensure your devices are HDCP-compliant:
Check Device Specifications
- The first step in ensuring HDCP compliance is to check the specifications of all devices in your setup.
- Make sure that both your source device (like a Blu-ray player, gaming console, or streaming box) and display device (such as a 4K TV or monitor) support the required HDCP version.
- For 4K content, you will need HDCP 2.2 or higher.
Use HDCP-Compliant Cables
- Not all HDMI or DisplayPort cables are created equal.
- To ensure HDCP compliance, use high-quality, certified cables that are designed to handle the data rates required for HDCP-protected content, especially when transmitting 4K or UHD signals.
- Low-quality cables may cause signal degradation and HDCP errors.
Update Firmware
- Outdated firmware can cause compatibility issues with HDCP.
- Make sure to regularly update the firmware on all devices in your setup, including TVs, streaming devices, Blu-ray players, and AV receivers.
- Manufacturers often release updates that improve HDCP compatibility and fix known issues.
Verify Device Connections
- Ensure that all devices in the signal chain are correctly connected.
- Make sure it supports HDCP 2.2 if you are transmitting 4K content if you are using an AV receiver.
- Direct connections between the source device & TV by bypassing the receiver can help identify HDCP-related problems.
Alternatives and the Future of Content Protection
As digital content consumption continues to grow, so does the need for robust content protection.
While HDCP has been a reliable solution for securing high-definition and 4K content, there are emerging alternatives and future trends in content protection that aim to address the limitations of HDCP and meet the evolving needs of both consumers and content creators.
Alternatives to HDCP
Digital Watermarking
It is an alternative that embeds an invisible, unique identifier into the content itself.
Unlike HDCP, which protects content during transmission, watermarking can trace the source of illegal copies by embedding information directly into the video or audio.
This method is gaining traction in the fight against piracy.
Encryption-Based DRM Systems
Microsoft PlayReady or Google Widevine are becoming more common on streaming platforms.
These systems encrypt content before transmission and only allow authorised devices to decrypt it, ensuring content remains protected.
PlayReady is widely used for streaming services like Netflix and Amazon Prime Video.
Blockchain for Content Protection
The rise of blockchain technology offers new opportunities for content protection systems.
By utilising decentralised ledgers, blockchain can provide transparent, tamper-proof records of content ownership and distribution.
This makes it easier to prevent unauthorised use or distribution.
The Future of Content Protection
The future of content protection requirements will likely involve more advanced encryption techniques, integrated AI-based monitoring for piracy detection, and greater interoperability between different DRM systems.
As streaming services and digital media continue to grow, content security will become even more sophisticated, balancing the needs of creators, distributors, and consumers while ensuring a seamless, secure experience.
What’s Next?
High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) plays a vital role in securing digital content, especially as the demand for high-quality 4K and UHD media continues to rise.
By preventing unauthorised copying and ensuring that only authorised devices can display protected content, HDCP helps protect the intellectual property of content creators and distributors.
While HDCP has faced its share of challenges, including compatibility issues and security concerns, it remains an essential tool in the fight against piracy.
As technology continues to evolve, HDCP and other content protection standards will adapt to meet the needs of both consumers and creators, ensuring a secure and seamless digital experience for all.
Protect your brand with Bytescare’s comprehensive Brand Protection Solutions. Our advanced system detects and prevents unauthorised use, phishing, and trademark infringement.
With proactive brand name scanning and infringement detection, you can safeguard your brand’s identity online. Ensure your brand’s security and reputation—contact us today for peace of mind!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
How do I fix high bandwidth digital content protection?
To fix HDCP issues, check device compatibility, use certified HDMI cables, update firmware, and ensure all devices in the chain support the correct HDCP version (e.g., HDCP 2.2 for 4K content).
What is the general function of high bandwidth digital content protection?
HDCP prevents unauthorised copying and distribution of high-definition content by encrypting signals between devices, ensuring only authorised devices can display protected media, and securing digital transmissions from piracy.
Is it illegal to remove HDCP?
Yes, removing or bypassing HDCP is illegal, as it violates copyright protection laws and the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). Removing HDCP can lead to legal consequences and infringement of intellectual property rights.
What happens if my device doesn’t support HDCP?
If your device doesn’t support HDCP, you may experience a blank screen, error messages, or inability to play protected content. Upgrading to HDCP-compliant devices is necessary to view protected media without issues.
What is HDCP and why is it important?
HDCP (High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection) is a technology designed to prevent piracy by encrypting digital signals. It ensures secure transmission of high-quality content like 4K movies and protects intellectual property for creators and distributors.
What is HDCP content protection standards?
HDCP content protection standards define the encryption protocols used to secure digital media. These standards, such as HDCP 2.2 and HDCP 2.3, ensure that content is transmitted securely between devices, preventing unauthorised copying and ensuring copyright protection.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

