Key Takeaways:
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) protect sensitive company information by legally preventing restricted parties from sharing confidential data with unauthorised individuals or entities.
- Non-Solicitation Agreements (NSAs) restrict the poaching of high-level employees, clients, or prospective customers, safeguarding business relationships and preventing unfair competition.
- Both agreements serve distinct purposes, ensuring confidentiality and stability while fostering trust and protecting business interests.
Trust and collaboration are the foundation of successful partnerships and employment relationships in the business contexts.
However, with trust comes the need for protection—especially when sensitive information or key company assets are at stake. That is where agreements like Non-Disclosure and Non-Solicitation come into play.
At first glance, these agreements might sound like legal jargon reserved for corporate giants, but they are just as essential for startups, freelancers, and small businesses.
Whether you are sharing trade secrets, entering a partnership, or hiring a new team member, these contracts act as a shield, safeguarding your business interests.
An NDA ensures that confidential information stays just that—confidential. It prevents others from leaking or misusing sensitive details like methods of operation, exclusive customer lists, or intellectual property.
On the other hand, an NSA ensures that your valuable relationships—be it with employees, clients, or partners—are not exploited after a deal ends.
Knowing the difference between Non Disclosure vs Non Solicitation Agreement is essential to know when to use them and why they matter.
Here, we will explore NDAs and NSAs in detail. This helps you protect what matters most to your business. After all, prevention is better than cure in the world of competitive business environment!
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What is a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)?
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is a legal contract designed to protect sensitive information shared between two or more parties.
Think of it as a promise to keep a secret. Whether you’re collaborating on a new project, sharing business strategies, or discussing confidential ideas, an NDA ensures that the information stays private and isn’t disclosed to anyone else.
For businesses, NDAs are essential when dealing with trade secrets, client details, or proprietary information.
For example, if you are hiring a contractor or pitching your idea to potential investors, an NDA prevents them from sharing or using your information without permission.
NDAs typically outline what information is considered confidential, how it can be used, and the consequences of breaking the agreement. It’s a simple yet powerful way to protect your business from unnecessary risks.
An NDA builds trust while safeguarding what matters most—your ideas and intellectual property.
Key Elements of Non-Disclosure Agreement
| Parties Involved | Clearly identifies who is sharing the information (Disclosing Party) and who is receiving it (Receiving Party). |
| Definition of Confidential Information | Specifies what qualifies as confidential, such as trade secrets, business strategies, or proprietary data. |
| Obligations of the Receiving Party | It outlines how long the non-solicitation obligations will last. It often ranges from months to a few years. |
| Exclusions from Confidentiality | Lists what doesn’t count as confidential, like publicly available information or details already known to the recipient. |
| Duration of Agreement | States how long the confidentiality obligation will last—often a few years or indefinitely. |
| Consequences of Breach | Details legal actions or penalties if the agreement is violated, such as fines or lawsuits. |
| Jurisdiction | Identifies the governing laws and location where disputes will be resolved if conflicts arise. |
| Signatures | Ensures both parties agree to the terms by signing the document, making it legally binding. |
Use Cases of Non-Disclosure Agreement
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are used in various situations where protecting confidential information is essential. Here are a few common use cases:
Business Partnerships
When two companies are exploring a potential partnership, they often share sensitive business plans, financial data, or trade secrets. An NDA ensures that neither party will disclose this information to outsiders during discussions.
Hiring Employees or Contractors
Companies use NDAs when hiring employees or contractors who will have access to proprietary data or client information. It ensures that these individuals won’t misuse or share this information after leaving the company.
Product Development
When working with suppliers, manufacturers, or other partners to develop a new product, an NDA protects intellectual property, preventing others from stealing or copying the concept.
Investors and Startups
Entrepreneurs use NDAs when pitching their ideas to investors, ensuring that their concepts or business strategies are kept confidential before securing funding.
What is a Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA)?

A Non-Solicitation Agreement is a legal contract that prevents one party from directly or indirectly poaching employees, clients, or prospective customers from another party.
It’s often used in business relationships, especially when companies want to protect their valuable networks and relationships after a contract ends.
For example, if you hire a consultant or enter a partnership with another business, an NSA ensures that the other party won’t approach your employees or clients to work with them instead.
This agreement is designed to prevent unfair competition and maintain the stability of your business operations.
NSAs are used when employees leave a company, when a business relationship is terminated, or after a merger or acquisition. The agreement outlines a specific period of time during which the non-solicitation restrictions apply.
An NSA helps safeguard business interests and reduces the risk of losing valuable contacts.
Key Elements of Non-Solicitation Agreement
| Parties Involved | Identifies who is bound by the agreement, typically the employer and employee or business and partner. |
| Scope of Restriction | Specifies what actions are restricted, such as approaching employees, clients, or customers for business purposes. |
| Duration of Restriction | It outlines how long the non-solicitation obligations will last. It often ranges from months to a few years. |
| Geographical Area | Defines the geographic scope where the non-solicitation applies, which can be local, national, or international. |
| Exclusions | Lists any exceptions, such as if the client or employee was already in contact with the other party before the agreement. |
| Consequences of Breach | Details the penalties or legal actions if the agreement is violated, like monetary damages or legal claims. |
| Jurisdiction | Identifies the legal framework and location for resolving any disputes or conflicts arising from the agreement. |
| Signatures | Confirms that both parties agree to the terms by signing the document, making it legally binding. |
Use Cases of Non-Solicitation Agreement
Non-Solicitation Agreements (NSAs) are commonly used in various situations to protect business interests. Here are a few typical use cases:
Employment Contracts
The employers often use NSAs to prevent former employees from recruiting colleagues for a competitor after leaving the company. This helps retain talent and safeguard client relationships.
Business Partnerships
When two companies collaborate, an NSA can prevent one business from enticing the other’s employees, clients, or names of customers after the partnership ends, ensuring the partnership’s stability.
Mergers and Acquisitions
In the event of a merger or acquisition, NSAs are used to prevent employees or clients of the acquired company from being solicited by the acquiring company, maintaining business continuity.
Consulting Agreements
Consultants or contractors may sign an NSA to ensure they don’t approach the company’s clients or employees after their contract expires.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Non Disclosure vs Non Solicitation Agreement: Key Differences
| Aspect | Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) | Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA) |
| Purpose | Protects confidential information from being shared with outsiders. | Prevents one party from poaching employees, clients, or customers. |
| Focus | Confidentiality of business secrets, ideas, and sensitive data. | Protects relationships and prevents unfair competition. |
| Common Use | Used when sharing sensitive information in partnerships or employment. | Used to prevent employees or business partners from soliciting clients or staff. |
| Duration | Typically applies as long as the information remains confidential. | Often applies for a set period after the agreement ends (e.g., 1-2 years). |
| Enforcement | Focuses on legal action if confidential information is disclosed. | Focuses on legal action if employees or clients are poached. |
| Scope of Restriction | Limits the sharing or use of sensitive data. | Limits the solicitation of clients, customers, or employees. |
Similarities Between Non Disclosure And Non Soliciation Agreement
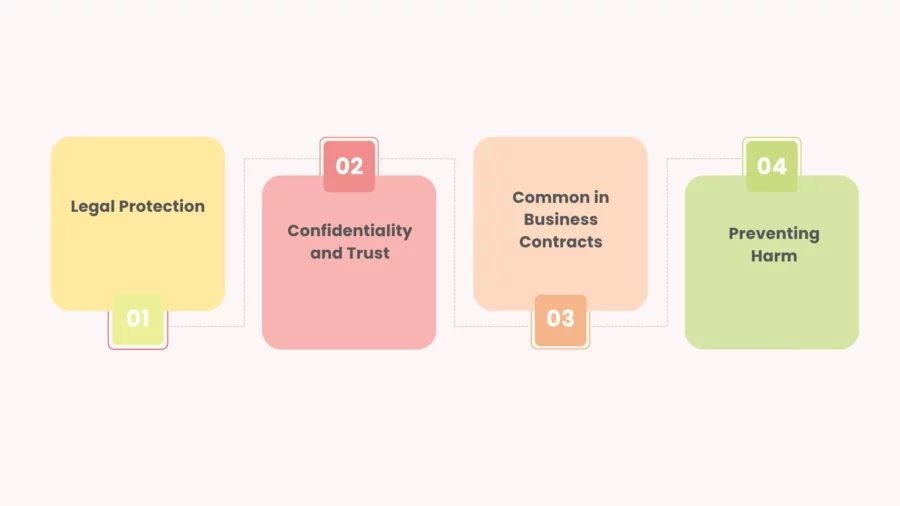
While Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and Non-Solicitation Agreements (NSAs) serve different purposes, they share several key similarities.
Both agreements are designed to protect business interests and ensure that parties involved in a professional relationship act in a way that doesn’t harm the other party’s competitive advantage or proprietary resources.
Legal Protection
Both non-compete and non-disclosure agreements are legally binding contracts. The injured party has the right to take legal action for damages or breach of contract if either agreement is violated. They provide a clear framework for resolving disputes.
Confidentiality and Trust
Both agreements are rooted in the idea of confidentiality. NDAs ensure that sensitive information, such as trade secrets or business strategies, remains private.
Similarly, NSAs maintain the integrity of business relationships by preventing one party from using personal or professional connections to unfairly benefit after the relationship ends.
Common in Business Contracts
Both non-compete and non-disclosure agreements are commonly used in business contracts. Whether you’re hiring an employee, forming a partnership, or engaging in a joint venture, these agreements are tools that help prevent exploitation of business assets, whether it’s sensitive information or valuable relationships.
Preventing Harm
The goal of both agreements is to prevent harm to the business. NDAs prevent the leakage of confidential data. NSAs prevent the disruption of key relationships by ensuring business stability.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
How to Draft Effective Non-Disclosure Agreements?
Drafting an effective Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) requires clarity, precision, and a solid knowledge of the sensitive information you’re trying to protect.
Here’s how to create a well-crafted NDA:
Define Confidential Information Clearly
Be specific about what constitutes confidential information. Vague terms can lead to confusion and legal challenges. Include details like business strategies, trade secrets, customer lists, and intellectual property.
Identify the Parties Involved
Clearly state who is sharing the information (the Disclosing Party) and who will receive it (the Receiving Party). Make sure both parties are correctly identified to avoid future misunderstandings.
Outline the Obligations
Specify what the Receiving Party can and cannot do with the confidential information. For example, they should agree not to disclose, share, or use the information for any purpose other than what’s agreed upon.
Set a Timeframe
Establish how long the confidentiality obligation lasts. It’s common to have the NDA in effect for a set number of years or until the information is no longer confidential (e.g., if it becomes publicly available).
Exclusions from Confidentiality
List what is not considered confidential. This could include information that is publicly available or already known to the Receiving Party.
Include Consequences for Breach
Clearly outline the penalties for violating the agreement. This could include legal action, financial penalties, or both.
Review and Seek Legal Advice
Have a legal professional review the NDA to ensure it complies with relevant laws and protects your interests effectively.
How to Draft Effective Non-Solicitation Agreements?
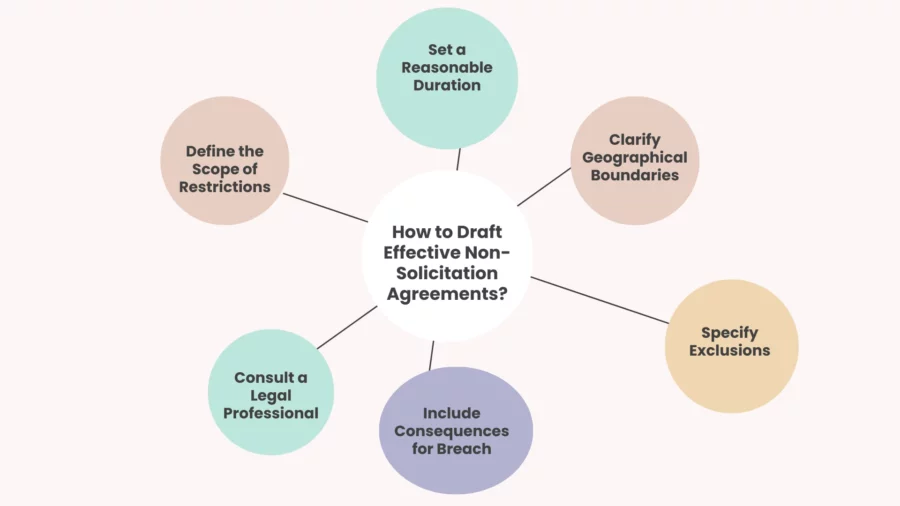
Drafting an effective Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA) is essential to protect your business relationships, employees, and clients.
Here are some key steps to ensure your NSA is clear, enforceable, and effective:
Define the Scope of Restrictions
Be specific about what is being restricted. This includes specifying whether the agreement applies to employees, clients, customers, or business partners.
Clearly outline what activities are prohibited, such as directly or indirectly soliciting business or recruiting employees.
Set a Reasonable Duration
The length of the non-solicitation period should be reasonable and justifiable. Typically, this ranges from 1 to 2 years after the termination of the relationship, but it should be based on the nature of your business and the level of protection required.
Clarify Geographical Boundaries
If applicable, specify the geographic region where the non-solicitation applies. This could be local, national, or international, depending on your business’s reach. Be careful not to make it too broad, as overly restrictive clauses may be unenforceable.
Specify Exclusions
Identify any exceptions, such as existing clients or employees that the other party was already in contact with before signing the agreement. This helps avoid ambiguity and protects both parties from unfair restrictions.
Include Consequences for Breach
Clearly state the consequences if the agreement is violated, such as legal action or financial penalties. This ensures both parties know the seriousness of the commitment.
Consult a Legal Professional
Have a lawyer review your NSA to ensure it’s legally sound and complies with local laws. A well-drafted agreement can safeguard your business relationships and reduce the risk of disputes.
Legal Considerations for Non Disclosure Non Soliciation Agreement
When drafting Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and Non-Solicitation Agreements (NSAs), it’s important to consider several legal factors to ensure they are enforceable and protect your interests effectively.
Clarity and Specificity
Both agreements must be clear and specific. Vague or overly broad terms can make the agreement unenforceable.
For an NDA, ensure that confidential information is well-defined, and for an NSA, clearly outline the scope of restricted activities (e.g., which employees or clients are off-limits and for how long).
Reasonable Duration and Scope
The terms of both agreements should be reasonable in duration and scope. For example, NDAs should not bind the receiving party indefinitely unless there’s a valid reason.
Similarly, NSAs should not impose overly long restrictions on soliciting employees or clients, as this could be deemed unfair or unreasonable by a court.
Jurisdiction and Governing Law
Specify the jurisdiction and governing law under which the agreement will be enforced. This ensures that any disputes will be resolved in a consistent legal framework and helps avoid confusion if the parties are in different locations.
Consideration
For both NDAs and NSAs to be enforceable, there must be consideration, meaning something of value exchanged between the parties. For instance, in an employment context, the job itself might serve as consideration.
State and Local Laws
Be aware of the specific laws governing NDAs and NSAs in your jurisdiction. Some states or countries may have laws that limit the enforceability of certain provisions, such as overly broad non-compete clauses.
Consult Legal Experts
Always have a legal professional review the agreement to ensure it aligns with local laws and is enforceable. A well-drafted agreement minimises the risk of disputes and provides clear legal recourse if violated.
Pros and Cons of NDAs and NSAs
Pros
| Aspect | Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) | Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA) |
| Protects Confidential Information | Safeguards sensitive data like trade secrets, client lists, and intellectual property. | Helps prevent unfair competition by protecting relationships with employees and clients. |
| Builds Trust | Fosters trust between parties by ensuring confidentiality is maintained. | Creates confidence by ensuring business relationships won’t be exploited after an agreement ends. |
| Clear Legal Framework | Provides a clear legal framework for handling confidential information. | Prevents disputes by clearly outlining restrictions on solicitation activities. |
| Deters Misuse of Information | Acts as a deterrent for sharing or using confidential information without permission. | Reduces the risk of employees or clients being poached after leaving or ending a partnership. |
Cons
| Aspect | Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) | Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA) |
| Potential Overreach | May limit business opportunities if terms are too broad or restrictive. | Can be viewed as overly restrictive, especially if the scope or duration is too long. |
| Enforcement Challenges | Difficult to enforce if the terms are vague or if the information is already publicly available. | Can be hard to enforce if the restrictions are too broad or unreasonable. |
| Limited Protection | Does not prevent others from independently discovering or using similar information. | Doesn’t prevent competitors from recruiting employees or clients in other ways. |
| Legal Complexity | Can involve complex legal language, requiring professional assistance for drafting and enforcement. | Similar to NDAs, NSAs can be legally complex and may require expert input to ensure fairness. |
How to Decide Which Agreement You Need?
Deciding between a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) and a Non-Solicitation Agreement (NSA) depends on your specific business needs.
If your primary concern is protecting sensitive information—such as trade secrets, client lists, or proprietary data—an NDA is the right choice.
NDAs are typically used when sharing confidential information with partners, employees, contractors, or investors to ensure that it remains private and isn’t used against your business.
On the other hand, if you want to protect your business relationships and prevent employees, clients, or business partners from poaching each other, an NSA is more appropriate.
NSAs are commonly used when you want to prevent someone from recruiting your employees or soliciting your clients after the business relationship ends.
In some cases, both agreements may be needed, especially in complex business relationships. Consulting with a legal expert can help you determine which agreement best suits your needs and provides the most protection.
What’s Next?
Both Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and Non-Solicitation Agreements (NSAs) are essential tools for protecting your business interests, but they serve different purposes.
An NDA safeguards sensitive information by ensuring confidentiality, while an NSA focuses on preventing the poaching of employees, clients, or customers.
Choosing between the two depends on your specific needs—whether it’s protecting intellectual property or maintaining key business relationships. In many cases, businesses may require both to provide comprehensive protection.
Ultimately, carefully drafting and knowing the terms of these agreements is essential. Consulting with a legal professional ensures that your agreements are clear, enforceable, and aligned with your business goals, helping you avoid future disputes and risks.
Protecting your brand starts with asserting your rights. Bytescare’s Brand Protection Solutions make issuing DMCA takedown notices easy, ensuring your identity and trademarks are safe from unauthorised use.
We help safeguard your intellectual property, keeping your brand’s integrity intact. Contact us today to learn how we can protect your brand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What is the difference between NCA and NDA?
An NCA (Non-Compete Agreement) restricts employees from working for competitors or starting a competing business, while an NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement) focuses on protecting confidential information from being shared or used without permission.
Are NDAs no longer legal?
No, NDAs are still legal and widely used to protect sensitive information. However, their enforceability may depend on the jurisdiction and how reasonably the terms are defined. Unreasonable restrictions may be deemed unenforceable.
What are the three types of non-disclosure?
The three type of agreement are:
Unilateral NDA (one party discloses confidential info).
Bilateral NDA (both parties share confidential info).
Multilateral NDA (multiple parties share confidential information).
How enforceable is a non-solicitation agreement?
Non-solicitation agreements are enforceable if they are reasonable in scope, duration, and geographic area. Courts will assess whether the terms protect legitimate business interests without being overly restrictive or harmful to the individual’s career.
Can an NDA and a non-solicitation agreement be combined into one document?
Yes, an NDA and a non-solicitation agreement can be combined into one document. This combined confidentiality agreement would address the restriction on soliciting employees or clients, making it easier to manage and enforce.
How long do NCA and NDA typically last?
An Non-compete agreements typically lasts 1-2 years after employment ends, depending on the jurisdiction. An NDA’s duration can vary, often lasting until the confidential information becomes public or is no longer relevant. Both should have a reasonable time frame.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

