Key Takeaways:
- Copyright protects your unique creative expression, not ideas or facts. Registering your copyright strengthens your legal position.
- Your website content is typically protected the moment it’s created, but formal registration offers significant advantages if infringement occurs.
- Use copyright notices, monitor for infringement, and take action if your rights are violated. Consult with an IP lawyer for personalised guidance.
As we progress deeper into the digital age, protection against the misappropriation of website content is increasingly essential.
While companies, bloggers, artists, and all other forms of content creators develop their presence online, learning the way to safeguard one’s work regarding its originality and integrity is equally essential.
Copyright law offers a great, strong legal mechanism that ascertains written articles, images, videos, and other creative materials are not misused by any person without permission.
In this all-encompassing guide, we’ll go over the copyright protection for website content.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Copyright Fundamentals
Copyright is another form of intellectual property protection granted to creators for their original works of authorship. The latter can include literary texts, photographs, and music compositions but also films, software codes, and web page content.
The laws on copyright vary slightly between jurisdictions, yet most of them are based upon common principles which are well-founded in international conventions such as the Berne Convention copyright for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works.
The philosophy of copyright is to spur creativity and innovation. In return for the legal protection of the right to decide how, when, and under what circumstances their works are used, society receives the ongoing production of new works.
The rights conferred by copyright usually include reproduction of the work, preparation of derivative works, distribution by sale of copies, public performance of the work, and public display of the work.
Originality and Fixation
For a work to fall within copyright protection, two simple things are needed: originality and fixation.
Originality: It must be created by the skill, judgment, and effort of a creator.
The standard for originality doesn’t require that the work must be novel or even inventive in nature; rather, it is enough that it is independently created and possesses something creative or even at the minimal degree.
Fixation: The work must be fixed in a tangible medium of expression.
In most instances, website contents are in the form of text, images, or other forms of multimedia, which, for the most part, are stored on servers and then displayed on web pages. This itself constitutes sufficient fixation for most jurisdictions.
Why Copyright Matters for Website Owners
Protection of Creative Investment
Developing a successful website involves a lot of time, resource, and talent investment. Protecting this investment is what copyright does.
It would be tragic indeed for the lack of strong copyright to allow anyone with a simple click of a copy-and-paste button to hijack your own unique content-your text, your multimedia, and your original designs.
Deterrence and Legal Recourse
One positive side of owning a copyright is that it gives the creator or lawful owner of the work the exclusive right. This acts as a kind of disincentive in itself towards potential infringers.
When people realise they risk possible legal consequences when copying or distributing your website content, that should also help keep the infringement at bay.
In the event of infringement, you can seek remedies including damages, injunctions to stop unauthorised use, and, in some cases, statutory damages and attorney’s fees, especially when you have registered your work with the relevant copyright office.
Brand Reputation
Apart from the purely financial loss, there could be serious repercussions if unique content or elements of your branding have been misappropriated. This will lead to some copycats diluting your brand and confusing the audience.
You would want enforcement of copyright so that the public view of a unique website and distinctive content would only belong to you and your business.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Common Types of Website Content Protected by Copyright
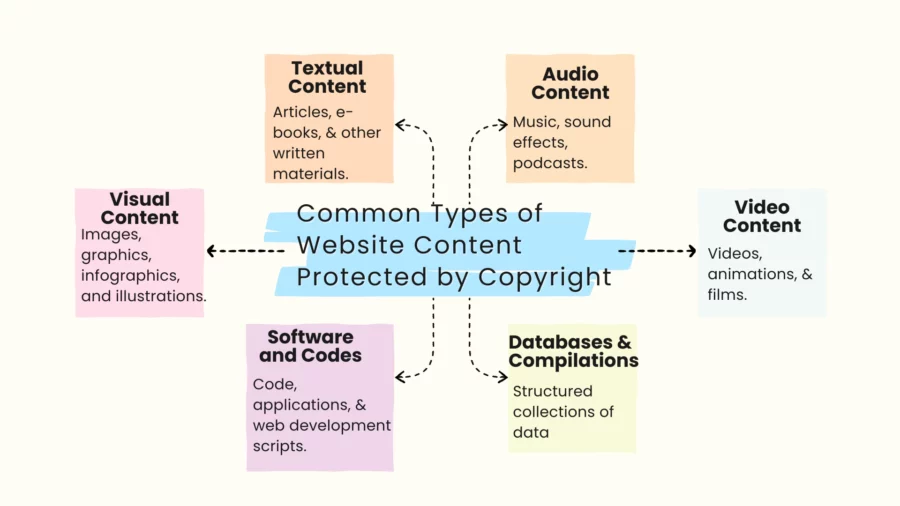
Written Text
Articles, blog posts, product descriptions, website copy, and other text fall under copyright as “literary works.”
For most website owners, the written word is the chief form of communication, ranging from long-form articles to short promotional taglines.
Images and Graphics
Picture and graphics, generally include photographs, logos, infographics, and illustrations – are usually considered to be any visual works, according to the definition under the Copyright Act.
Even many design elements are protected upon the creation of the overall look and feel for your site, whether in its entirety or just a part thereof.
The protection under copyright will extend for as long as any of these subjects meet the twin basic requirements of some originality and reduction to some tangible form of expression.
Audio and Video Content
The audiovisual content on your site, including but not limited to, podcasts, webinars, tutorials, promotional videos, and all other multimedia creations, are similarly entitled to copyright protection.
Protection covers the audio and video components of these works, and any underlying script or musical work may also be separately entitled to copyright protection.
Software and Code
Website owners who write or adapt their own software or code to operate a site can have copyright protection for those items, to the extent required that such works are original. This includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or other code that has been written or adapted specifically for the website’s functionality and appearance.
Databases and Compilations
Databases or compilations of information, such as directories or lists of resources, may be copyrighted if they exhibit sufficient creativity in the selection or presentation of the data.
The fact that information is collected is not enough to create a copyright, but many selective lists or databases will meet the requirement.
How to Protect Your Website Content
Now that it has defined what copyright is and why it is so important, it looks at ways you can protect your website content from unauthorised use.
Register Your Copyright
While copyright protection is automatic, the formal copyright registration of your work through the U.S. Office of Copyrights, or its equivalent in your country, offers a whole host of added benefits. These include:
Public Record: Registration provides a public record of your work, facilitating the process of proving ownership.
Legal Action: A registered copyright also allows you to sue for statutory damages and attorney’s fees, both of which are not available for unregistered works, in case someone decides to infringe on your work.
To register, you will be required to fill out an application and submit a copy of your work. There is a fee involved in registration, but it is well worth it.
Use Copyright Notices
Though not compulsory, a copyright notice placed on the website may, © 2025, [Your Name or Company], be quite effective in making viewers aware that your work is protected and may discourage infringers from misusing your material.
Here’s how to effectively do it:
Placement: The copyright notice should be placed in the footer of your website so that it is easily viewable on every page.
Format: The notice of copyright must include the © symbol, the first year of publication and your name, or that of your firm. Example: Copyright 2023 by Your Name. All rights reserved.
Additional Information: You may also want to include a statement about the terms of use for your online content, indicating that reproduction or distribution without permission is prohibited.
Add Terms and Conditions
Establish clear Terms of Use (TOU) or Terms and Conditions that spell out how visitors may interact with your site.
These terms can state that the content on your site is protected by copyright, specify how others may link to or quote your material, and provide guidelines for user-generated content.
While this will not halt every potential infringer, it provides clarity and can strengthen your legal position in the event of a dispute.
Watermark Your Images
Watermarking, which is allowed in visual arts, such as photography and graphics, is one of the most standard ways to protect your work.
By applying a visible or invisible watermark, you will make it more difficult for others to steal and misuse your images without giving credit.
Monitor for Infringement
Routinely search for instances of others using your information without permission.
Utilise Google Reverse Image Search, Bytescare, and other plagiarism detection tools to find unauthorised use. When you find one, you can take steps to have the content removed.
Licensing Your Content
You license your content in case you would like to make it available for use by third parties but wish to still have some control over the way that third party uses the content. Thus, licensing can allow third-party use of your content under specific terms and conditions.
You can allow people to use your blog posts provided they provide credit or pay some fee.
Use Digital Rights Management (DRM) Tools
For websites offering downloadable content, DRM tools can prevent unauthorised copying or distribution. They simply make the duplication of your content much harder for any other person unauthorised to do so.
Create a Schedule to Copyright New Material on a Regular Basis
Copyright protection isn’t a one-time thing; it’s something that requires time, especially when you’re always producing new works.
Creating a schedule to copyright new materials will ensure all your works are protected. Here’s how you can create a schedule:
Set Regular Intervals: Decide how often you will review and register new content. This could be monthly, quarterly, or biannually, depending on your digital content creation frequency.
Keep Records: Keep a log of all new works created, including dates and descriptions. This will make it easier to compile materials for subsequent registrations.
Old Content Review: From time to time, go through your existing content to see whether it’s still protected or not. In case of considerable changes, re-register accordingly.
Keep Yourself Informed: Copyright laws and regulations are always changing; it is thus pertinent to keep one abreast of these changes. It will also serve to vary your strategy of copyright accordingly.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Level Up Your Copyright: Protecting Your Website Content in a Changing World
| Idea | Description | Key Considerations |
| Blockchain for Copyright Management | Leveraging blockchain to create a decentralised and transparent system for registering, managing, and tracking copyright ownership. | Scalability, interoperability with existing systems, legal recognition of blockchain-based records. |
| AI-Powered Infringement Detection | Utilising AI algorithms to scan the web and identify instances of copyright infringement, including text, images, and code. | Accuracy of detection, potential for false positives, ethical implications of mass surveillance. |
| NFTs and Copyright | Exploring the use of NFTs to represent copyright ownership and facilitate fractional ownership, easier transfer, and new monetisation models. | Legal uncertainties surrounding NFT-based copyright, potential for speculation and market manipulation. |
| Copyright of User-Generated Content | Addressing the responsibilities of website owners regarding infringing content uploaded by users, DMCA safe harbor provisions, and content moderation best practices. | Balancing user freedom of expression with copyright protection, the effectiveness of notice-and-takedown systems. |
| Copyright in the Metaverse | Examining copyright challenges in virtual worlds, including ownership of virtual creations, avatars, virtual real estate, and other digital assets. | Jurisdictional issues, application of existing copyright law to virtual environments, new forms of infringement. |
| Copyright and Website Accessibility | Exploring the intersection of copyright and making website content accessible for users with disabilities. | Balancing copyright restrictions with the need to adapt content for accessibility, fair use considerations. |
| AI-Generated Content and Copyright | Addressing copyright ownership for content generated by AI, the potential for AI to infringe on copyrights, and adapting copyright law to AI technology. | Defining authorship in the context of AI, legal status of AI-generated works, liability for AI infringement. |
| Strategic Use of Creative Commons | Analysing the strategic use of different Creative Commons licenses to align with website owners’ goals for content sharing and control. | Knowing the implications of different CC licenses, educating users about proper attribution and use. |
| Educating Users about Copyright | Emphasising the importance of educating website users about copyright law and promoting best practices for respecting intellectual property rights. | Developing clear and accessible educational resources, integrating copyright information into website design. |
| Copyright in a Decentralised Web | Exploring the implications of Web3 technologies like blockchain and IPFS for copyright enforcement, licensing, and content distribution in a decentralised online environment. | Challenges of enforcing copyright in a decentralised system, potential for new models of content licensing and distribution. |
Emerging Website Content & Copyright: Challenges and Solutions
| Emerging Technology/Content Type | Key Copyright Considerations | Example Use Case | Strategies & Best Practices | Legal Basis |
| AR/VR Website Experiences | • Ownership of 3D assets, environments, audio-visual elements. • Protecting user-generated modifications. | Real estate virtual tours; E-commerce AR previews. | • Register 3D models & sounds. • User agreements for UGC ownership/licensing. • Watermarking & blockchain. | Copyright Act; DMCA (for UGC) |
| Dynamic Content & Personalisation | • Ownership (website vs. user). • Protection for algorithmically generated outputs. | Personalised news feeds; Customised learning resources. | • Clear Terms of Use on ownership. • Database /compilation copyright for data. • Access controls against scraping. | Copyright Act (compilation copyright); Contract law |
| Voice Search Optimisation | • Fair use of voice assistant snippets. • Preventing audio duplication. | Voice assistants reading recipes/blog excerpts. | • Copyright in structured metadata. • Usage guidelines for voice snippets. • Monitor platforms for compliance. | Copyright Act (fair use) |
| AI-Generated Content | • Ownership of AI outputs (summaries, chatbot responses). • Preventing unauthorised derivative works. | AI blog summaries; Chatbots using site content. | • API Terms of Service respecting copyright. • Register original content. • Monitor for unauthorised replication. | Copyright Act (derivative works) |
| Embedded Social Feeds & UGC | • Ownership of embedded content. • User uploads of infringing material. | News aggregators with live feeds; Forums with user-uploaded media. | • Content policies & moderation. • Verify embedding is permitted. • DMCA safe harbor practices (takedowns). | Copyright Act; DMCA (safe harbor) |
| NFT-Enabled Website Assets | • Proving ownership of digital files used for NFTs. • Rights transfer/licensing via smart contracts. | Selling digital art NFTs; NFT-gated content. | • Mint NFTs on reputable blockchains. • Clear smart contract usage rights. • Register original artwork. • Watermarks /cryptographic signatures. | Copyright Act; Smart Contract Law |
| Mixed Reality Live Streams | • Copyrighting real-time interactive content. • Ownership of user-driven modifications during live streams. | Interactive conference keynotes; AR overlays on eSports streams. | • Event recording agreements. • Licensing terms for user modifications. • Archive recordings/screenshots post-event. | Copyright Act; Contract Law |
| Hyper-Personalised Marketing & Product Customisers | • User creative input vs. site-owned base designs. • Licensing for user creations in promotional materials. | Custom T-shirt designers; Furniture configurators. | • Clear licensing terms for user creations. • Distinguish original vs. derivative works. • Content filters for 3rd-party infringement. | Copyright Act (derivative works); Contract Law |
| Website Accessibility & Copyright | • Adapting content (alt text, captions) for accessibility while respecting copyright. | Providing alt text for images; Audio descriptions for videos. | • Fair use considerations for accessibility modifications. • Licensing accessible versions of content. | Copyright Act (fair use) |
| Copyright & Data Scraping | • Preventing unauthorised copying of website data (text, images, databases). | Scraping product prices, articles, or user reviews. | • Terms of Service prohibiting scraping. • Technical measures (robots.txt, rate limiting). • Legal action against infringers. | Copyright Act (database rights, compilation copyright) |
| Website Archiving & Copyright | • Preserving copyrighted content for historical/research purposes. | Archiving websites for future access. | • Fair use considerations for archiving. • Obtaining permission from copyright holders. • Compliance with legal deposit requirements. | Copyright Act (fair use); National Library/Archive Laws |
What’s Next?
Copyright protection for website content is essential for safeguarding the rights of the copyright owner and ensuring that original creations are not misused.
By using the copyright symbol, content owners can assert their rights over their work, including blog articles, images, and other creative elements.
The legal form of protection helps prevent duplicate content and unauthorised use, allowing content writers to maintain control over their copyrightable elements.
From a copyright perspective, it is crucial for content owners to keep a record of ownership and understand their content rights. In cases of infringement, a takedown notice can be issued to address unauthorised use effectively. Additionally, offering limited licenses can provide flexibility while protecting the integrity of the work.
Ultimately, protecting your digital content is vital in online marketplace.
Book a demo today to see how Bytescare can protect your digital content and let you rest easy. From its many features, Bytescare is here to protect the things that mean most to you in a digital world.
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQs
What are the basic principles of copyright protection for website content?
Copyright protection grants creators exclusive rights to their original works, including the right to reproduce, distribute, and display their content. This protection applies automatically upon the creation of the work, provided it is fixed in a tangible medium. Copyright does not protect ideas or facts but does cover the expression of those ideas.
How can I ensure my website content is protected under copyright law?
To ensure your website content is protected, you should include a copyright notice (© year your name) on your site, register your works with the U.S. Copyright Office, and maintain organised records of your original creations. Regularly updating your content and monitoring for unauthorised use can also help.
What should I do if I discover my website content has been copied without permission?
If you find that your content has been copied, you should first document the infringement. Then, consider sending a takedown notice to the infringing party or their hosting provider. If necessary, consult with an intellectual property attorney to explore further legal action.
Are there specific symbols or notices I should include to indicate copyright protection on my website?
Yes, you should include a copyright notice that consists of the © symbol, the year of first publication, and your name or the name of your business. This notice serves as a clear indication of your copyright ownership and helps deter potential infringers.
How does copyright protection for website content differ from other forms of intellectual property?
Copyright protection specifically covers original works of authorship, such as text, images, and videos. In contrast, other forms of intellectual property, like trademarks, protect brand names and logos, while patents protect inventions and processes. Each type of intellectual property has its own legal framework and requirements.
Are there any exceptions to copyright protection for website content?
Yes, there are exceptions, such as the fair use doctrine, which allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, or research. Additionally, certain public domain works are not protected by copyright and can be freely used.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

