Key Takeaways:
- Trademarks serve as a standard of recognition for famous brands, aiding in consumer identification.
- Effective trademarks offer security and exclusive rights against unauthorised use, allowing the owner to take legal action against infringement.
- Key characteristics of trademark include distinctiveness, non-generic nature, use in trade and commerce, and enforceable rights.
Trademark registration in India is a key marketing tool. It helps establish brand identity and protect intellectual property. Strongest trademarks are the heart of a company’s brand, showing who they are and what they stand for.
They help products stand out, show where they come from, and assure quality. This makes them important for brand awareness among consumers.
Trademarks have distinct features like being unique and not generic. They must be used in business and have enforceable rights. They get legal protection forever, which is vital for a brand’s long-term success.
With the growth of social media and online shopping, strong trademark registration is more crucial than ever. It helps protect a brand’s name and stops others from using it without permission.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Basics of Trademark Protection
Trademarks are key for businesses. They help tell products apart, show quality, and fight against fake goods. They also help with advertising and build brand recognition.
Having a trademark can make a business stand out. It helps keep customers loyal and boosts success. It gives a competitive advantage by making a brand more memorable.
What Qualifies as a Trademark?
The Trade Marks Act, 1999, says a “mark” can be many things. It can be a logo, name, or even a color.
To qualify as a trademark, the mark must be graphically representable and must uniquely identify the goods or services of a specific entity. This distinctiveness is crucial for establishing brand identity and preventing consumer confusion.
Legal Framework for Trademark Protection
The Trade Marks Act, 1999, is the law for trademark protection in India. It talks about different kinds of trademarks. Each has its own role.
This legislation outlines the various types of trademarks, including product marks, service marks, collective marks, and certification marks, each serving distinct purposes. The Act provides guidelines for the registration process, rights conferred upon trademark owners, and the legal remedies available in cases of infringement.
Role of Trademarks in Business
Trademarks play a multifaceted role in business by indicating the source of goods and ensuring consistent quality. They help establish brand identity, making it easier for consumers to recognise and choose products. By protecting against counterfeit goods, trademarks safeguard both the brand’s reputation and consumer trust.
Service marks are like trademarks but for services. They are used in areas like entertainment and hotels. They help identify services.
| Trademark Type | Purpose |
| Registered Trademarks | Indicate the source of goods and services |
| Certification Trademarks | Certify that goods or services meet specific standards |
| Collective Trademarks | Indicate the source of goods or services for a group of organisations |
Characteristics of Trademark
In India, trademarks are key for businesses to stand out and get legal protection. The Trade Marks Act of 1999 explains what makes a trademark effective. This ensures it works well in the business world.
A trademark must be unique and not just describe what it’s for. It should be able to be shown graphically, with fancy, made-up, or hint-like elements. Being unique is key to making a brand stand out and be different from others.
Trademarks need to be useful in trade and commerce. They give the owner the right to stop others from using their mark. By registering a trademark, businesses can protect their brand and reputation across the country.
Good trademarks help build trust with customers, show the quality of products, and help with marketing. They are seen as valuable assets that can make a company more worth and competitive.
Trademarks are essential elements of branding and intellectual property law. Here are some key characteristics of trademarks:
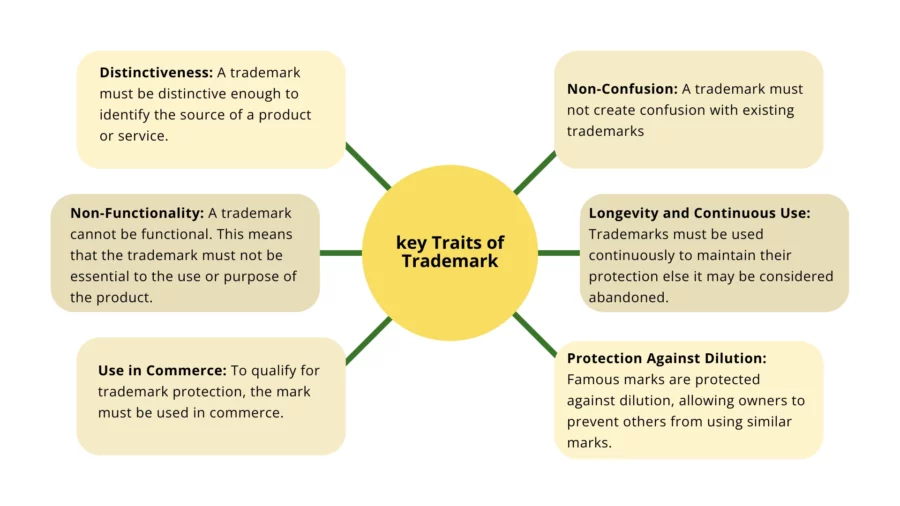
Distinctiveness: A trademark must be distinctive enough to identify the source of a product or service. Distinctiveness can range from arbitrary or fanciful (e.g., “Apple” for computers) to suggestive (e.g., “Netflix” for streaming services) to descriptive (e.g., “Best Coffee” for a coffee shop), with generic mark being ineligible for trademark protection.
Non-Functionality: A trademark cannot serve a functional purpose. It must be used primarily as a source identifier rather than to describe the product’s key features or benefits.
Use in Commerce: To qualify for trademark protection, the mark must be used in commerce. This means it should be used in the sale or advertising of goods or services.
Descriptiveness: While descriptive term for trade marks can indicate the nature or quality of goods or services, they are generally less protectable unless they acquire distinctiveness through extensive use in the market.
Memorability: A good trademark should be easy to remember. Memorable trademarks help consumers recall the brand and can enhance marketing efforts.
Protection Against Dilution: Famous trademarks enjoy additional protection against dilution, which occurs when a mark’s distinctiveness is weakened through unauthorised use, even in unrelated goods or services.
Durability: Trademarks can last indefinitely as long as they are actively used and maintained. Regular renewal and continued use are essential to retain trademark rights.
Universality: Trademarks can be recognised across different markets and cultures, although their effectiveness may vary based on local laws and consumer perceptions.
Legality: A trademark must comply with legal requirements and cannot infringe on existing trademarks. It should not be misleading or deceptive to consumers.
Adaptability: A strong trademark can evolve with the brand and adapt to changes in the market or consumer preferences while maintaining its core identity.
Brand Alignment: A trademark should align with the overall brand strategy and values, reinforcing the brand’s message and positioning in the marketplace.
Protection: Trademarks provide legal protection against unauthorised use by others, helping to safeguard the brand’s identity and reputation.
Non-Infringing: A trademark must not infringe on the rights of existing trademarks. Conducting thorough searches and due diligence is essential to avoid potential legal conflicts.
Cultural and International Considerations: Trademarks should be sensitive to cultural differences and international laws. A mark that is effective in one country may not resonate or may even be offensive in another, so knowing local contexts is crucial for global branding.
These characteristics are vital for businesses and individuals to consider when developing and protecting their trademarks, ensuring they effectively represent their brand and comply with legal standards.
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
Legal Protection and Enforcement Rights
Registered trademarks in India give owners strong legal protection. They can stop others from using similar marks that might confuse people. This helps keep their brand identity safe and protects their intellectual property rights.
India’s laws offer several ways to deal with trademark violations. These include stopping the infringing use, getting money for losses, and making the infringer give up their profits.
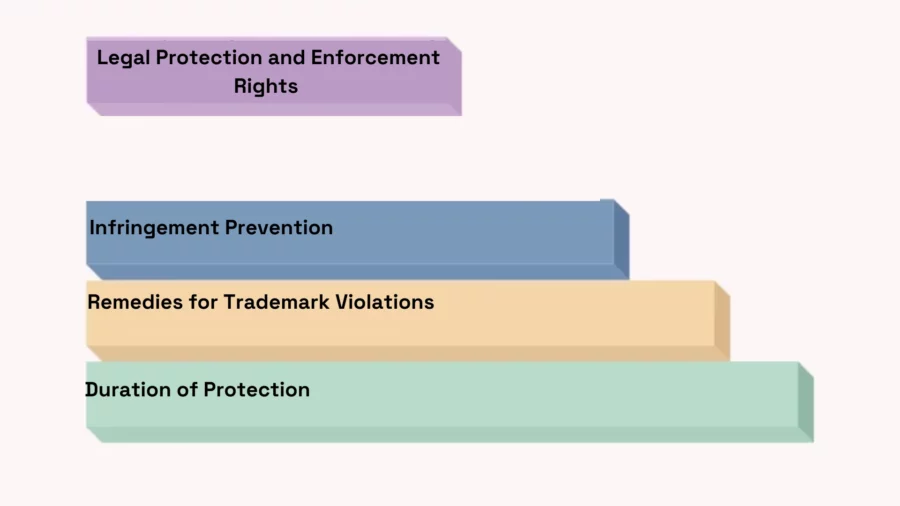
Infringement Prevention
Trademark laws in India let owners fight against those who misuse similar marks. This helps keep trademarks unique and distinct. It makes sure people can tell where goods and services come from.
Remedies for Trademark Violations
- Injunctions: Courts can stop infringing use of a trademark to protect the brand owner.
- Damages: Owners can get money for the losses caused by the infringement.
- Account of Profits: Sometimes, the infringer must give up the profits made from using the trademark without permission.
Duration of Protection
Trademark protection in India can last forever. It requires the mark to be used in business and renewal applications to be filed regularly. This long protection helps brand owners keep their brand recognition and trust with consumers over time.
| Trademark Protection in India | Key Aspects |
| Infringement Prevention | Legal action against similar marks that could cause consumer confusion |
| Remedies for Violations | Injunctions, damages, and account of profits |
| Duration of Protection | Indefinite, subject to renewal and continuous use |
India’s laws give trademark owners strong tools to protect their rights. By enforcing their trademarks, businesses can protect their investments and keep consumer trust. This supports their growth and success over the long term.
Grounds for Trademark Refusal
Getting a trademark registered can be tricky. In India, the Trademark Act, 1999 lists reasons why applications might get refused. These reasons fall into two main categories: absolute and relative grounds.
Absolute Grounds for Refusal
Section 9 of the Trademark Act talks about absolute grounds for refusal. These include marks that:
- Lack distinctive character or are incapable of distinguishing goods and services
- Are descriptive of the goods or services they represent
- May deceive the public or hurt religious sentiments
- Contain scandalous or obscene matter
- Are prohibited under the Emblems and Names Act, such as the use of national symbols
Relative Grounds for Refusal
Relative grounds for refusal are covered in Section 11 of the Trademark Act. These involve situations where the proposed trademark is:
- Identical or similar to an earlier registered trademark, leading to a likelihood of confusion
- Likely to take unfair advantage of or be detrimental to the distinctive character or repute of an earlier well-known trademark
It’s important for businesses to know these grounds for refusal when trying to register trademarks in India. By creating unique, non-descriptive marks that don’t step on others’ toes, companies can better navigate the trademark registration process. This helps avoid legal legal requirements issues.
| Grounds for Refusal | Description | Examples |
| Lack of distinctiveness | Marks that are not capable of distinguishing the goods or services of one business from another | A generic term like “Auto” for motor vehicles |
| Prohibited marks | Marks that contain scandalous or obscene matter, or are prohibited under the Emblems and Names Act | Use of national symbols or religious deities on certain products |
| Likelihood of confusion | Marks that are identical or similar to earlier registered trademarks, leading to a likelihood of confusion | A new trademark that is highly similar to an existing well-known brand |
Protect Your Brand & Recover Revenue With Bytescare's Brand Protection software
What’s Next?
Trademarks are key to a brand’s success, ensuring legal protection and driving growth. They help companies stand out, show product quality, and gain consumer trust. By picking the right trademark, businesses can make their products unique and different from others.
Keeping an eye on trademark rights is essential to protect brand value and stop others from using your mark. With trademarks, companies can grow and succeed over time. As markets change, trademarks will become even more important for brand identity and legal safety.
For businesses to succeed today, they need a strong trademark strategy. This strategy should match their brand, marketing, and legal plans. By doing this, companies can fully use their trademarks and achieve lasting success.
To support this effort, it’s vital to protect your trademarks from unauthorised use. Bytescare offers advanced protection solutions designed to safeguard your brand’s identity and integrity. Ready to protect your trademarks? Contact us today and experience our solution firsthand!
The Most Widely Used Brand Protection Software
Find, track, and remove counterfeit listings and sellers with Bytescare Brand Protection software

FAQ
What is the legal framework for trade mark protection in India?
India’s trade mark law protects trade marks. Registered trade marks give their owners enforceable rights. This allows them to stop unauthorised use and take legal action against infringers.
How do trade marks contribute to business success?
Trade marks help businesses stand out by differentiating their products. They ensure quality and help with advertising. They also protect against counterfeiting, boosting brand recognition and loyalty.
What is the importance of trade mark distinctiveness?
Distinctiveness is key for trade marks. They must be unique and not confused with other marks in the same field. It’s important to avoid descriptive words to keep the distinctive mark unique.
How do trade marks serve as indicators of a product’s source or origin?
Trade marks represent a product’s attributes, like technology and service. They help consumers recognise products and make choices based on brand reputation.
What is the role of trade marks in quality assurance and brand recognition?
Trade marks show consistent quality, building trust and loyalty. Brands must keep quality high to protect their reputation and trade mark value. This prevents unauthorised use and keeps the mark associated with quality.
How do trade marks serve advertising and marketing functions?
Trade marks simplify brand promotion by acting as a visual shortcut. Established trade marks evoke emotions and values, making them memorable and differentiating in crowded markets.
Ready to Secure Your Online Presence?
You are at the right place, contact us to know more.

